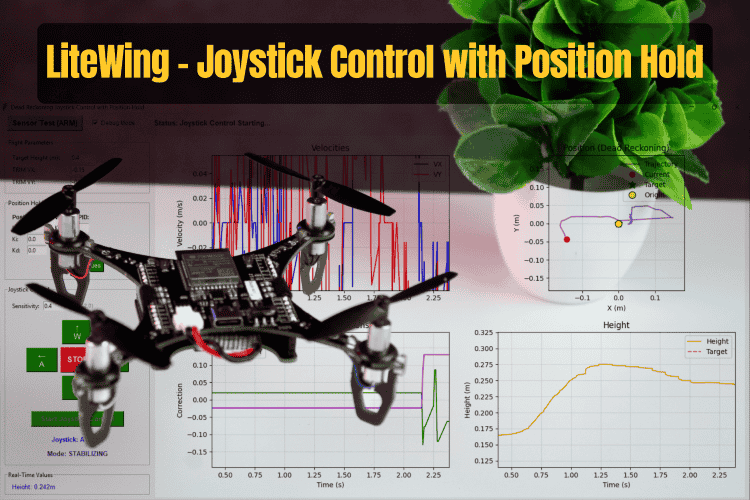
In this guide, we will explore how to implement a control system where you can command the drone's movement using keyboard controls (WASD keys), and when you release those controls, the drone automatically maintains its position in space. This creates an intuitive flying experience where you get the precision of manual control when you need it, combined with the stability of autonomous hover when you don't. Explore practical DIY drone projects, including Wi-Fi-controlled, gesture-controlled, and sensor-enhanced drone tutorials with step-by-step instructions
The system achieves this by using dead reckoning to estimate position through integrating velocity measurements from the optical flow sensor, then applying PID control to maintain the estimated position and counteract drift. This tutorial is demonstrated using the Litewing ESP32 Drone and Litewing Drone Positioning Module.
Table of Contents
How drone position hold works without GPS
The joystick position hold system we're implementing operates in two distinct modes that transition seamlessly based on your input. Understanding how these modes work and when the system switches between them is essential for getting the most out of this control scheme.
When you are actively pressing one or more of the WASD keys, the system operates in Joystick Mode. During this phase, you have direct velocity control over the drone. Pressing W commands forward motion, S commands backward motion, A moves left, and D moves right. The speed of this motion is determined by the sensitivity setting you configure. In this mode, the system temporarily disables position integration, allowing the drone to move freely according to your commands. The velocity commands you generate are sent directly to the flight controller without any position hold corrections applied.
The moment you release all directional keys, the system transitions into Position Hold Mode. At the instant of this transition, the system captures the drone's current estimated position and sets that as the new target position to maintain. From that point forward, PID controllers activate and begin working to counteract any drift from this held position. The optical flow sensor continues to measure velocity, and those measurements are fed into the control loop. The PID controllers compute correction commands that oppose any detected motion, effectively creating a virtual anchor point in space. This continues until you press a directional key again, at which point the system immediately returns to Joystick Mode.
This dual-mode behavior creates what we call a "fly-and-hold" control scheme. It's particularly useful for indoor navigation tasks where you might want to move to a specific location, inspect something while hovering steadily, then move to the next location. It's also an excellent tool for learning autonomous flight concepts because you can directly observe how the position hold controller responds to disturbances.
Hardware Setup
Before we can work with the joystick position hold system, you need to ensure that your LiteWing drone is properly equipped with the LiteWing Flight Positioning Module and is running compatible firmware. If you have not yet installed the module or updated the drone's firmware to support the module, you should refer to the LiteWing Flight Positioning Module User Guide. That document covers the complete hardware installation process and walks you through the firmware flashing steps. Make sure your drone is running the compatible firmware before continuing with this guide.
Software Setup
Setting up your development environment correctly is critical for working with the position hold system. You need Python installed on your PC, along with the cflib library and its dependencies configured properly. Additionally, you must be able to establish a CRTP communication link between your PC and the LiteWing drone. Since cflib has a few prerequisites that must be met before it will function correctly, we recommend that you refer to the LiteWing Python SDK Programming Guide. That document provides detailed instructions for installing dependencies, setting up cflib, connecting to the LiteWing Wi-Fi interface, and validating your communication setup with a simple test script. Completing that setup process is a necessary prerequisite before attempting to interact with any sensor on the Flight Positioning Module.
How Dead Reckoning Position Hold Works
The position hold system we're implementing relies on a technique called dead reckoning. Unlike GPS-based systems that receive absolute position information from satellites, dead reckoning estimates position by integrating velocity measurements over time. This means we build up a relative position estimate starting from an arbitrary origin point, which we set at takeoff or whenever we reset the system.
The fundamental principle behind dead reckoning is simple. If you know how fast you're moving and in which direction, you can estimate how far you've traveled by multiplying velocity by time. The optical flow sensor provides us with velocity measurements in the X and Y directions. By integrating these velocities over time at each sensor update, we can estimate how far the drone has traveled from its starting position. Mathematically, this integration is expressed as:
In these equations, vx and vy represent the velocity in meters per second along each axis, and △t is the time interval between samples. This integration runs continuously during flight, building up a position estimate relative to the takeoff point.
Once we have this position estimate, implementing position hold becomes straightforward. When you release all joystick inputs and the system transitions to Position Hold Mode, it captures the current estimated position and designates that as the target position to maintain. From that moment on, a series of calculations runs at approximately 50 times per second. First, the system computes the position error, which is simply the difference between where the drone should be (the target) and where it currently is (the estimated position). Second, it computes the velocity error, which is how fast the drone is currently moving (remember, we want zero velocity when holding position). These two error signals are fed into PID controllers that compute velocity correction commands. These corrections are sent to the flight controller, which adjusts the drone's thrust and tilt to counteract the detected errors.
The control law that governs this behavior combines both position error and velocity error. Position error tells us how far we've drifted from the target, and can be expressed as:
Velocity error tells us how fast we're moving when we should be stationary:
The correction command that gets sent to the drone combines contributions from both error signals:
This dual-loop approach is often called cascaded control. The position controller provides a restoring force that pulls the drone back toward the target position, while the velocity controller provides damping that prevents oscillation. Without the velocity damping, the position controller might cause the drone to overshoot the target position repeatedly, creating a bouncing behavior. The velocity term smooths this out.
One challenge inherent to all dead reckoning systems is drift accumulation. Small inaccuracies in velocity measurements, when integrated over time, result in position errors that grow continuously. A velocity measurement that is off by just 1 cm/s will cause a position error of 60 cm after one minute. To mitigate this problem without resorting to absolute position references, we implement two complementary mechanisms.
The first mechanism is velocity smoothing and thresholding. Raw optical flow data contains noise that varies from sample to sample. We filter this using an exponential moving average, which smooths out random fluctuations while maintaining responsiveness to real motion. Additionally, we apply a velocity threshold: any velocity measurement below a very small value (typically 0.005 m/s) is clamped to exactly zero. This prevents the system from integrating tiny noise values when the drone is actually stationary.
The second mechanism is integral decay. When the drone is nearly stationary (velocity magnitude close to zero), we apply a small decay term that gradually pulls the estimated position back toward the origin. This acts like a weak spring that slowly centers the position estimate. The decay is only applied during low-velocity conditions, so it doesn't interfere with tracking actual motion. The rate of decay is tunable, and the default value provides a good balance between drift suppression and tracking accuracy.
PID Control System
The position hold implementation uses cascaded PID controllers for both position and velocity. Although the default configuration uses proportional-only control (what we call P-control), the full PID structure is available if you want to tune the system for optimal performance in your specific environment.
Understanding how these controllers work will help you tune them effectively. A PID controller computes its output as the sum of three terms: proportional, integral, and derivative. The proportional term responds to the current error magnitude. The integral term accumulates error over time and responds to persistent offsets. The derivative term responds to the rate of change of the error and provides predictive damping.
Our position PID controller attempts to drive the position error to zero. Its output is computed as:
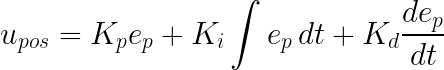
The default gains for the position controller are shown in this table:
| Gain | Default Value | Effect |
| POSITION_KP | 1.2 | Main restoring force toward target position |
| POSITION_KI | 0.03 | Eliminates steady-state offset |
| POSITION_KD | 0.0 | Provides additional damping (disabled by default) |
The proportional term provides the main restoring force. A higher proportional gain creates stronger position correction, pulling the drone back toward the target more aggressively. However, if you set this gain too high, the system becomes unstable and oscillates. Too low, and the drone drifts away from the target position without sufficient correction.
Our velocity PID controller provides active damping by opposing any residual velocity. Its output is computed as:
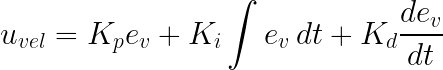
The default gains for the velocity controller are:
| Gain | Default Value | Effect |
| VELOCITY_KP | 1.2 | Active damping to prevent overshoot |
| VELOCITY_KI | 0.0 | Typically not needed |
| VELOCITY_KD | 0.0 | Typically not needed |
The velocity controller acts as active damping. When the position controller commands a correction, it creates motion. The velocity controller opposes that motion, preventing overshoot and oscillation. This is why we can use relatively high position gains without instability, the velocity loop provides the necessary damping.
The final velocity command sent to the drone's low-level controller combines both PID outputs:
total_correction_vx = u_pos_x + u_vel_x
total_correction_vy = u_pos_y + u_vel_yThese corrections are clamped to safe limits to prevent aggressive maneuvers that could destabilize the drone. The default limit is ±0.1 m/s, which provides smooth, controlled corrections without sudden motions.
CRTP Communication for Position Hold
The joystick position hold script communicates with the drone using the same CRTP log variables we introduced in the Optical Flow Sensor guide. We stream three primary variables at a rate of 100 Hz (every 10 milliseconds) to provide sufficient update frequency for the control loop.
| Variable | Type | Purpose |
| motion.deltaX | int16_t | Pixel shift in X direction from optical flow sensor |
| motion.deltaY | int16_t | Pixel shift in Y direction from optical flow sensor |
| stateEstimate.z | float | Fused altitude estimate in meters |
The motion deltas come directly from the PMW3901MB optical flow sensor and represent how many pixels the ground pattern has moved between consecutive sensor frames. The height value comes from the drone's state estimator, which fuses data from the VL53L1X Time-of-Flight sensor with barometric and IMU measurements to provide a stable height reading.
To convert the raw pixel deltas into velocities expressed in meters per second, we apply a geometry-based scaling calculation that accounts for the sensor's field of view, optical resolution, and sample rate. The conversion follows this formula:
velocity_constant = (4.4 * DEG_TO_RAD) / (30.0 * DT)
velocity = delta_value * altitude * velocity_constantThe constant 4.4 represents the effective field of view in degrees. The value 30 corresponds to the optical resolution (how many pixels span that field of view). DT is the sample period in seconds, typically 0.01 for our 10ms logging interval. This scaling produces velocities in meters per second that we can use for position integration and control calculations.
Code Walkthrough
The complete script implementation is available on the LiteWing GitHub repository under the Python-Scripts/Flight_Positioning_Module/ directory. You can access it at:
The file we're examining is named dead-reckoning-joystick-position-hold.py. In the following sections, we'll walk through the key components of this implementation to understand how everything fits together.
Configuration Parameters
The script begins with a comprehensive set of configuration parameters that control the drone's connection, flight behavior, control timing, and PID tuning. These parameters are defined as constants at the top of the file, making them easy to locate and modify without searching through the code.
# Connection Configuration
DRONE_URI = "udp://192.168.43.42"
TARGET_HEIGHT = 0.4 # Target hover height in meters
TAKEOFF_TIME = 0.5 # Time allocated for takeoff sequence
LANDING_TIME = 0.5 # Time allocated for landing sequence
DEBUG_MODE = False # Set to True to disable motors for testing
# Control Loop Timing
CONTROL_UPDATE_RATE = 0.02 # 50Hz control loop (20ms period)
SENSOR_PERIOD_MS = 10 # 100Hz sensor data streaming
DT = SENSOR_PERIOD_MS / 1000.0 # Convert to seconds
# Trim Corrections (manual bias adjustments)
TRIM_VX = 0.0
TRIM_VY = 0.0
# Position PID Controller Gains
POSITION_KP = 1.2
POSITION_KI = 0.0
POSITION_KD = 0.0
# Velocity PID Controller Gains
VELOCITY_KP = 1.2
VELOCITY_KI = 0.0
VELOCITY_KD = 0.0
# Control Limits and Safety
MAX_CORRECTION = 0.1 # Maximum velocity correction (m/s)
DRIFT_COMPENSATION_RATE = 0.15 # Position decay rate when stationary
MAX_POSITION_ERROR = 2.0 # Position estimate clamp limit
# Joystick Control
JOYSTICK_SENSITIVITY = 0.4 # Commanded velocity in manual mode (m/s)Several of these parameters deserve special attention. The CONTROL_UPDATE_RATE determines how frequently the position hold calculations run. At 50 Hz (every 20ms), we get responsive corrections without overwhelming the drone's command interface. The TARGET_HEIGHT sets your preferred hover altitude after takeoff. TRIM_VX and TRIM_VY allow you to compensate for asymmetric flight characteristics; if your drone tends to drift in a particular direction even when commanded to hold, you can add a small bias here to counteract that tendency.
The PID gain parameters define the aggressiveness of the position hold controller. The default values work well for typical indoor environments with good optical flow tracking. The MAX_CORRECTION parameter acts as a safety limit, clamping the velocity commands to prevent the position controller from commanding dangerously aggressive maneuvers if it detects a large position error. JOYSTICK_SENSITIVITY controls how fast the drone moves when you press a directional key. Increase this for faster manual flight, or decrease it for more precise, gentle movements.
Global State Variables
The script maintains several categories of state variables that track the complete status of the control system from raw sensor readings through computed position to PID controller internal state. Understanding what these variables represent will help you follow the control flow.
# Raw sensor data from the drone
current_height = 0.0
motion_delta_x = 0
motion_delta_y = 0
sensor_data_ready = False
current_battery_voltage = 0.0
battery_data_ready = False
# Computed velocities (m/s)
current_vx = 0.0
current_vy = 0.0
velocity_x_history = [0.0, 0.0] # For smoothing filter
velocity_y_history = [0.0, 0.0]
# Integrated position estimate (dead reckoning)
integrated_position_x = 0.0
integrated_position_y = 0.0
last_integration_time = time.time()
position_integration_enabled = False
# PID controller internal state
position_integral_x = 0.0
position_integral_y = 0.0
last_position_error_x = 0.0
last_position_error_y = 0.0
velocity_integral_x = 0.0
velocity_integral_y = 0.0
last_velocity_error_x = 0.0
last_velocity_error_y = 0.0
# Target position for hold mode
target_position_x = 0.0
target_position_y = 0.0
# Control outputs sent to drone
current_correction_vx = 0.0
current_correction_vy = 0.0
# Mode flags
joystick_mode_active = FalseThe sensor data variables hold the most recent values received from the drone. The velocity variables contain both raw and smoothed velocity estimates computed from the optical flow deltas. The integrated position variables represent our dead reckoning estimate of where the drone is relative to the origin. The PID state variables store the integral accumulation and previous error values needed for the I and D terms. The target position variables define where we want to hold when in Position Hold Mode. Finally, the mode flag tells us whether we're currently in Joystick Mode or Position Hold Mode.
Velocity Calculation and Smoothing
Raw optical flow deltas must be converted to velocities and smoothed before use. Two functions handle this processing.
def calculate_velocity(delta_value, altitude):
"""Convert optical flow delta to linear velocity"""
if altitude <= 0:
return 0.0
# Geometry constant based on sensor FOV and sample rate
velocity_constant = (4.4 * DEG_TO_RAD) / (30.0 * DT)
velocity = delta_value * altitude * velocity_constant
return velocityThe calculate_velocity function takes a raw pixel delta from the optical flow sensor and the current altitude, then returns the corresponding linear velocity in meters per second. The calculation accounts for the sensor's 4.4-degree field of view, 30-pixel resolution, and our logging sample period. If altitude is zero or negative, the function returns zero velocity because we cannot reliably compute velocity without valid altitude information.
def smooth_velocity(new_velocity, history):
"""Simple 2-point smoothing filter"""
history[1] = history[0]
history[0] = new_velocity
alpha = VELOCITY_SMOOTHING_ALPHA # Typically 0.9
smoothed = (history[0] * alpha) + (history[1] * (1 - alpha))
# Suppress very small velocities to prevent drift
if abs(smoothed) < VELOCITY_THRESHOLD:
smoothed = 0.0
return smoothedThe smooth_velocity function implements a simple exponential moving average filter. We maintain a two-point history for each axis, and the smoothed output is a weighted combination of the current and previous values. The alpha parameter (typically 0.9) controls the balance between new and old data. A higher alpha value produces smoother output but with slightly more lag. After smoothing, we apply a threshold test: velocities smaller than a tiny value (0.005 m/s by default) are clamped to exactly zero. This prevents the integration of noise when the drone is actually stationary.
Position Integration
Velocities are integrated over time to estimate position through dead reckoning. The integrate_position function handles this calculation along with drift compensation and bounds checking.
def integrate_position(vx, vy, dt):
"""Dead reckoning: integrate velocity to position"""
global integrated_position_x, integrated_position_y
# Sanity check on time step
if dt <= 0 or dt > 0.1:
return
# Basic integration step
integrated_position_x += vx * dt
integrated_position_y += vy * dt
# Apply drift compensation when velocity magnitude is low
velocity_magnitude = (vx * vx + vy * vy) ** 0.5
if velocity_magnitude < VELOCITY_THRESHOLD * 2:
integrated_position_x -= integrated_position_x * DRIFT_COMPENSATION_RATE * dt
integrated_position_y -= integrated_position_y * DRIFT_COMPENSATION_RATE * dt
# Clamp position to reasonable bounds
integrated_position_x = max(-MAX_POSITION_ERROR,
min(MAX_POSITION_ERROR, integrated_position_x))
integrated_position_y = max(-MAX_POSITION_ERROR,
min(MAX_POSITION_ERROR, integrated_position_y))The function begins by validating the time step. If dt is zero, negative, or unreasonably large (which could happen if the logging temporarily paused), we skip the integration to avoid creating a large jump in the position estimate. The core integration is straightforward: we simply add the product of velocity and time to the current position.
The drift compensation mechanism activates when the velocity magnitude is very small, indicating the drone is nearly stationary. In this condition, we apply a small decay that gradually pulls the position estimate back toward zero. The decay rate is proportional to the current position error, so larger errors decay faster. This acts like a weak centering spring that helps counteract long-term drift without interfering with tracking real motion.
Finally, we clamp the position estimate to reasonable bounds. If sensor errors or other problems cause the integration to run away, the clamp prevents absurdly large position values. The default limit of ±2 meters is sufficient for typical indoor flight spaces.
Position Hold Reset
When transitioning from Joystick Mode to Position Hold Mode, we need to reset the control system to treat the current location as the new target. The set_current_position_as_target function handles this critical transition.
def set_current_position_as_target():
"""Reset position tracking to treat current location as new origin"""
global integrated_position_x, integrated_position_y
global target_position_x, target_position_y
global position_integral_x, position_integral_y
global velocity_integral_x, velocity_integral_y
global last_position_error_x, last_position_error_y
global last_velocity_error_x, last_velocity_error_y
global current_correction_vx, current_correction_vy
global velocity_x_history, velocity_y_history
# Set current location as new origin
integrated_position_x = 0.0
integrated_position_y = 0.0
target_position_x = 0.0
target_position_y = 0.0
# Reset all PID controller internal state
position_integral_x = 0.0
position_integral_y = 0.0
last_position_error_x = 0.0
last_position_error_y = 0.0
velocity_integral_x = 0.0
velocity_integral_y = 0.0
last_velocity_error_x = 0.0
last_velocity_error_y = 0.0
# Clear any pending corrections
current_correction_vx = 0.0
current_correction_vy = 0.0
# Reset velocity smoothing history
velocity_x_history[0] = 0.0
velocity_x_history[1] = 0.0
velocity_y_history[0] = 0.0
velocity_y_history[1] = 0.0This function performs a complete state reset. We set both the current position estimate and the target position to zero, effectively redefining the origin at the drone's current location. All PID controller internal state gets cleared, which includes the integral accumulators and the stored previous errors. If we didn't clear these, the controller would "remember" errors from the previous hold position and incorrectly apply them to the new hold position. We also clear any pending correction commands and reset the velocity smoothing history to prevent residual artifacts from affecting the new position hold attempt.
PID Control Calculation
The calculate_position_hold_corrections function implements the core position hold logic by combining position and velocity PID controllers to compute the correction commands.
def calculate_position_hold_corrections():
"""Calculate control corrections using PID controllers"""
global current_correction_vx, current_correction_vy
global position_integral_x, position_integral_y
global last_position_error_x, last_position_error_y
global velocity_integral_x, velocity_integral_y
global last_velocity_error_x, last_velocity_error_y
# Safety check
if not sensor_data_ready or current_height <= 0:
current_correction_vx = 0.0
current_correction_vy = 0.0
return 0.0, 0.0
# Compute errors (negative because we want to reduce error)
position_error_x = -(integrated_position_x - target_position_x)
position_error_y = -(integrated_position_y - target_position_y)
velocity_error_x = -current_vx
velocity_error_y = -current_vy
# Position PID - X axis
position_p_x = position_error_x * POSITION_KP
position_integral_x += position_error_x * CONTROL_UPDATE_RATE
position_integral_x = max(-0.1, min(0.1, position_integral_x))
position_i_x = position_integral_x * POSITION_KI
position_derivative_x = (position_error_x - last_position_error_x) / CONTROL_UPDATE_RATE
position_d_x = position_derivative_x * POSITION_KD
last_position_error_x = position_error_x
# Position PID - Y axis
position_p_y = position_error_y * POSITION_KP
position_integral_y += position_error_y * CONTROL_UPDATE_RATE
position_integral_y = max(-0.1, min(0.1, position_integral_y))
position_i_y = position_integral_y * POSITION_KI
position_derivative_y = (position_error_y - last_position_error_y) / CONTROL_UPDATE_RATE
position_d_y = position_derivative_y * POSITION_KD
last_position_error_y = position_error_y
# Velocity PID - X axis
velocity_p_x = velocity_error_x * VELOCITY_KP
velocity_integral_x += velocity_error_x * CONTROL_UPDATE_RATE
velocity_integral_x = max(-0.05, min(0.05, velocity_integral_x))
velocity_i_x = velocity_integral_x * VELOCITY_KI
velocity_derivative_x = (velocity_error_x - last_velocity_error_x) / CONTROL_UPDATE_RATE
velocity_d_x = velocity_derivative_x * VELOCITY_KD
last_velocity_error_x = velocity_error_x
# Velocity PID - Y axis
velocity_p_y = velocity_error_y * VELOCITY_KP
velocity_integral_y += velocity_error_y * CONTROL_UPDATE_RATE
velocity_integral_y = max(-0.05, min(0.05, velocity_integral_y))
velocity_i_y = velocity_integral_y * VELOCITY_KI
velocity_derivative_y = (velocity_error_y - last_velocity_error_y) / CONTROL_UPDATE_RATE
velocity_d_y = velocity_derivative_y * VELOCITY_KD
last_velocity_error_y = velocity_error_y
# Combine both controllers
total_vx = (position_p_x + position_i_x + position_d_x) + \
(velocity_p_x + velocity_i_x + velocity_d_x)
total_vy = (position_p_y + position_i_y + position_d_y) + \
(velocity_p_y + velocity_i_y + velocity_d_y)
# Apply safety limits
total_vx = max(-MAX_CORRECTION, min(MAX_CORRECTION, total_vx))
total_vy = max(-MAX_CORRECTION, min(MAX_CORRECTION, total_vy))
# Store for monitoring
current_correction_vx = total_vx
current_correction_vy = total_vy
return total_vx, total_vyThis function implements the full cascaded PID architecture. We compute position errors by comparing where we are to where we want to be, and velocity errors by comparing our current velocity to the desired velocity of zero. For each axis, we calculate the P, I, and D terms of both the position and velocity controllers. The integral terms are accumulated over time and clamped to prevent windup. The derivative terms are computed as the rate of change of the error. Finally, we sum all contributions from both controllers and apply a safety clamp to ensure the commanded corrections stay within reasonable bounds.
Motion Sensor Callback
The motion_callback function receives optical flow data from the drone and processes it into velocity and position estimates.
def motion_callback(timestamp, data, logconf):
"""Motion sensor data callback"""
global current_height, motion_delta_x, motion_delta_y
global current_vx, current_vy, sensor_data_ready
global last_integration_time
# Extract sensor readings
current_height = data.get("stateEstimate.z", 0)
motion_delta_x = data.get("motion.deltaX", 0)
motion_delta_y = data.get("motion.deltaY", 0)
sensor_data_ready = True
# Calculate velocities from optical flow deltas
raw_velocity_x = calculate_velocity(motion_delta_x, current_height)
raw_velocity_y = calculate_velocity(motion_delta_y, current_height)
# Apply smoothing filter
current_vx = smooth_velocity(raw_velocity_x, velocity_x_history)
current_vy = smooth_velocity(raw_velocity_y, velocity_y_history)
# Integrate position (only when NOT in joystick mode)
current_time = time.time()
dt = current_time - last_integration_time
if 0.001 <= dt <= 0.1 and position_integration_enabled and not joystick_mode_active:
integrate_position(current_vx, current_vy, dt)
last_integration_time = current_time
update_history()This callback runs every time we receive a new packet of sensor data from the drone, which happens at 100 Hz. We extract the altitude and optical flow deltas, convert the deltas to velocities, apply smoothing, and check whether we should integrate the position. Note the condition that checks joystick_mode_active. When this flag is True (meaning you're actively pressing directional keys), we skip position integration. This allows you to move freely during manual control without the position estimate fighting against your commands.
Joystick Input Handling
The GUI captures keyboard input through event handlers that update the key state flags.
def on_key_press(self, event):
"""Handle key press events"""
key = event.keysym.lower()
if key in self.joystick_keys:
self.joystick_keys[key] = True
self.key_pressed_flags[key] = True
def on_key_release(self, event):
"""Handle key release events"""
key = event.keysym.lower()
if key in self.joystick_keys:
self.joystick_keys[key] = FalseThese simple event handlers maintain a dictionary that tracks which directional keys are currently pressed. The control loop uses this dictionary to determine what velocity commands to send and whether to activate position hold.
Joystick Control Loop
A separate thread continuously evaluates the joystick state and sends appropriate commands to the drone.
def joystick_control_loop(self):
"""Main joystick control loop with position hold"""
global joystick_mode_active
while self.joystick_active and scf_instance is not None:
# Check if any directional keys are pressed
any_key_pressed = any(self.joystick_keys.values())
if any_key_pressed:
# ===== JOYSTICK MODE =====
joystick_mode_active = True
# Build velocity command from key states
vx_cmd = 0.0
vy_cmd = 0.0
if self.joystick_keys['w']: # Forward
vy_cmd += JOYSTICK_SENSITIVITY
if self.joystick_keys['s']: # Backward
vy_cmd -= JOYSTICK_SENSITIVITY
if self.joystick_keys['a']: # Left
vx_cmd -= JOYSTICK_SENSITIVITY
if self.joystick_keys['d']: # Right
vx_cmd += JOYSTICK_SENSITIVITY
# Apply trim corrections
vx_cmd += TRIM_VX
vy_cmd += TRIM_VY
# Send velocity command to drone
cf.commander.send_velocity_world_setpoint(vx_cmd, vy_cmd, 0, 0)
else:
# ===== POSITION HOLD MODE =====
if joystick_mode_active:
# Just transitioned from joystick to hold
set_current_position_as_target()
joystick_mode_active = False
# Calculate PID corrections
corr_vx, corr_vy = calculate_position_hold_corrections()
# Apply trim corrections
corr_vx += TRIM_VX
corr_vy += TRIM_VY
# Send correction command to drone
cf.commander.send_velocity_world_setpoint(corr_vx, corr_vy, 0, 0)
# Run at control loop rate
time.sleep(CONTROL_UPDATE_RATE)This loop runs continuously at 50 Hz (every 20ms). On each iteration, it checks whether any directional keys are pressed. If yes, we're in Joystick Mode: we build a velocity command based on which keys are active, apply any trim corrections, and send that command to the drone. If no keys are pressed, we're in Position Hold Mode: we first check if we just transitioned into this mode (in which case we reset the target position), then we calculate PID corrections, apply trim, and send those corrections to the drone.
GUI and Visualization
The parameter adjustment panel allows you to modify critical system parameters without editing the code and restarting. You can change the target height, which determines how high the drone hovers after takeoff. The TRIM VX and TRIM VY parameters let you add small bias corrections if you notice the drone consistently drifts in a particular direction. The PID gain sliders (or entry boxes, depending on the implementation) allow you to adjust both the position and velocity controller gains. The joystick sensitivity control determines how fast the drone moves when you press the directional keys. All of these parameters can be adjusted in real-time, though some changes (particularly PID gains) take effect on the next control cycle.
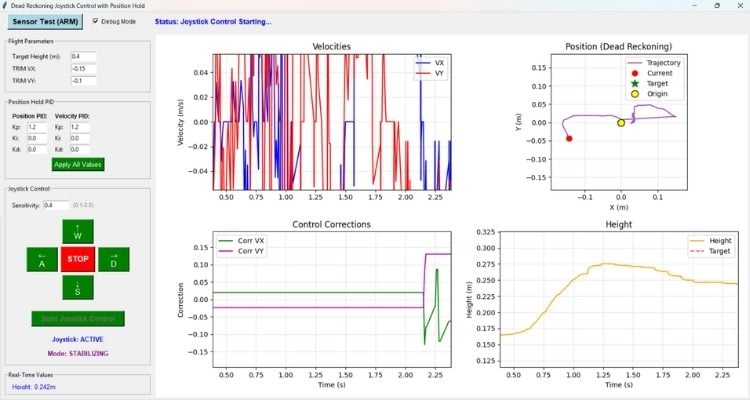
The real-time status display section shows you the current values of important system variables. You can see the current height as measured by the sensors, the battery voltage (which helps you know when it's time to land), the estimated velocities in X and Y, the estimated position from dead reckoning, the computed correction values being sent to the drone, and the current flight phase. The flight phase indicator tells you whether the system is idle, taking off, in joystick control, holding position, or landing.
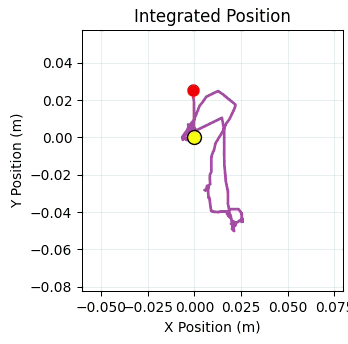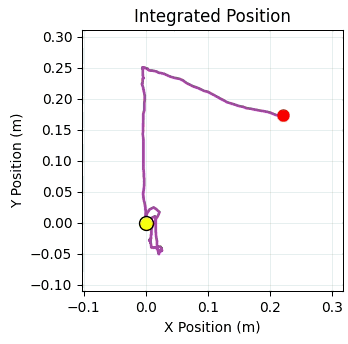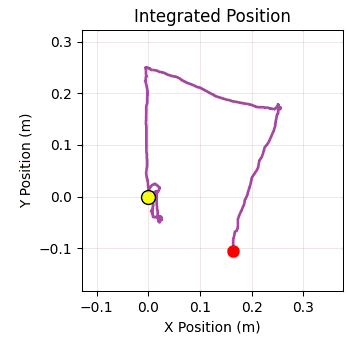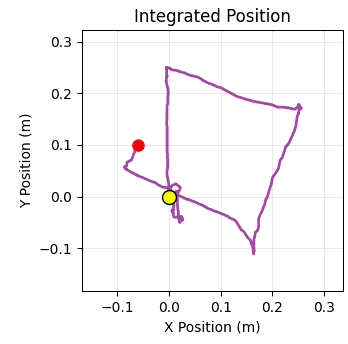
The trajectory visualization uses four matplotlib plots embedded in the Tkinter window. The first plot shows the estimated velocities in X and Y over time, giving you a sense of how the drone is moving. The second plot displays the integrated 2D position estimate, which is your dead reckoning trajectory, with your current position marked by a red dot. The third plot shows the control corrections being applied by the PID controller, which helps you understand how hard the system is working to maintain position. The fourth plot tracks height over time with a reference line indicating your target altitude.
PID Tuning for Stable Drone Hover
| Parameter | What It Does | Effect When Increased | Effect When Too High | Effect When Too Low | Typical / Default Values |
| POSITION_KP | Controls how aggressively the drone returns to the target position | Faster, stronger correction toward target | Oscillation and instability (bouncing around target) | Drift and weak correction | Typical: 1.0-1.5 Default: 1.2 |
| POSITION_KI | Accumulates position error over time to eliminate steady-state offset | Reduces persistent position offset | Integral windup, instability | Persistent offset remains | Typical: 0.0-0.05 Start at 0.0 |
| POSITION_KD | Reacts to rate of position error change (predictive damping) | Adds damping to position response | Can amplify noise or conflict with velocity loop | Usually unnecessary | Typically 0.0 |
| VELOCITY_KP | Provides damping by opposing motion (acts like a brake) | Reduces overshoot and oscillation | Sluggish, overly damped response | Overshoot and oscillation | Default: 1.2 |
| VELOCITY_KI | Integrates velocity error over time | Rarely beneficial in this architecture | Instability, windup | N/A | Typically 0.0 |
| VELOCITY_KD | Responds to rate of velocity error change | Rarely beneficial in this architecture | Noise amplification | N/A | Typically 0.0 |
When tuning the PID controller, follow this systematic procedure. Start with the default P-only control where POSITION_KP equals 1.2, VELOCITY_KP equals 1.2, and all other gains are 0.0. Test the position hold performance by commanding the drone to hover, then releasing the controls and observing how well it maintains position. If you see visible oscillation where the drone bounces back and forth, reduce the position proportional gain by steps of 0.1 until the oscillation stops. If you see excessive drift where the drone slowly wanders away from the target position, increase the position proportional gain by steps of 0.1 until the drift becomes acceptable. If after adjusting the proportional gain you still observe a persistent steady-state offset (the drone consistently sits offset from the target by a small, constant amount), add a small integral term by setting POSITION_KI to a value between 0.01 and 0.05. If you need more aggressive damping to prevent overshoot, increase VELOCITY_KP. Test each change thoroughly before making additional adjustments.
Testing our Optical Flow Sensor-Based Indoor Drone Positioning
Start by launching the script and clicking the "Sensor Test" button to connect to the drone and verify that all sensors are functioning correctly. The GUI will display status messages indicating whether the connection succeeded and whether the optical flow sensor and height sensor are providing data. Once the sensor test completes successfully, you can adjust the target height if you want to hover at an altitude different from the default 0.4 meters. When ready, click "Start Joystick Control" to initiate the autonomous takeoff sequence. The drone will rise to the target height and automatically enter Position Hold Mode.
Once the drone is hovering stably, you can test the manual control functionality. Press the W key and observe that the drone moves forward (in the positive Y direction relative to the drone's coordinate frame). Release the key and verify that the drone transitions smoothly into position hold, stopping its forward motion and maintaining that position. Repeat this test with the other directional keys: S for backward motion (negative Y), A for leftward motion (negative X), and D for rightward motion (positive X). The trajectory plot in the GUI should show your commanded path as a line trace, and when you release the controls, the position estimate should remain relatively stable.
Document Index
Complete Project Code
"""
Dead Reckoning Joystick Control with Position Hold
===================================================
Combined script that provides joystick control (WASD) for drone movement.
When no joystick input is detected, the drone automatically holds its position.
Features:
- WASD keyboard control for drone movement
- Automatic position hold when no input is given
- Adjustable TRIM, Height, and PID parameters
- Real-time velocity, position, and correction feedback
- Safety checks for battery and sensors
Usage:
1. Connect to the drone via UDP
2. Click "Sensor Test" to arm and verify sensors
3. Adjust parameters if needed
4. Click "Start Joystick Control" to takeoff
5. Use W/A/S/D keys to move - release to hold position
6. Click "Stop" or press Enter for emergency stop
Author: Dharageswaran S
Version: 1.0
"""
import time
import threading
import cflib.crtp
from cflib.crazyflie import Crazyflie
from cflib.crazyflie.log import LogConfig
from cflib.crazyflie.syncCrazyflie import SyncCrazyflie
import tkinter as tk
from tkinter import ttk
from matplotlib.backends.backend_tkagg import FigureCanvasTkAgg
from matplotlib.figure import Figure
import matplotlib.animation as animation
import csv
from datetime import datetime
# === CONFIGURATION PARAMETERS ===
DRONE_URI = "udp://192.168.43.42"
TARGET_HEIGHT = 0.4 # Target hover height in meters
TAKEOFF_TIME = 0.5 # Time to takeoff and stabilize
LANDING_TIME = 0.5 # Time to land
DEBUG_MODE = False # Set to True to disable motors
# Velocity and control parameters
VELOCITY_SMOOTHING_ALPHA = 0.9
VELOCITY_THRESHOLD = 0.005
CONTROL_UPDATE_RATE = 0.02 # 50Hz control loop
SENSOR_PERIOD_MS = 10
DT = SENSOR_PERIOD_MS / 1000.0
# Basic trim corrections
TRIM_VX = 0.0
TRIM_VY = 0.0
# Battery monitoring
LOW_BATTERY_THRESHOLD = 2.9
# Height sensor safety
HEIGHT_SENSOR_MIN_CHANGE = 0.015
# PID Controller Parameters
POSITION_KP = 1.2
POSITION_KI = 0.0
POSITION_KD = 0.0
VELOCITY_KP = 1.2
VELOCITY_KI = 0.0
VELOCITY_KD = 0.0
# Control limits
MAX_CORRECTION = 0.1
DRIFT_COMPENSATION_RATE = 0.15
MAX_POSITION_ERROR = 2.0
# Velocity calculation constants
DEG_TO_RAD = 3.1415926535 / 180.0
OPTICAL_FLOW_SCALE = 4.4
USE_HEIGHT_SCALING = True
# Joystick parameters
JOYSTICK_SENSITIVITY = 0.4
# === GLOBAL VARIABLES ===
current_height = 0.0
motion_delta_x = 0
motion_delta_y = 0
sensor_data_ready = False
current_battery_voltage = 0.0
battery_data_ready = False
current_vx = 0.0
current_vy = 0.0
velocity_x_history = [0.0, 0.0]
velocity_y_history = [0.0, 0.0]
integrated_position_x = 0.0
integrated_position_y = 0.0
last_integration_time = time.time()
position_integration_enabled = False
# Control corrections
current_correction_vx = 0.0
current_correction_vy = 0.0
# PID Controller state
position_integral_x = 0.0
position_integral_y = 0.0
last_position_error_x = 0.0
last_position_error_y = 0.0
velocity_integral_x = 0.0
velocity_integral_y = 0.0
last_velocity_error_x = 0.0
last_velocity_error_y = 0.0
# Target position for position hold
target_position_x = 0.0
target_position_y = 0.0
# Flight state
flight_phase = "IDLE"
flight_active = False
sensor_test_active = False
scf_instance = None
joystick_mode_active = False # When True, position integration is disabled
# Data history for plotting
max_history_points = 200
time_history = []
velocity_x_history_plot = []
velocity_y_history_plot = []
position_x_history = []
position_y_history = []
correction_vx_history = []
correction_vy_history = []
height_history = []
complete_trajectory_x = []
complete_trajectory_y = []
start_time = None
# CSV logging
log_file = None
log_writer = None
# === HELPER FUNCTIONS ===
def calculate_velocity(delta_value, altitude):
"""Convert optical flow delta to linear velocity"""
if altitude <= 0:
return 0.0
if USE_HEIGHT_SCALING:
velocity_constant = (4.4 * DEG_TO_RAD) / (30.0 * DT)
velocity = delta_value * altitude * velocity_constant
else:
velocity = delta_value * OPTICAL_FLOW_SCALE * DT
return velocity
def smooth_velocity(new_velocity, history):
"""Simple 2-point smoothing filter"""
history[1] = history[0]
history[0] = new_velocity
alpha = VELOCITY_SMOOTHING_ALPHA
smoothed = (history[0] * alpha) + (history[1] * (1 - alpha))
if abs(smoothed) < VELOCITY_THRESHOLD:
smoothed = 0.0
return smoothed
def integrate_position(vx, vy, dt):
"""Dead reckoning: integrate velocity to position"""
global integrated_position_x, integrated_position_y
if dt <= 0 or dt > 0.1:
return
integrated_position_x += vx * dt
integrated_position_y += vy * dt
velocity_magnitude = (vx * vx + vy * vy) ** 0.5
if velocity_magnitude < VELOCITY_THRESHOLD * 2:
integrated_position_x -= integrated_position_x * DRIFT_COMPENSATION_RATE * dt
integrated_position_y -= integrated_position_y * DRIFT_COMPENSATION_RATE * dt
integrated_position_x = max(-MAX_POSITION_ERROR, min(MAX_POSITION_ERROR, integrated_position_x))
integrated_position_y = max(-MAX_POSITION_ERROR, min(MAX_POSITION_ERROR, integrated_position_y))
def reset_position_tracking():
"""Reset integrated position tracking"""
global integrated_position_x, integrated_position_y, last_integration_time
global position_integration_enabled
global position_integral_x, position_integral_y, velocity_integral_x, velocity_integral_y
global last_position_error_x, last_position_error_y, last_velocity_error_x, last_velocity_error_y
global target_position_x, target_position_y
integrated_position_x = 0.0
integrated_position_y = 0.0
target_position_x = 0.0
target_position_y = 0.0
last_integration_time = time.time()
position_integration_enabled = True
position_integral_x = 0.0
position_integral_y = 0.0
velocity_integral_x = 0.0
velocity_integral_y = 0.0
last_position_error_x = 0.0
last_position_error_y = 0.0
last_velocity_error_x = 0.0
last_velocity_error_y = 0.0
def set_current_position_as_target():
"""Reset position tracking to treat current location as new origin (0,0)"""
global integrated_position_x, integrated_position_y
global target_position_x, target_position_y
global position_integral_x, position_integral_y
global last_position_error_x, last_position_error_y
global velocity_integral_x, velocity_integral_y
global last_velocity_error_x, last_velocity_error_y
global current_correction_vx, current_correction_vy
global velocity_x_history, velocity_y_history
# Reset integrated position to zero - current location becomes new origin
integrated_position_x = 0.0
integrated_position_y = 0.0
# Target is also at origin (hold current position)
target_position_x = 0.0
target_position_y = 0.0
# Reset ALL PID state for clean start
position_integral_x = 0.0
position_integral_y = 0.0
last_position_error_x = 0.0
last_position_error_y = 0.0
velocity_integral_x = 0.0
velocity_integral_y = 0.0
last_velocity_error_x = 0.0
last_velocity_error_y = 0.0
# Reset corrections
current_correction_vx = 0.0
current_correction_vy = 0.0
# Reset velocity smoothing history to prevent residual artifacts
velocity_x_history[0] = 0.0
velocity_x_history[1] = 0.0
velocity_y_history[0] = 0.0
velocity_y_history[1] = 0.0
def calculate_position_hold_corrections():
"""Calculate control corrections using PID controllers"""
global current_correction_vx, current_correction_vy
global position_integral_x, position_integral_y
global last_position_error_x, last_position_error_y
global velocity_integral_x, velocity_integral_y
global last_velocity_error_x, last_velocity_error_y
if not sensor_data_ready or current_height <= 0:
current_correction_vx = 0.0
current_correction_vy = 0.0
return 0.0, 0.0
position_error_x = -(integrated_position_x - target_position_x)
position_error_y = -(integrated_position_y - target_position_y)
velocity_error_x = -current_vx
velocity_error_y = -current_vy
# Position PID
position_p_x = position_error_x * POSITION_KP
position_p_y = position_error_y * POSITION_KP
position_integral_x += position_error_x * CONTROL_UPDATE_RATE
position_integral_y += position_error_y * CONTROL_UPDATE_RATE
position_integral_x = max(-0.1, min(0.1, position_integral_x))
position_integral_y = max(-0.1, min(0.1, position_integral_y))
position_i_x = position_integral_x * POSITION_KI
position_i_y = position_integral_y * POSITION_KI
position_derivative_x = (position_error_x - last_position_error_x) / CONTROL_UPDATE_RATE
position_derivative_y = (position_error_y - last_position_error_y) / CONTROL_UPDATE_RATE
position_d_x = position_derivative_x * POSITION_KD
position_d_y = position_derivative_y * POSITION_KD
last_position_error_x = position_error_x
last_position_error_y = position_error_y
# Velocity PID
velocity_p_x = velocity_error_x * VELOCITY_KP
velocity_p_y = velocity_error_y * VELOCITY_KP
velocity_integral_x += velocity_error_x * CONTROL_UPDATE_RATE
velocity_integral_y += velocity_error_y * CONTROL_UPDATE_RATE
velocity_integral_x = max(-0.05, min(0.05, velocity_integral_x))
velocity_integral_y = max(-0.05, min(0.05, velocity_integral_y))
velocity_i_x = velocity_integral_x * VELOCITY_KI
velocity_i_y = velocity_integral_y * VELOCITY_KI
velocity_derivative_x = (velocity_error_x - last_velocity_error_x) / CONTROL_UPDATE_RATE
velocity_derivative_y = (velocity_error_y - last_velocity_error_y) / CONTROL_UPDATE_RATE
velocity_d_x = velocity_derivative_x * VELOCITY_KD
velocity_d_y = velocity_derivative_y * VELOCITY_KD
last_velocity_error_x = velocity_error_x
last_velocity_error_y = velocity_error_y
# Combine
total_vx = (position_p_x + position_i_x + position_d_x) + (velocity_p_x + velocity_i_x + velocity_d_x)
total_vy = (position_p_y + position_i_y + position_d_y) + (velocity_p_y + velocity_i_y + velocity_d_y)
total_vx = max(-MAX_CORRECTION, min(MAX_CORRECTION, total_vx))
total_vy = max(-MAX_CORRECTION, min(MAX_CORRECTION, total_vy))
current_correction_vx = total_vx
current_correction_vy = total_vy
return total_vx, total_vy
def update_history():
"""Update data history for plotting"""
global start_time
if start_time is None:
start_time = time.time()
current_time = time.time() - start_time
time_history.append(current_time)
velocity_x_history_plot.append(current_vx)
velocity_y_history_plot.append(current_vy)
position_x_history.append(integrated_position_x)
position_y_history.append(integrated_position_y)
correction_vx_history.append(current_correction_vx)
correction_vy_history.append(current_correction_vy)
height_history.append(current_height)
complete_trajectory_x.append(integrated_position_x)
complete_trajectory_y.append(integrated_position_y)
if len(time_history) > max_history_points:
time_history.pop(0)
velocity_x_history_plot.pop(0)
velocity_y_history_plot.pop(0)
position_x_history.pop(0)
position_y_history.pop(0)
correction_vx_history.pop(0)
correction_vy_history.pop(0)
height_history.pop(0)
def motion_callback(timestamp, data, logconf):
"""Motion sensor data callback"""
global current_height, motion_delta_x, motion_delta_y, sensor_data_ready
global current_vx, current_vy, last_integration_time
current_height = data.get("stateEstimate.z", 0)
motion_delta_x = data.get("motion.deltaX", 0)
motion_delta_y = data.get("motion.deltaY", 0)
sensor_data_ready = True
raw_velocity_x = calculate_velocity(motion_delta_x, current_height)
raw_velocity_y = calculate_velocity(motion_delta_y, current_height)
current_vx = smooth_velocity(raw_velocity_x, velocity_x_history)
current_vy = smooth_velocity(raw_velocity_y, velocity_y_history)
current_time = time.time()
dt = current_time - last_integration_time
# Only integrate position during position hold mode (not during joystick mode)
if 0.001 <= dt <= 0.1 and position_integration_enabled and not joystick_mode_active:
integrate_position(current_vx, current_vy, dt)
last_integration_time = current_time
update_history()
def battery_callback(timestamp, data, logconf):
"""Battery voltage data callback"""
global current_battery_voltage, battery_data_ready
current_battery_voltage = data.get("pm.vbat", 0.0)
battery_data_ready = True
def setup_logging(cf, logger=None):
"""Setup motion sensor and battery voltage logging"""
log_motion = LogConfig(name="Motion", period_in_ms=SENSOR_PERIOD_MS)
log_battery = LogConfig(name="Battery", period_in_ms=500)
try:
toc = cf.log.toc.toc
motion_variables = [
("motion.deltaX", "int16_t"),
("motion.deltaY", "int16_t"),
("stateEstimate.z", "float"),
]
added_motion_vars = []
for var_name, var_type in motion_variables:
group, name = var_name.split(".")
if group in toc and name in toc[group]:
try:
log_motion.add_variable(var_name, var_type)
added_motion_vars.append(var_name)
except Exception as e:
if logger:
logger(f"Failed to add motion variable {var_name}: {e}")
if len(added_motion_vars) < 2:
if logger:
logger("ERROR: Not enough motion variables found!")
return None, None
battery_variables = [("pm.vbat", "float")]
added_battery_vars = []
for var_name, var_type in battery_variables:
group, name = var_name.split(".")
if group in toc and name in toc[group]:
try:
log_battery.add_variable(var_name, var_type)
added_battery_vars.append(var_name)
except Exception as e:
if logger:
logger(f"Failed to add battery variable {var_name}: {e}")
log_motion.data_received_cb.add_callback(motion_callback)
if len(added_battery_vars) > 0:
log_battery.data_received_cb.add_callback(battery_callback)
cf.log.add_config(log_motion)
if len(added_battery_vars) > 0:
cf.log.add_config(log_battery)
time.sleep(0.5)
if not log_motion.valid:
if logger:
logger("ERROR: Motion log configuration invalid!")
return None, None
if len(added_battery_vars) > 0 and not log_battery.valid:
log_battery = None
log_motion.start()
if log_battery:
log_battery.start()
time.sleep(0.5)
if logger:
logger(f"Logging started - Motion: {len(added_motion_vars)} vars")
return log_motion, log_battery
except Exception as e:
if logger:
logger(f"Logging setup failed: {str(e)}")
raise Exception(f"Logging setup failed: {str(e)}")
def init_csv_logging(logger=None):
"""Initialize CSV logging"""
global log_file, log_writer
timestamp = datetime.now().strftime("%Y%m%d_%H%M%S")
log_filename = f"joystick_position_hold_log_{timestamp}.csv"
log_file = open(log_filename, mode="w", newline="")
log_writer = csv.writer(log_file)
log_writer.writerow([
"Timestamp (s)", "Position X (m)", "Position Y (m)",
"Height (m)", "Velocity X (m/s)", "Velocity Y (m/s)",
"Correction VX", "Correction VY", "Mode"
])
if logger:
logger(f"Logging to CSV: {log_filename}")
def log_to_csv(mode=""):
"""Log current state to CSV"""
global log_writer, start_time
if log_writer is None or start_time is None:
return
elapsed = time.time() - start_time
log_writer.writerow([
f"{elapsed:.3f}", f"{integrated_position_x:.6f}", f"{integrated_position_y:.6f}",
f"{current_height:.6f}", f"{current_vx:.6f}", f"{current_vy:.6f}",
f"{current_correction_vx:.6f}", f"{current_correction_vy:.6f}", mode
])
def close_csv_logging(logger=None):
"""Close CSV log file"""
global log_file
if log_file:
log_file.close()
log_file = None
if logger:
logger("CSV log closed.")
class JoystickPositionHoldGUI:
"""
GUI for Joystick Control with Automatic Position Hold
When WASD keys are pressed, the drone moves in that direction.
When no keys are pressed, the drone holds its current position.
"""
def __init__(self, root):
self.root = root
self.root.title("Dead Reckoning Joystick Control with Position Hold")
self.root.geometry("1200x800")
self.joystick_thread = None
self.joystick_active = False
self.sensor_test_thread = None
self.sensor_test_running = False
self.joystick_keys = {"w": False, "a": False, "s": False, "d": False}
self.key_pressed_flags = {"w": False, "a": False, "s": False, "d": False}
self.position_hold_active = False # Track if position hold is active
self.create_ui()
self.setup_plots()
self.anim = animation.FuncAnimation(
self.fig, self.update_plots, interval=100, cache_frame_data=False
)
self.root.bind("<KeyPress>", self.on_key_press)
self.root.bind("<KeyRelease>", self.on_key_release)
self.root.focus_set()
def create_ui(self):
"""Create the user interface"""
control_frame = tk.Frame(self.root)
control_frame.pack(fill=tk.X, padx=10, pady=5)
self.sensor_test_button = tk.Button(
control_frame, text="Sensor Test (ARM)",
command=self.start_sensor_test,
bg="lightblue", fg="black", font=("Arial", 11, "bold"), width=16
)
self.sensor_test_button.pack(side=tk.LEFT, padx=5)
self.debug_mode_var = tk.BooleanVar(value=DEBUG_MODE)
tk.Checkbutton(
control_frame, text="Debug Mode", variable=self.debug_mode_var,
command=self.toggle_debug_mode, font=("Arial", 9)
).pack(side=tk.LEFT, padx=10)
self.status_var = tk.StringVar(value="Status: Ready - Run Sensor Test to ARM")
tk.Label(
control_frame, textvariable=self.status_var,
font=("Arial", 11, "bold"), fg="blue"
).pack(side=tk.LEFT, padx=20)
main_frame = tk.Frame(self.root)
main_frame.pack(fill=tk.BOTH, expand=True, padx=10, pady=5)
left_frame = tk.Frame(main_frame)
left_frame.pack(side=tk.LEFT, fill=tk.Y, padx=(0, 5))
# Flight Parameters
params_frame = tk.LabelFrame(left_frame, text="Flight Parameters", padx=10, pady=10)
params_frame.pack(fill=tk.X, pady=5)
height_frame = tk.Frame(params_frame)
height_frame.pack(fill=tk.X, pady=2)
tk.Label(height_frame, text="Target Height (m):", width=16, anchor=tk.W).pack(side=tk.LEFT)
self.height_entry_var = tk.StringVar(value=str(TARGET_HEIGHT))
tk.Entry(height_frame, textvariable=self.height_entry_var, width=8).pack(side=tk.LEFT, padx=5)
trim_vx_frame = tk.Frame(params_frame)
trim_vx_frame.pack(fill=tk.X, pady=2)
tk.Label(trim_vx_frame, text="TRIM VX:", width=16, anchor=tk.W).pack(side=tk.LEFT)
self.trim_vx_var = tk.StringVar(value=str(TRIM_VX))
tk.Entry(trim_vx_frame, textvariable=self.trim_vx_var, width=8).pack(side=tk.LEFT, padx=5)
trim_vy_frame = tk.Frame(params_frame)
trim_vy_frame.pack(fill=tk.X, pady=2)
tk.Label(trim_vy_frame, text="TRIM VY:", width=16, anchor=tk.W).pack(side=tk.LEFT)
self.trim_vy_var = tk.StringVar(value=str(TRIM_VY))
tk.Entry(trim_vy_frame, textvariable=self.trim_vy_var, width=8).pack(side=tk.LEFT, padx=5)
# PID Parameters
pid_frame = tk.LabelFrame(left_frame, text="Position Hold PID", padx=10, pady=10)
pid_frame.pack(fill=tk.X, pady=5)
pid_columns = tk.Frame(pid_frame)
pid_columns.pack(fill=tk.X)
pos_column = tk.Frame(pid_columns)
pos_column.pack(side=tk.LEFT, fill=tk.Y, padx=(0, 10))
tk.Label(pos_column, text="Position PID:", font=("Arial", 9, "bold")).pack(anchor=tk.W)
pos_kp_frame = tk.Frame(pos_column)
pos_kp_frame.pack(fill=tk.X, pady=1)
tk.Label(pos_kp_frame, text="Kp:", width=4, anchor=tk.W).pack(side=tk.LEFT)
self.pos_kp_var = tk.StringVar(value=str(POSITION_KP))
tk.Entry(pos_kp_frame, textvariable=self.pos_kp_var, width=6).pack(side=tk.LEFT)
pos_ki_frame = tk.Frame(pos_column)
pos_ki_frame.pack(fill=tk.X, pady=1)
tk.Label(pos_ki_frame, text="Ki:", width=4, anchor=tk.W).pack(side=tk.LEFT)
self.pos_ki_var = tk.StringVar(value=str(POSITION_KI))
tk.Entry(pos_ki_frame, textvariable=self.pos_ki_var, width=6).pack(side=tk.LEFT)
pos_kd_frame = tk.Frame(pos_column)
pos_kd_frame.pack(fill=tk.X, pady=1)
tk.Label(pos_kd_frame, text="Kd:", width=4, anchor=tk.W).pack(side=tk.LEFT)
self.pos_kd_var = tk.StringVar(value=str(POSITION_KD))
tk.Entry(pos_kd_frame, textvariable=self.pos_kd_var, width=6).pack(side=tk.LEFT)
vel_column = tk.Frame(pid_columns)
vel_column.pack(side=tk.LEFT, fill=tk.Y)
tk.Label(vel_column, text="Velocity PID:", font=("Arial", 9, "bold")).pack(anchor=tk.W)
vel_kp_frame = tk.Frame(vel_column)
vel_kp_frame.pack(fill=tk.X, pady=1)
tk.Label(vel_kp_frame, text="Kp:", width=4, anchor=tk.W).pack(side=tk.LEFT)
self.vel_kp_var = tk.StringVar(value=str(VELOCITY_KP))
tk.Entry(vel_kp_frame, textvariable=self.vel_kp_var, width=6).pack(side=tk.LEFT)
vel_ki_frame = tk.Frame(vel_column)
vel_ki_frame.pack(fill=tk.X, pady=1)
tk.Label(vel_ki_frame, text="Ki:", width=4, anchor=tk.W).pack(side=tk.LEFT)
self.vel_ki_var = tk.StringVar(value=str(VELOCITY_KI))
tk.Entry(vel_ki_frame, textvariable=self.vel_ki_var, width=6).pack(side=tk.LEFT)
vel_kd_frame = tk.Frame(vel_column)
vel_kd_frame.pack(fill=tk.X, pady=1)
tk.Label(vel_kd_frame, text="Kd:", width=4, anchor=tk.W).pack(side=tk.LEFT)
self.vel_kd_var = tk.StringVar(value=str(VELOCITY_KD))
tk.Entry(vel_kd_frame, textvariable=self.vel_kd_var, width=6).pack(side=tk.LEFT)
tk.Button(
pid_frame, text="Apply All Values", command=self.apply_values,
bg="green", fg="white", font=("Arial", 10)
).pack(pady=5)
# Joystick Control
joystick_frame = tk.LabelFrame(left_frame, text="Joystick Control", padx=10, pady=10)
joystick_frame.pack(fill=tk.X, pady=5)
sensitivity_frame = tk.Frame(joystick_frame)
sensitivity_frame.pack(fill=tk.X, pady=5)
tk.Label(sensitivity_frame, text="Sensitivity:").pack(side=tk.LEFT)
self.sensitivity_var = tk.StringVar(value=str(JOYSTICK_SENSITIVITY))
tk.Entry(sensitivity_frame, textvariable=self.sensitivity_var, width=8).pack(side=tk.LEFT, padx=5)
tk.Label(sensitivity_frame, text="(0.1-2.0)", font=("Arial", 8), fg="gray").pack(side=tk.LEFT)
buttons_frame = tk.Frame(joystick_frame)
buttons_frame.pack(pady=10)
self.btn_forward = tk.Button(buttons_frame, text="↑\nW", bg="green", fg="white", font=("Arial", 12), width=6, height=2)
self.btn_forward.grid(row=0, column=1, padx=3, pady=3)
self.btn_forward.bind("<ButtonPress>", lambda e: self.start_continuous_movement("w"))
self.btn_forward.bind("<ButtonRelease>", lambda e: self.stop_continuous_movement("w"))
self.btn_left = tk.Button(buttons_frame, text="←\nA", bg="green", fg="white", font=("Arial", 12), width=6, height=2)
self.btn_left.grid(row=1, column=0, padx=3, pady=3)
self.btn_left.bind("<ButtonPress>", lambda e: self.start_continuous_movement("a"))
self.btn_left.bind("<ButtonRelease>", lambda e: self.stop_continuous_movement("a"))
self.btn_stop = tk.Button(buttons_frame, text="STOP", bg="red", fg="white", font=("Arial", 12, "bold"), width=6, height=2, command=self.stop_joystick_control)
self.btn_stop.grid(row=1, column=1, padx=3, pady=3)
self.btn_right = tk.Button(buttons_frame, text="→\nD", bg="green", fg="white", font=("Arial", 12), width=6, height=2)
self.btn_right.grid(row=1, column=2, padx=3, pady=3)
self.btn_right.bind("<ButtonPress>", lambda e: self.start_continuous_movement("d"))
self.btn_right.bind("<ButtonRelease>", lambda e: self.stop_continuous_movement("d"))
self.btn_backward = tk.Button(buttons_frame, text="↓\nS", bg="green", fg="white", font=("Arial", 12), width=6, height=2)
self.btn_backward.grid(row=2, column=1, padx=3, pady=3)
self.btn_backward.bind("<ButtonPress>", lambda e: self.start_continuous_movement("s"))
self.btn_backward.bind("<ButtonRelease>", lambda e: self.stop_continuous_movement("s"))
self.start_button = tk.Button(
joystick_frame, text="Start Joystick Control",
command=self.start_joystick_control,
bg="green", fg="white", font=("Arial", 11, "bold"), width=20
)
self.start_button.pack(pady=10)
self.joystick_status_var = tk.StringVar(value="Joystick: INACTIVE")
tk.Label(joystick_frame, textvariable=self.joystick_status_var, font=("Arial", 10, "bold"), fg="blue").pack(pady=5)
self.mode_var = tk.StringVar(value="Mode: ---")
tk.Label(joystick_frame, textvariable=self.mode_var, font=("Arial", 10, "bold"), fg="purple").pack(pady=2)
# Real-time values
values_frame = tk.LabelFrame(left_frame, text="Real-Time Values", padx=10, pady=10)
values_frame.pack(fill=tk.X, pady=5)
self.height_var = tk.StringVar(value="Height: 0.000m")
self.battery_var = tk.StringVar(value="Battery: N/A")
self.vx_var = tk.StringVar(value="VX: 0.000 m/s")
self.vy_var = tk.StringVar(value="VY: 0.000 m/s")
self.pos_x_var = tk.StringVar(value="Pos X: 0.000m")
self.pos_y_var = tk.StringVar(value="Pos Y: 0.000m")
self.corr_vx_var = tk.StringVar(value="Corr VX: 0.000")
self.corr_vy_var = tk.StringVar(value="Corr VY: 0.000")
self.phase_var = tk.StringVar(value="Phase: IDLE")
tk.Label(values_frame, textvariable=self.height_var, font=("Arial", 10), fg="blue").pack(anchor=tk.W)
tk.Label(values_frame, textvariable=self.battery_var, font=("Arial", 10), fg="orange").pack(anchor=tk.W)
tk.Label(values_frame, textvariable=self.vx_var, font=("Arial", 10)).pack(anchor=tk.W)
tk.Label(values_frame, textvariable=self.vy_var, font=("Arial", 10)).pack(anchor=tk.W)
tk.Label(values_frame, textvariable=self.pos_x_var, font=("Arial", 10), fg="darkgreen").pack(anchor=tk.W)
tk.Label(values_frame, textvariable=self.pos_y_var, font=("Arial", 10), fg="darkgreen").pack(anchor=tk.W)
tk.Label(values_frame, textvariable=self.corr_vx_var, font=("Arial", 10), fg="red").pack(anchor=tk.W)
tk.Label(values_frame, textvariable=self.corr_vy_var, font=("Arial", 10), fg="red").pack(anchor=tk.W)
tk.Label(values_frame, textvariable=self.phase_var, font=("Arial", 10, "bold"), fg="purple").pack(anchor=tk.W)
# Output log
output_frame = tk.LabelFrame(left_frame, text="Output Log", padx=5, pady=5)
output_frame.pack(fill=tk.BOTH, expand=True, pady=5)
self.output_text = tk.Text(output_frame, height=6, width=40, font=("Consolas", 9))
self.output_text.pack(fill=tk.BOTH, expand=True)
# Right side - Plots
right_frame = tk.Frame(main_frame)
right_frame.pack(side=tk.RIGHT, fill=tk.BOTH, expand=True, padx=(5, 0))
self.fig = Figure(figsize=(9, 7))
self.canvas = FigureCanvasTkAgg(self.fig, master=right_frame)
self.canvas.get_tk_widget().pack(fill=tk.BOTH, expand=True)
def setup_plots(self):
"""Setup matplotlib plots"""
self.ax1 = self.fig.add_subplot(2, 2, 1)
self.ax2 = self.fig.add_subplot(2, 2, 2)
self.ax3 = self.fig.add_subplot(2, 2, 3)
self.ax4 = self.fig.add_subplot(2, 2, 4)
self.ax1.set_title("Velocities")
self.ax1.set_ylabel("Velocity (m/s)")
self.ax1.grid(True, alpha=0.3)
(self.line_vx,) = self.ax1.plot([], [], "b-", label="VX")
(self.line_vy,) = self.ax1.plot([], [], "r-", label="VY")
self.ax1.legend()
self.ax2.set_title("Position (Dead Reckoning)")
self.ax2.set_xlabel("X (m)")
self.ax2.set_ylabel("Y (m)")
self.ax2.set_aspect("equal")
self.ax2.grid(True, alpha=0.3)
(self.line_pos,) = self.ax2.plot([], [], "purple", alpha=0.7, label="Trajectory")
(self.current_pos,) = self.ax2.plot([], [], "ro", markersize=8, label="Current")
(self.target_pos,) = self.ax2.plot([], [], "g*", markersize=12, label="Target")
self.ax2.plot(0, 0, "ko", markersize=10, markerfacecolor="yellow", label="Origin")
self.ax2.legend()
self.ax3.set_title("Control Corrections")
self.ax3.set_xlabel("Time (s)")
self.ax3.set_ylabel("Correction")
self.ax3.grid(True, alpha=0.3)
(self.line_corr_vx,) = self.ax3.plot([], [], "g-", label="Corr VX")
(self.line_corr_vy,) = self.ax3.plot([], [], "m-", label="Corr VY")
self.ax3.legend()
self.ax4.set_title("Height")
self.ax4.set_xlabel("Time (s)")
self.ax4.set_ylabel("Height (m)")
self.ax4.grid(True, alpha=0.3)
(self.line_height,) = self.ax4.plot([], [], "orange", label="Height")
self.target_height_line = self.ax4.axhline(y=TARGET_HEIGHT, color="red", linestyle="--", alpha=0.7, label="Target")
self.ax4.legend()
self.fig.tight_layout()
def update_plots(self, frame):
"""Update all plots with new data"""
if not time_history:
return []
self.height_var.set(f"Height: {current_height:.3f}m")
self.phase_var.set(f"Phase: {flight_phase}")
if current_battery_voltage > 0:
self.battery_var.set(f"Battery: {current_battery_voltage:.2f}V")
self.vx_var.set(f"VX: {current_vx:.3f} m/s")
self.vy_var.set(f"VY: {current_vy:.3f} m/s")
self.pos_x_var.set(f"Pos X: {integrated_position_x:.3f}m")
self.pos_y_var.set(f"Pos Y: {integrated_position_y:.3f}m")
self.corr_vx_var.set(f"Corr VX: {current_correction_vx:.3f}")
self.corr_vy_var.set(f"Corr VY: {current_correction_vy:.3f}")
try:
self.line_vx.set_data(time_history, velocity_x_history_plot)
self.line_vy.set_data(time_history, velocity_y_history_plot)
if complete_trajectory_x and complete_trajectory_y:
plot_x = [-x for x in complete_trajectory_x]
self.line_pos.set_data(plot_x, complete_trajectory_y)
self.current_pos.set_data([-integrated_position_x], [integrated_position_y])
self.target_pos.set_data([-target_position_x], [target_position_y])
self.line_corr_vx.set_data(time_history, correction_vx_history)
self.line_corr_vy.set_data(time_history, correction_vy_history)
self.line_height.set_data(time_history, height_history)
if len(time_history) > 1:
for ax in [self.ax1, self.ax3, self.ax4]:
ax.set_xlim(min(time_history), max(time_history))
if complete_trajectory_x and complete_trajectory_y:
plot_x = [-x for x in complete_trajectory_x]
margin = max(max(plot_x) - min(plot_x), max(complete_trajectory_y) - min(complete_trajectory_y), 0.05) * 0.6
center_x = (max(plot_x) + min(plot_x)) / 2
center_y = (max(complete_trajectory_y) + min(complete_trajectory_y)) / 2
self.ax2.set_xlim(center_x - margin, center_x + margin)
self.ax2.set_ylim(center_y - margin, center_y + margin)
if height_history:
self.ax3.set_ylim(-MAX_CORRECTION * 1.5, MAX_CORRECTION * 1.5)
self.ax4.set_ylim(min(height_history) - 0.05, max(height_history) + 0.05)
except Exception:
pass
return [self.line_vx, self.line_vy, self.line_pos, self.current_pos, self.line_height]
def log_to_output(self, message):
"""Log a message to the output window"""
timestamp = time.strftime("%H:%M:%S")
self.output_text.insert(tk.END, f"[{timestamp}] {message}\n")
self.output_text.see(tk.END)
def clear_output(self):
"""Clear the output log"""
self.output_text.delete(1.0, tk.END)
def clear_graphs(self):
"""Clear all graph data"""
global time_history, velocity_x_history_plot, velocity_y_history_plot
global position_x_history, position_y_history, height_history
global correction_vx_history, correction_vy_history
global complete_trajectory_x, complete_trajectory_y, start_time
time_history.clear()
velocity_x_history_plot.clear()
velocity_y_history_plot.clear()
position_x_history.clear()
position_y_history.clear()
correction_vx_history.clear()
correction_vy_history.clear()
height_history.clear()
complete_trajectory_x.clear()
complete_trajectory_y.clear()
start_time = None
def apply_values(self):
"""Apply flight parameter values from UI"""
global TARGET_HEIGHT, TRIM_VX, TRIM_VY
global POSITION_KP, POSITION_KI, POSITION_KD
global VELOCITY_KP, VELOCITY_KI, VELOCITY_KD
try:
TARGET_HEIGHT = float(self.height_entry_var.get())
TRIM_VX = float(self.trim_vx_var.get())
TRIM_VY = float(self.trim_vy_var.get())
POSITION_KP = float(self.pos_kp_var.get())
POSITION_KI = float(self.pos_ki_var.get())
POSITION_KD = float(self.pos_kd_var.get())
VELOCITY_KP = float(self.vel_kp_var.get())
VELOCITY_KI = float(self.vel_ki_var.get())
VELOCITY_KD = float(self.vel_kd_var.get())
self.target_height_line.set_ydata([TARGET_HEIGHT, TARGET_HEIGHT])
self.log_to_output(f"Applied: Height={TARGET_HEIGHT:.2f}m")
self.status_var.set(f"Status: Values applied")
except ValueError as e:
self.status_var.set(f"Status: Invalid value - {str(e)}")
def toggle_debug_mode(self):
"""Toggle debug mode"""
global DEBUG_MODE
DEBUG_MODE = self.debug_mode_var.get()
mode_text = "ON (motors disabled)" if DEBUG_MODE else "OFF"
self.log_to_output(f"Debug mode: {mode_text}")
def start_continuous_movement(self, key):
"""Start continuous movement for GUI buttons"""
if not self.joystick_active:
return
key = key.lower()
if key in ["w", "a", "s", "d"]:
self.joystick_keys[key] = True
active_keys = [k.upper() for k, v in self.joystick_keys.items() if v]
self.joystick_status_var.set(f"Joystick: MOVING ({','.join(active_keys)})")
self.mode_var.set("Mode: JOYSTICK CONTROL")
def stop_continuous_movement(self, key):
"""Stop continuous movement for GUI buttons"""
if not self.joystick_active:
return
key = key.lower()
if key in ["w", "a", "s", "d"]:
self.joystick_keys[key] = False
active_keys = [k.upper() for k, v in self.joystick_keys.items() if v]
if active_keys:
self.joystick_status_var.set(f"Joystick: MOVING ({','.join(active_keys)})")
self.mode_var.set("Mode: JOYSTICK CONTROL")
else:
self.joystick_status_var.set("Joystick: ACTIVE")
self.mode_var.set("Mode: POSITION HOLD")
def _key_to_direction(self, key):
"""Convert key to direction name"""
directions = {"w": "Forward", "a": "Left", "s": "Backward", "d": "Right"}
return directions.get(key, key.upper())
# ==================== SENSOR TEST ====================
def start_sensor_test(self):
"""Start sensor test to ARM the drone"""
if not self.sensor_test_running and not self.joystick_active:
self.sensor_test_running = True
self.sensor_test_button.config(text="Stop Sensor Test", command=self.stop_sensor_test, bg="red")
self.status_var.set("Status: Sensor Test Running - ARMING...")
self.sensor_test_thread = threading.Thread(target=self.sensor_test_controller_thread)
self.sensor_test_thread.daemon = True
self.sensor_test_thread.start()
elif self.joystick_active:
self.status_var.set("Status: Cannot run Sensor Test while Joystick is active")
def stop_sensor_test(self):
"""Stop sensor test"""
global sensor_test_active
if self.sensor_test_running:
sensor_test_active = False
self.sensor_test_running = False
if self.sensor_test_thread and self.sensor_test_thread.is_alive():
self.sensor_test_thread.join(timeout=2.0)
self.status_var.set("Status: Sensor Test Stopped - ARMED ✓")
self.sensor_test_button.config(text="Sensor Test (ARM)", command=self.start_sensor_test, bg="lightblue")
def sensor_test_controller_thread(self):
"""Sensor test thread"""
global flight_phase, sensor_test_active, scf_instance
global current_battery_voltage, battery_data_ready
self.root.after(0, self.clear_output)
self.root.after(0, self.clear_graphs)
sensor_test_active = True
flight_phase = "SENSOR_TEST"
current_battery_voltage = 0.0
battery_data_ready = False
cflib.crtp.init_drivers()
cf = Crazyflie(rw_cache="./cache")
log_motion = None
log_battery = None
try:
with SyncCrazyflie(DRONE_URI, cf=cf) as scf:
scf_instance = scf
log_motion, log_battery = setup_logging(cf, logger=self.log_to_output)
if log_motion is not None:
time.sleep(1.0)
if not DEBUG_MODE:
cf.commander.send_setpoint(0, 0, 0, 0)
time.sleep(0.1)
cf.param.set_value("commander.enHighLevel", "1")
time.sleep(0.5)
reset_position_tracking()
self.log_to_output("Sensor test running - reading sensors...")
while sensor_test_active:
if sensor_data_ready:
calculate_position_hold_corrections()
time.sleep(CONTROL_UPDATE_RATE)
except Exception as e:
flight_phase = "ERROR"
self.log_to_output(f"Sensor Test Error: {str(e)}")
finally:
if log_motion:
try:
log_motion.stop()
except:
pass
if log_battery:
try:
log_battery.stop()
except:
pass
sensor_test_active = False
flight_phase = "IDLE"
self.sensor_test_running = False
self.root.after(0, lambda: self.sensor_test_button.config(
text="Sensor Test (ARM)", command=self.start_sensor_test, bg="lightblue"
))
self.root.after(0, lambda: self.status_var.set("Status: Sensor Test Stopped - ARMED ✓"))
# ==================== JOYSTICK CONTROL ====================
def start_joystick_control(self):
"""Start joystick control with position hold"""
if self.joystick_active or self.sensor_test_running:
if self.sensor_test_running:
self.status_var.set("Status: Stop Sensor Test first!")
return
try:
sensitivity = float(self.sensitivity_var.get())
if sensitivity < 0.1 or sensitivity > 2.0:
raise ValueError("Sensitivity must be between 0.1 and 2.0")
self.apply_values()
if current_battery_voltage > 0 and current_battery_voltage < LOW_BATTERY_THRESHOLD:
self.status_var.set(f"Status: Battery too low ({current_battery_voltage:.2f}V)!")
return
elif current_battery_voltage == 0.0:
self.log_to_output("WARNING: Battery unknown - run Sensor Test first!")
self.status_var.set("Status: Run Sensor Test first!")
return
if not sensor_data_ready:
self.status_var.set("Status: Sensor data not ready - Run Sensor Test first!")
return
if current_height <= 0.0:
self.status_var.set("Status: Invalid height reading!")
return
self.joystick_active = True
self.start_button.config(state=tk.DISABLED)
self.joystick_status_var.set("Joystick: ACTIVE")
self.mode_var.set("Mode: STARTING...")
self.status_var.set("Status: Joystick Control Starting...")
self.log_to_output("Joystick control with position hold started")
self.root.focus_force()
self.joystick_thread = threading.Thread(target=self.joystick_control_thread)
self.joystick_thread.daemon = True
self.joystick_thread.start()
except ValueError as e:
self.status_var.set(f"Status: {str(e)}")
def stop_joystick_control(self):
"""Stop joystick control"""
if self.joystick_active:
self.joystick_active = False
global flight_active
flight_active = False
if self.joystick_thread and self.joystick_thread.is_alive():
self.joystick_thread.join(timeout=1.0)
self.start_button.config(state=tk.NORMAL)
self.joystick_status_var.set("Joystick: INACTIVE")
self.mode_var.set("Mode: ---")
self.status_var.set("Status: Joystick Control Stopped")
self.log_to_output("Joystick control stopped")
def emergency_stop(self):
"""Emergency stop"""
global flight_active, sensor_test_active
flight_active = False
sensor_test_active = False
self.joystick_active = False
self.sensor_test_running = False
self.joystick_keys = {"w": False, "a": False, "s": False, "d": False}
self.key_pressed_flags = {"w": False, "a": False, "s": False, "d": False}
self.start_button.config(state=tk.NORMAL)
self.sensor_test_button.config(text="Sensor Test (ARM)", command=self.start_sensor_test, bg="lightblue")
self.joystick_status_var.set("Joystick: EMERGENCY STOP")
self.mode_var.set("Mode: STOPPED")
self.status_var.set("Status: EMERGENCY STOPPED")
self.log_to_output("EMERGENCY STOP!")
def joystick_control_thread(self):
"""Joystick control thread with automatic position hold"""
global flight_active, flight_phase
global current_battery_voltage, battery_data_ready
global position_integration_enabled
global joystick_mode_active
self.root.after(0, self.clear_output)
self.root.after(0, self.clear_graphs)
cflib.crtp.init_drivers()
cf = Crazyflie(rw_cache="./cache")
log_motion = None
log_battery = None
current_battery_voltage = 0.0
battery_data_ready = False
was_moving = False # Track if we were moving in the previous loop
try:
with SyncCrazyflie(DRONE_URI, cf=cf) as scf:
scf_instance = scf
flight_active = True
log_motion, log_battery = setup_logging(cf, logger=self.log_to_output)
if log_motion is not None:
time.sleep(1.0)
reset_position_tracking()
if not DEBUG_MODE:
cf.commander.send_setpoint(0, 0, 0, 0)
time.sleep(0.1)
cf.param.set_value("commander.enHighLevel", "1")
time.sleep(0.5)
else:
self.log_to_output("DEBUG MODE: Motors disabled")
# Takeoff
flight_phase = "TAKEOFF"
start_time_local = time.time()
init_csv_logging(logger=self.log_to_output)
while time.time() - start_time_local < TAKEOFF_TIME and self.joystick_active:
if not DEBUG_MODE:
cf.commander.send_hover_setpoint(TRIM_VX, TRIM_VY, 0, TARGET_HEIGHT)
log_to_csv("TAKEOFF")
time.sleep(0.01)
# Stabilization
flight_phase = "STABILIZING"
self.root.after(0, lambda: self.mode_var.set("Mode: STABILIZING"))
stabilization_start = time.time()
while time.time() - stabilization_start < 2.0 and self.joystick_active:
if sensor_data_ready:
motion_vx, motion_vy = calculate_position_hold_corrections()
else:
motion_vx, motion_vy = 0.0, 0.0
total_vx = TRIM_VX + motion_vy
total_vy = TRIM_VY + motion_vx
if not DEBUG_MODE:
cf.commander.send_hover_setpoint(total_vx, total_vy, 0, TARGET_HEIGHT)
log_to_csv("STABILIZING")
time.sleep(CONTROL_UPDATE_RATE)
# Set initial position as target and start in position hold mode
joystick_mode_active = False # Start with position hold active
set_current_position_as_target()
self.log_to_output("Joystick control active - use WASD to move")
self.log_to_output("Release keys to hold position")
# Main control loop
flight_phase = "JOYSTICK_POSITION_HOLD"
while self.joystick_active:
try:
sensitivity = float(self.sensitivity_var.get())
except:
sensitivity = JOYSTICK_SENSITIVITY
# Check if any keys are pressed
any_key_pressed = any(self.joystick_keys.values())
if any_key_pressed:
# JOYSTICK MODE: Direct control
if not was_moving:
# First entering joystick mode - reset position tracking
# This clears any accumulated errors before direct control
joystick_mode_active = True # Disable position integration
set_current_position_as_target()
self.log_to_output("Joystick input detected - MOVING")
was_moving = True
joystick_vx = 0.0
joystick_vy = 0.0
if self.joystick_keys["w"]:
joystick_vy += sensitivity
if self.joystick_keys["s"]:
joystick_vy -= sensitivity
if self.joystick_keys["a"]:
joystick_vx += sensitivity
if self.joystick_keys["d"]:
joystick_vx -= sensitivity
total_vx = TRIM_VX + joystick_vy
total_vy = TRIM_VY + joystick_vx
self.root.after(0, lambda: self.mode_var.set("Mode: JOYSTICK CONTROL"))
log_to_csv("JOYSTICK")
else:
# POSITION HOLD MODE: Hold current position
if was_moving:
# Just stopped moving - enable position hold
joystick_mode_active = False # Enable position integration
set_current_position_as_target()
self.log_to_output("Keys released - POSITION HOLD activated")
was_moving = False
if sensor_data_ready:
motion_vx, motion_vy = calculate_position_hold_corrections()
else:
motion_vx, motion_vy = 0.0, 0.0
total_vx = TRIM_VX + motion_vy
total_vy = TRIM_VY + motion_vx
self.root.after(0, lambda: self.mode_var.set("Mode: POSITION HOLD"))
log_to_csv("POSITION_HOLD")
if not DEBUG_MODE:
cf.commander.send_hover_setpoint(total_vx, total_vy, 0, TARGET_HEIGHT)
time.sleep(CONTROL_UPDATE_RATE)
# Landing
flight_phase = "LANDING"
self.root.after(0, lambda: self.mode_var.set("Mode: LANDING"))
landing_start = time.time()
while time.time() - landing_start < LANDING_TIME and flight_active:
if not DEBUG_MODE:
cf.commander.send_hover_setpoint(TRIM_VX, TRIM_VY, 0, 0)
log_to_csv("LANDING")
time.sleep(0.01)
if not DEBUG_MODE:
cf.commander.send_setpoint(0, 0, 0, 0)
flight_phase = "COMPLETE"
self.log_to_output("Flight complete")
except Exception as e:
flight_phase = "ERROR"
self.log_to_output(f"Error: {str(e)}")
finally:
close_csv_logging(logger=self.log_to_output)
if log_motion:
try:
log_motion.stop()
except:
pass
if log_battery:
try:
log_battery.stop()
except:
pass
flight_active = False
self.joystick_active = False
self.root.after(0, lambda: self.start_button.config(state=tk.NORMAL))
self.root.after(0, lambda: self.joystick_status_var.set("Joystick: INACTIVE"))
self.root.after(0, lambda: self.mode_var.set("Mode: ---"))
self.root.after(0, lambda: self.status_var.set("Status: Flight Complete"))
def on_key_press(self, event):
"""Handle key press events"""
if event.keysym in ("Return", "KP_Enter"):
self.emergency_stop()
self.log_to_output("EMERGENCY STOP: Enter key pressed")
return
if not self.joystick_active:
return
key = event.char.lower()
if key in ["w", "a", "s", "d"]:
if not self.key_pressed_flags[key]:
self.key_pressed_flags[key] = True
self.joystick_keys[key] = True
active_keys = [k.upper() for k, v in self.joystick_keys.items() if v]
self.joystick_status_var.set(f"Joystick: MOVING ({','.join(active_keys)})")
else:
self.joystick_keys[key] = True
def on_key_release(self, event):
"""Handle key release events"""
if not self.joystick_active:
return
key = event.char.lower()
if key in ["w", "a", "s", "d"]:
if self.key_pressed_flags[key]:
self.key_pressed_flags[key] = False
self.joystick_keys[key] = False
active_keys = [k.upper() for k, v in self.joystick_keys.items() if v]
if active_keys:
self.joystick_status_var.set(f"Joystick: MOVING ({','.join(active_keys)})")
else:
self.joystick_status_var.set("Joystick: ACTIVE")
else:
self.joystick_keys[key] = False
def main():
"""Main entry point"""
try:
cflib.crtp.init_drivers()
print("Crazyflie CRTP drivers initialized")
except Exception as e:
print(f"Warning: cflib.crtp.init_drivers() failed: {e}")
root = tk.Tk()
app = JoystickPositionHoldGUI(root)
def on_closing():
global flight_active, sensor_test_active
flight_active = False
sensor_test_active = False
root.quit()
root.destroy()
root.protocol("WM_DELETE_WINDOW", on_closing)
root.mainloop()
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()





