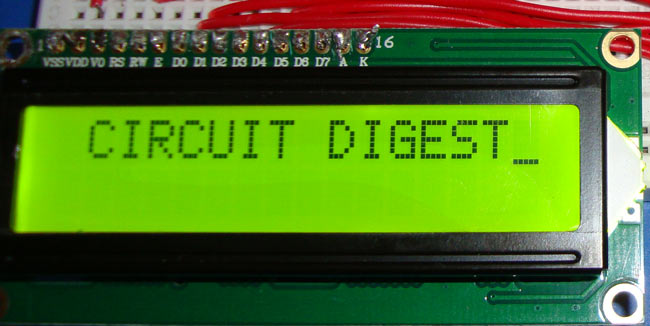
The interfacing of a 16x2 LCD display with 8051 microcontroller is very popular and one of the most important in embedded systems programming. This tutorial will explain the complete LCD interfacing of 8051 C program, circuit connections, and coding strategies in a program with the use of the AT89S52 microcontroller.
The display units are the most important output devices in embedded projects and electronics products. The 16X2 LCD module is designed to display characters per line, which means in this case sixteen characters across two lines. Each character occupies a 5x7 matrix space on display. Interfacing LCD with 8051 microcontroller is a little complicated at the beginning, but when one properly understands the 16-pin configuration and control signals, it becomes direct and easy to design for practical applications.
Table of Contents
- Understanding 16x2 LCD Display Module Pinout
- Control Pins Detailed Explanation (RS, RW, E)
- Diagram and Hardware Setup
- Diagram and Explanation
- └ Hardware Connections and Wiring Guide
- └ Power Supply and Contrast Adjustment Setup
- C Program Explanation
- Typical Problems and Solutions
- Frequently Asked Questions
- GitHub Repository
- Explore More LCD Interfacing Projects
Understanding 16x2 LCD Display Module Pinout
Before interfacing LCD with 8051 diagram, there are some important things to note about the 16-pin configuration. In order to perform 16x2 LCD display interfacing with the 8051 microcontroller, we need to connect power pins, control pins, data pins, backlight pins etc.to complete the communication properly.
We can divide it into five categories: Power Pins, contrast pin, Control Pins, Data pins and Backlight pins.
Category | Pin NO. | Pin Name | Function |
Power Pins | 1 | VSS | Ground Pin, connected to Ground |
2 | VDD or Vcc | Voltage Pin +5V | |
Contrast Pin | 3 | V0 or VEE | Contrast Setting, connected to Vcc thorough a variable resistor. |
Control Pins | 4 | RS | Register Select Pin, RS=0 Command mode, RS=1 Data mode |
5 | RW | Read/ Write pin, RW=0 Write mode, RW=1 Read mode | |
6 | E | Enable, a high to low pulse need to enable the LCD | |
Data Pins | 7-14 | D0-D7 | Data Pins, Stores the Data to be displayed on LCD or the command instructions |
Backlight Pins | 15 | LED+ or A | To power the Backlight +5V |
16 | LED- or K | Backlight Ground |
Control Pins Detailed Explanation (RS, RW, E)
The control pins are a key component in interfacing LCD with 8051 microcontroller. Without learning how they work, the communication to the LCD will not be successful:
All the pins are understandable by their name and functions, except the control pins, so they are explained below:
RS: RS is the register select pin. We need to set it to 1 if we are sending some data to be displayed on the LCD. And we will set it to 0 if we are sending some command instruction like clear the screen (hex code 01).
RW: This is a read/write pin; we will set it to 0 if we are going to write some data on the LCD. And set it to 1, if we are reading from the LCD module. Generally, this is set to 0, because we do not need to read data from the LCD. Only one instruction, “Get LCD status”, needs to be read some times. In most LCD interfacing with 8051 C program implementations, this pin is kept at 0 since reading from LCD is rarely required.
E: This pin is used to enable the module when a high-to-low pulse is given to it. A pulse of 450 ns should be given. That transition from HIGH to LOW makes the module ENABLE.
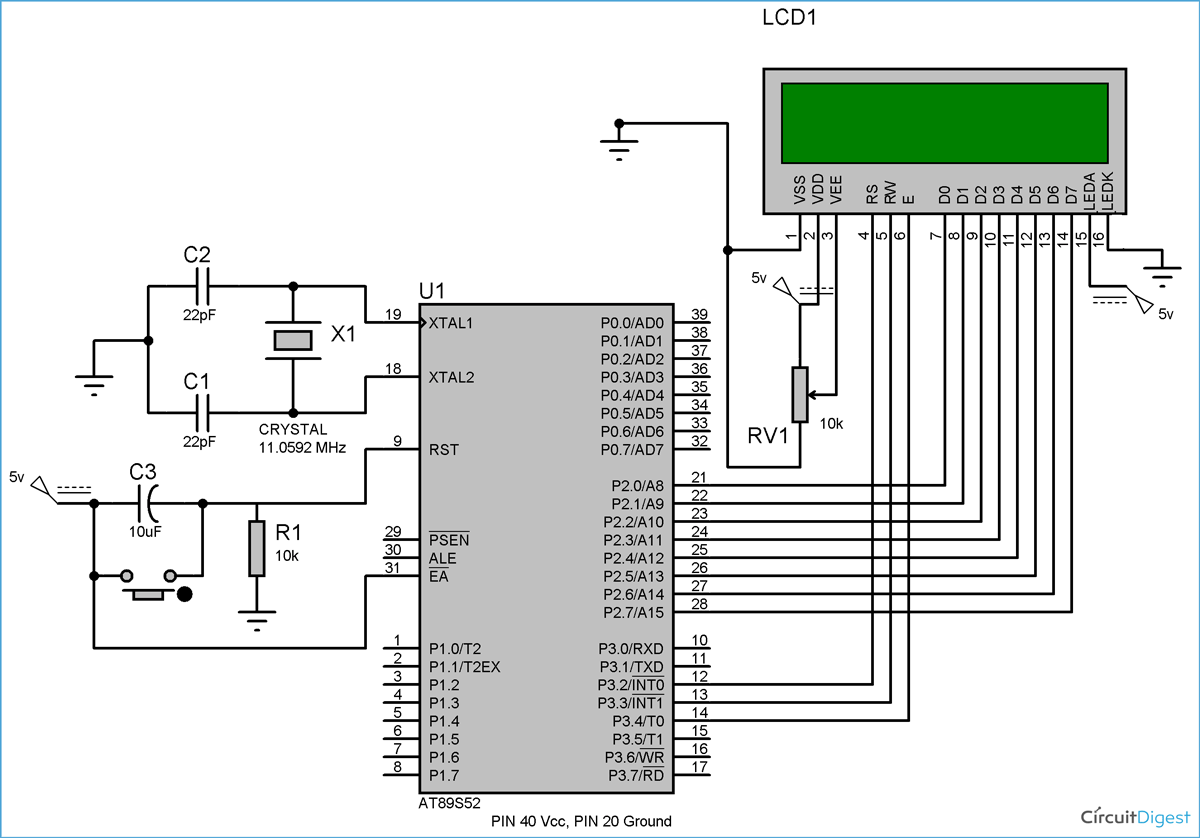
LCD Interfacing with 8051 Diagram and Hardware Setup
The circuit diagram for interfacing the LCD with 8051 shows all of the hardware connections needed to successfully connect the AT89S52 microcontroller and the 16x2 LCD module. Having your wiring right is important to ensure proper functionality.
There are some preset command instructions on the LCD. We have used them in our program below to prepare the LCD (in the lcd_init() function). Some important command instructions are given below:
| Hex Code | Command to LCD Instruction Register |
| 0F | LCD ON, cursor ON |
| 01 | Clear display screen |
| 02 | Return home |
| 04 | Decrement cursor (shift cursor to left) |
| 06 | Increment cursor (shift cursor to right) |
| 05 | Shift display right |
| 07 | Shift display left |
| 0E | Display ON, cursor blinking |
| 80 | Force cursor to beginning of first line |
| C0 | Force cursor to beginning of second line |
| 38 | 2 lines and 5×7 matrix |
| 83 | Cursor line 1 position 3 |
| 3C | Activate second line |
| 08 | Display OFF, cursor OFF |
| C1 | Jump to second line, position 1 |
| OC | Display ON, cursor OFF |
| C1 | Jump to second line, position 1 |
| C2 | Jump to second line, position 2 |
LCD Interfacing with 8051 Diagram and Explanation
The circuit diagram for LCD interfacing with 8051 microcontroller is shown in the above figure. If you have a basic understanding of 8051, then you must know about EA(PIN 31), XTAL1 & XTAL2, RST pin(PIN 9), Vcc and Ground Pin of the 8051 microcontroller. I have used these Pins in the above circuit. If you don’t have any idea about that, then I recommend that you read this Article, LED Interfacing with 8051 Microcontroller, before going through LCD interfacing.
Hardware Connections and Wiring Guide
So besides these above pins, we have connected the data pins (D0-D7) of the LCD to the Port 2 (P2_0–P2_7) microcontroller. And control pins RS, RW and E to the pins 12,13,14 (pins 2,3,4 of port 3) of the microcontroller, respectively.
Power Supply and Contrast Adjustment Setup
PIN 2(VDD) and PIN 15(Backlight supply) of the LCD are connected to a voltage (5V), and PIN 1 (VSS) and PIN 16(Backlight ground) are connected to ground.
Pin 3(V0) is connected to the voltage (Vcc) through a variable resistor of 10k to adjust the contrast of the LCD. The middle leg of the variable resistor is connected to PIN 3, and the other two legs are connected to the voltage supply and Ground.
LCD Interfacing with 8051 C Program Explanation
I have tried to explain the code through comments (in the code itself).
As I have explained earlier about command mode and data mode, you can see that while sending a command (function lcd_cmd), we have set RS=0, RW=0 and a HIGH to LOW pulse is given to E by making it 1, then 0. Also, when sending data (function lcd_data) to LCD, we have set RS=1, RW=0 and a HIGH to LOW pulse is given to E by making it 1 to 0. Function msdelay() has been created to create a delay in milliseconds and is called frequently in the program, it is called so that the LCD module can have sufficient time to execute the internal operations and commands.
A while loop has been created to print the string, which calls the lcd_data function each time to print a character until the last character (null terminator- ‘\0’).
We have used the LCD_init () function to get the LCD ready by using the preset command instructions (explained above).
Typical Problems and Solutions
Problem: LCD displays covered in black squares (or no display at all)
Solution: Check power connections and adjust contrast with the variable resistor. Ensure that Vcc is +5V.
Problem: Garbage characters are displayed
Solution: Check data line connections, make sure the lcd_init() function has the proper initialisation sequence.
Problem: LCD not responding to commands
Solution: Check RS, RW, and E control pin connections. Check the timing of the enable pulse in your code.
Problem: Characters are displayed but scrambled
Solution: Increase the delay values in the msdelay() function, and check that the correct command/data mode is used when switching between modes.
Frequently Asked Questions
⇥ Why does my LCD have a blank screen with the 8051?
Nothing appearing on the LCD for 8051 interfacing would typically indicate that we have incorrect power connections (as an example, check to make sure +5V is connected where VDD is located), we have not set the contrast correctly (remember to use the variable resistor at 10kΩ), we forgot to issue the initialization commands, or we connected the LCD wrong. We can check all connections (i.e., we powered the correct pins of the LCD), check the power supply (ensure that it is +5V), and ensure that we called the lcd_init() function before we wrote anything to the LCD.
⇥ What are the basic LCD commands for 8051 programming?
The basic LCD commands for 8051 programming are: 0x38 (function set - 2 lines, 5x7 matrix), 0x0C (display ON, cursor off), 0x06 (entry mode - increment cursor), 0x01 (clear display), 0x80 (cursor to line 1), and 0xC0 (cursor to line 2). With all the above commands, we can initialise and control the LCD in the long term.
⇥ How do I display text on the LCD using the 8051 microcontroller?
In order to write text on an LCD using the 8051, we first need to call lcd_init() to initialise the LCD, and then we need to write each character using the lcd_data() function and with RS=1 (data mode). This can be done in a loop to add the complete string character by character until a null terminator is received. If I want to write in the first line, I send the command 0x80 to set the cursor in the first line. The same is done with 0xC0 for the second line.
⇥ What is the difference between 4-bit and 8-bit interfacing an LCD with 8051?
With 8-bit interfacing of an LCD with 8051, all 8 data pins (D0-D7) are used, so 11 microcontroller pins are used in total. In 4-bit interfacing, only the upper 4 pins are used (D4-D7), so I only use 7 pins. The benefit is that I save I/O ports. I send the data in 4-bit mode in 2 nibbles, so it is more complicated code, but it saves my pins. In 8-bit mode, it is much simpler code and 8 pins are removed from the schematic.
GitHub Repository
Explore More LCD Interfacing Projects
Deepen your understanding of 16x2 LCD modules by diving into these diverse microcontroller-based interfacing projects.
Interfacing a 16x2 LCD with Arduino
In this article, we discussed about 16x2 LCD, its working, pinout, and also how to use the 16x2 LCD with Arduino. We provided a Circuit Diagram, Complete Arduino Code, and a step-by-step guide.
16x2 LCD with Atmega16 AVR Microcontroller in 4-Bit Mode
In this tutorial, we will see how to interface a 16x2 LCD with an Atmega16 AVR microcontroller and display a simple welcome message.
16x2 LCD with ARM7-LPC2148 in 4-Bit Mode
In this tutorial, we will see how to interface a 16x2 LCD with the ARM7-LPC2148 microcontroller and display a simple welcome message.
Complete Project Code
// Program for LCD Interfacing with 8051 Microcontroller (AT89S52)
#include<reg51.h>
#define display_port P2 //Data pins connected to port 2 on microcontroller
sbit rs = P3^2; //RS pin connected to pin 2 of port 3
sbit rw = P3^3; // RW pin connected to pin 3 of port 3
sbit e = P3^4; //E pin connected to pin 4 of port 3
void msdelay(unsigned int time) // Function for creating delay in milliseconds.
{
unsigned i,j ;
for(i=0;i<time;i++)
for(j=0;j<1275;j++);
}
void lcd_cmd(unsigned char command) //Function to send command instruction to LCD
{
display_port = command;
rs= 0;
rw=0;
e=1;
msdelay(1);
e=0;
}
void lcd_data(unsigned char disp_data) //Function to send display data to LCD
{
display_port = disp_data;
rs= 1;
rw=0;
e=1;
msdelay(1);
e=0;
}
void lcd_init() //Function to prepare the LCD and get it ready
{
lcd_cmd(0x38); // for using 2 lines and 5X7 matrix of LCD
msdelay(10);
lcd_cmd(0x0F); // turn display ON, cursor blinking
msdelay(10);
lcd_cmd(0x01); //clear screen
msdelay(10);
lcd_cmd(0x81); // bring cursor to position 1 of line 1
msdelay(10);
}
void main()
{
unsigned char a[15]="CIRCUIT DIGEST"; //string of 14 characters with a null terminator.
int l=0;
lcd_init();
while(a[l] != '\0') // searching the null terminator in the sentence
{
lcd_data(a[l]);
l++;
msdelay(50);
}
}
Comments
Please refer this: Getting Started with 8051 Microcontroller
What is the difference b\w 8051 and 89s52
liquid crystal display is working but it is not display anything like circuit digest.
how can i fix that sir
programme uploading done
and programme is correct
but it is not work
pls tell any idea sir
Check your circuit connections again.
Agree with you harish kumar
If you got the solution kindly share with us
hey..!!! your lcd interfacing code wwas really helpful.
can you please provide me a code for interfacing LCD in 4 Bit Mode.
sir i m not getting the display on lcd it is running but there is display of CIRCUIT DIGEST
Thanku for ur explanation and code.Can u tell me how to store multiple strings into LCD?
sir, i want program for the ardino uno adc program
sir, i used this code it is working while simulation(Proteus s/w) in laptop....but in hardware not displaying words in LCD.....it's showing blocks...plz tell what might be the problem..
i will love to be part of you guys
the program can be erased on at89s52
Hello circuit digest!
Can I use blue character display instead of green.
hey circuit digest...
how can display fix value on LCD interfacing with 8051..and give me assembly language
........plz
The above video shows lcd interface on bread board
Can this project be shown on general purpose board???
Also on pcb???
Very useful article









what kind of programmer did you use and which software