The pace and variety of electrification across many aspects of our daily lives continue, driven by the convergence of multiple factors. These include increased renewable sources such as solar power from photovoltaic panels and wind power via large turbines paired with higher-density, lower-cost rechargeable batteries for storage, sophisticated battery-management systems to monitor their charging/discharging, and inverters to convert the stored energy into usable power.
We’re seeing a wide span of applications, from highly visible grid-scale installations and medium-size office and residential applications to increased adoption of electric vehicles (EVs) and their chargers (Figure 1) and even less visible roles such as propane-free industrial forklifts. The size and scope of these systems range from wide-scale and regional to highly focused and localized.

Figure 1: This row of electric vehicle charging stations is evidence of the further penetration of electric power in daily life and the associated challenges. (Source: Noel - stock.adobe.com)
The Challenge is in the Details
Regardless of the size or scope of a project, there’s one truism that every engineer with any real-world experience knows: It is the less-visible and less-glamorous components that often make the difference between a system that works to some level but has multiple shortcomings and performance issues, versus one which is solid, tight, reliable, and also meets the many safety and regulatory standards governing its operation.
Components with precise functions—such as solar panels, windmill turbines, battery management systems (BMS), and power inverters—get much of the design effort and attention. The public even recognizes them to some extent due to their high profile. Nonetheless, the reality is that many more “smaller” components are needed for a complete and properly functioning system. For example, in addition to the major blocks of a modest solar-inverter installation (Figure 2), smaller and critical functions are needed.

Figure 2: A basic solar-inverter installation has large functional blocks and smaller yet vital functions. (Source: TE Connectivity)
Two of these are:
Contactors (orange circle 3) are high-capacity, electrically controllable on/off switches (similar to a relay) used for power distribution, main switch functions, and overall control. The contactor makes it possible to switch and control power paths.
EMI filters (orange circle 4) provide needed attenuation of common mode and differential mode interference and electromagnetic interference (EMI), which is unavoidably created by the switching power inverters. Without these filters, the Battery Energy Storage Systems (BESS) create excessive interference, which affects not only its operation but nearby systems as well and will also likely fail certification to regulatory limits.
Size, Materials Must Scale
While these contractors and filters have schematic diagrams and functions similar to their counterparts in the low-power system, the similarities end there (Figures 3 and 4).

Figure 3: The contactor is an electrically controllable high voltage/current switch, similar to a relay, used to route power. (Source: Mouser Electronics)
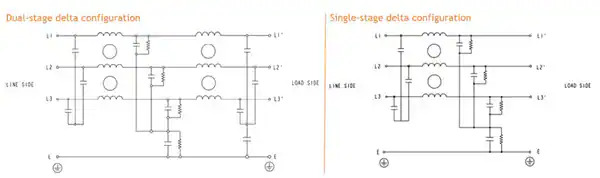
Figure 4: EMI filters are offered in dual- and single-stage configurations and are essential for attenuating common- and differential-mode interference and electromagnetic interference (EMI). (Source: Mouser Electronics)
The components must be physically more significant, have more robust internal and external contacts and connections, use different materials and contact plating, and be suitable for rugged handling and exposed installations. Due to the higher voltages and currents, there are concerns related to contact erosion, localized heating, and high-voltage flashover and sparking, which could degrade performance or cause outright failure.
A closer look at a contactor and a filter provides a sense of these functions in higher-power applications.
The ECK150/200/250 series of high-voltage DC contactors from TE Connectivity (TE) is designed for control in EV charging stations, solar inverters, battery energy storage systems, automated guided vehicles (AGV), and battery-powered forklifts (Figure 5). The units can be used for DC breaking voltage at 1000VDC and breaking current of 2000A (both maximums) with a continuous carry current of 250A.
To achieve this performance, they are packaged in hermetically sealed cylindrical enclosures using ceramic technology, making them safe and reliable.

Figure 5: The ECK150/200/250 series of high-voltage DC contactors use ceramic-sealing technology for reliability under challenging conditions. (Source: Mouser Electronics)
The contractors are 52 millimeters long with a 56mm diameter while meeting all relevant UL, CE, and CCC approvals. As a further benefit, the built-in pulse-width modulated “economizer” activator means that the required contactor hold power is just 1.7W despite the high voltage/current ratings, which minimizes wasted energy and thermal dissipation.
The Corcom AHV series of Three-Phase High-Performance EMI Filters, also from TE Connectivity, are modules with a rated voltage of up to 760VAC and a current rating of up to 1000A. They feature a single- or dual-stage delta configuration in a compact bookshelf or chassis design, along with a small footprint to save space and costs (Figure 6); the smallest unit (7A) measures approximately 300mm deep × 140mm high × 70mm wide while the corresponding dimensions of the largest unit (180 A) are 310 × 265 × 165mm.

Figure 6: The Corcom AHV series of Three-Phase High-Performance EMI Filters are available in single- or dual-stage models to provide different levels of noise attenuation. (Source: Mouser Electronics)
They are well suited for renewable-energy converters/inverters, EV charging facilities, and other industrial equipment and devices. They are available in single- and dual-stage configurations to meet the required EMI suppression goals. For example, the 75-A single-stage bookshelf unit with terminal block input and output has these common-mode and differential-mode insertion losses in dB (Figure 7):

Figure 7: The common- and differential-mode attenuation (in dB) from 0.01 to 30MHz for a 75A, single-stage Corcom AHV-series filter is high. (Source: TE Connectivity)
In contrast, the corresponding 75A dual-stage bookshelf unit has somewhat higher attenuation for both modes across all frequencies (Figure 8).

Figure 8: If the attenuation provided by a single-stage unit is insufficient for the system or regulatory mandates, the dual-stage unit adds another approximately 10 to 20dB across the same frequency spectrum. (Source: TE Connectivity)
Conclusion
While the higher-profile functional blocks of a BESS or more minor system are critical, it’s important for designers also to pay attention when selecting passive, less-visible components such as contactors, EMI filters, and even connectors. Choosing devices that don’t have the needed ratings or mechanical or electrical, mechanical, or environmental ruggedness leads to immediate performance shortcomings, regulatory issues, and short- and longer-term reliability concerns. TE Connectivity offers a full range of products, in a wide selection of ratings and form factors, to meet these needs and fill in the large and small pieces for successful energy-storage and -delivery systems.
Original Source: Mouser
Author
 Bill Schweber is a contributing writer for Mouser Electronics and an electronics engineer who has written three textbooks on electronic communications systems, as well as hundreds of technical articles, opinion columns, and product features. In past roles, he worked as a technical website manager for multiple topic-specific sites for EE Times and as the Executive Editor and Analog Editor at EDN.
Bill Schweber is a contributing writer for Mouser Electronics and an electronics engineer who has written three textbooks on electronic communications systems, as well as hundreds of technical articles, opinion columns, and product features. In past roles, he worked as a technical website manager for multiple topic-specific sites for EE Times and as the Executive Editor and Analog Editor at EDN.
He has an MSEE (Univ. of Mass) and BSEE (Columbia Univ.), is a Registered Professional Engineer, and holds an Advanced Class amateur radio license. Bill has also planned, written, and presented online courses on a variety of engineering topics, including MOSFET basics, ADC selection, and driving LEDs.









 Bill Schweber is a contributing writer for Mouser Electronics and an electronics engineer who has written three textbooks on electronic communications systems, as well as hundreds of technical articles, opinion columns, and product features. In past roles, he worked as a technical website manager for multiple topic-specific sites for EE Times and as the Executive Editor and Analog Editor at EDN.
Bill Schweber is a contributing writer for Mouser Electronics and an electronics engineer who has written three textbooks on electronic communications systems, as well as hundreds of technical articles, opinion columns, and product features. In past roles, he worked as a technical website manager for multiple topic-specific sites for EE Times and as the Executive Editor and Analog Editor at EDN.
















 Michael Parks, P.E. is the co-founder of Green Shoe Garage, a custom electronics design studio and embedded security research firm located in Western Maryland. He produces the Gears of Resistance Podcast to help raise public awareness of technical and scientific matters. Michael is also a licensed Professional Engineer in the state of Maryland and holds a Master’s degree in systems engineering from Johns Hopkins University.
Michael Parks, P.E. is the co-founder of Green Shoe Garage, a custom electronics design studio and embedded security research firm located in Western Maryland. He produces the Gears of Resistance Podcast to help raise public awareness of technical and scientific matters. Michael is also a licensed Professional Engineer in the state of Maryland and holds a Master’s degree in systems engineering from Johns Hopkins University.