Artificial Intelligence (AI) is changing science fiction into reality and this technology is taking over the world. Inspired by Iron man and Jarvis we decided to build something similar which can be controlled just by hand gestures. This system detects the hand and identifies the gesture with the help of artificial intelligence and based on that, it controls the appliances. It can be programmed to recognize different gestures and control the appliances accordingly. It can be used in a smart home to control AC appliances with just hand gestures, control the speed of the fan, control volume, control brightness of the lights, or even open/close the door stopper through gestures (with the use of servo motor), this can be very helpful for old age people who have limited mobility. Find out our already built some cool ai and robotic projects.
If you are interested in more gesture controlled projects, you can check out the below
1. Gesture controlled Robot Car
2. Gesture controlled Robotic Arm
3. Gesture controlled Video Player
4. Gesture controlled Home Automation
Required Components
- Arduino Uno/Nano
- LEDs
- Micro-Servo Motor
- Webcam (For prototype)
- 330-ohm Resistors
- Raspberry Pi (For prototype, Internal processor of PC is used)
Softwares
- Pycharm (OpenCV library, Mediapipe library, PySerial library),
- Python,
- Arduino IDE
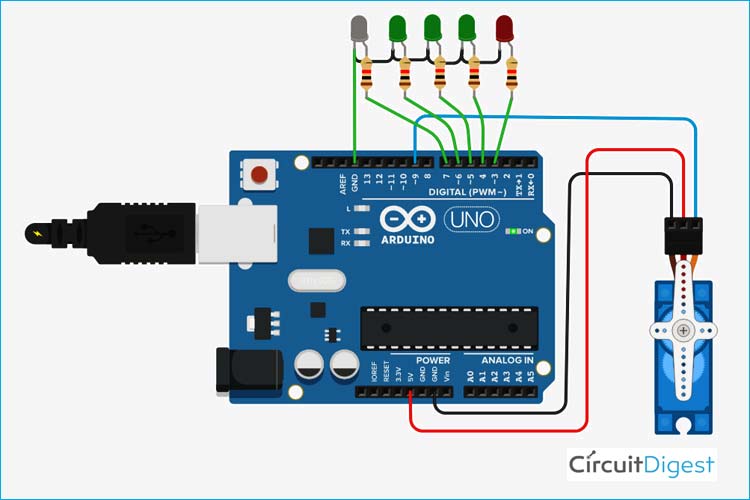
Circuit Diagram
For this prototype, LEDs are connected to pin numbers 3,4,5,6, and 7 respectively, and a servo motor is connected to pin number 9. Relays can be connected in place of LEDs to control AC appliances. You can connect as many appliances as you want till you run out of pins or gestures.
Gesture based Intelligent Appliance Control

For the prototype, we have used LEDs and Servo Motor to demonstrate how it works. Arduino is selected because it is easily available and open-source. It uses OpenCV and mediapipe library for real-time hand land mark detection from the webcam and based on that it returns the coordinates of the hand landmarks. Once the coordinates are obtained, some mathematical algorithms are applied to check how many fingers are raised (by that gesture is detected) and that number is stored in a variable. With the help of pyserial library, it is passed to the Arduino serially, now with this information, Arduino is programmed to perform certain tasks based on the information got from the python script. We used small LEDs for the demonstration, but AC appliances can also be controlled by the use of relay (electro-mechanical switches). For the prototype version, inbuilt microprocessor of the laptop and webcam is used for real-time tracking and gesture recognition, which can be replaced with a raspberry pi and a piCam at the final stage.
Complete Project Code
# PYTHON CODE (Main code)
import cv2
import time
import HandTrackingModule as htm
import serial
# code reference from cvzone
ser1 = serial.Serial('COM8',9600) #change according to your arduino COM port
ser1.timeout = 1
wCam, hCam = 640, 480
cap = cv2.VideoCapture(0)
cap.set(3, wCam)
cap.set(4, hCam)
pTime = 0
detector = htm.handDetector(detectionCon=0.75,maxHands=1)
tipIds = [4, 8, 12, 16, 20]
while True:
success, img = cap.read()
img = detector.findHands(img)
lmList = detector.findPosition(img, draw=False)
if len(lmList) != 0:
fingers = []
# Thumb
if lmList[tipIds[0]][1] > lmList[tipIds[0] - 1][1]:
fingers.append(1)
else:
fingers.append(0)
# 4 Fingers
for id in range(1, 5):
if lmList[tipIds[id]][2] < lmList[tipIds[id] - 2][2]:
fingers.append(1)
else:
fingers.append(0)
# print(fingers)
totalFingers = fingers.count(1)
print(100+totalFingers)
ser1.write(str(100+totalFingers).encode())
cv2.rectangle(img, (20, 225), (170, 425), (0, 255, 250), cv2.FILLED)
cv2.putText(img, str(totalFingers), (45, 375), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_PLAIN,
10, (255, 0, 0), 25)
cTime = time.time()
fps = 1 / (cTime - pTime)
pTime = cTime
cv2.putText(img, f'FPS: {int(fps)}', (400, 70), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_PLAIN,
3, (255, 0, 0), 3)
cv2.imshow("Image", img)
cv2.waitKey(1)
# ser1.close()
//ARDUINO CODE
include
int incomingByte = 0;
int num;
Servo myservo;
int pos = 0;
void setup() {
// put your setup code here, to run once:
Serial.begin(9600);
myservo.attach(9);
pinMode(3,OUTPUT);
pinMode(4,OUTPUT);
pinMode(5,OUTPUT);
pinMode(6,OUTPUT);
pinMode(7,OUTPUT);
}
void loop() {
// put your main code here, to run repeatedly:
char sdata[3];
if (Serial.available()>0){
incomingByte = Serial.readBytes(sdata,3);
int d1 = sdata[0]-'0';
int d2 = sdata[1]-'0';
int d3 = sdata[2]-'0';
// if (d3==-38){ // because when 2 dig no. is entered d3 == -38
// num = d1*10 + d2;
// Serial.println(num);
// pos = map(num,100,105,0,170);
// myservo.write(pos);
//
// if(num==101){
// digitalWrite(3,1);
// }
// else{
// digitalWrite(3,0);
// }
//
// }
if(d3!=-38){
int num = d1*100 + d2*10 + d3;
if (num>0){
Serial.println(num);
pos = map(num,100,105,0,170);
myservo.write(pos);
if(num==101){ // switch case can be used
digitalWrite(3,1);
digitalWrite(4,0);
digitalWrite(5,0);
digitalWrite(6,0);
digitalWrite(7,0);
}
else if(num==102){
digitalWrite(3,1);
digitalWrite(4,1);
digitalWrite(5,0);
digitalWrite(6,0);
digitalWrite(7,0);
}
else if(num==103){
digitalWrite(3,1);
digitalWrite(4,1);
digitalWrite(5,1);
digitalWrite(6,0);
digitalWrite(7,0);
}
else if(num==104){
digitalWrite(3,1);
digitalWrite(4,1);
digitalWrite(5,1);
digitalWrite(6,1);
digitalWrite(7,0);
}
else if(num==105){
digitalWrite(3,1);
digitalWrite(4,1);
digitalWrite(5,1);
digitalWrite(6,1);
digitalWrite(7,1);
}
else{
digitalWrite(3,0);
digitalWrite(4,0);
digitalWrite(5,0);
digitalWrite(6,0);
digitalWrite(7,0);
}
}
}
}
}
#HAND TRACKING MODULE (put this in the same folder as the main code with name HandTrackingModule.py)
#code from cvzone
import cv2
import mediapipe as mp
import time
class handDetector():
def __init__(self, mode=False, maxHands=2, detectionCon=0.5, trackCon=0.5):
self.mode = mode
self.maxHands = maxHands
self.detectionCon = detectionCon
self.trackCon = trackCon
self.mpHands = mp.solutions.hands
self.hands = self.mpHands.Hands(self.mode, self.maxHands,
self.detectionCon, self.trackCon)
self.mpDraw = mp.solutions.drawing_utils
def findHands(self, img, draw=True):
imgRGB = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
self.results = self.hands.process(imgRGB)
# print(results.multi_hand_landmarks)
if self.results.multi_hand_landmarks:
for handLms in self.results.multi_hand_landmarks:
if draw:
self.mpDraw.draw_landmarks(img, handLms,
self.mpHands.HAND_CONNECTIONS)
return img
def findPosition(self, img, handNo=0, draw=True):
lmList = []
if self.results.multi_hand_landmarks:
myHand = self.results.multi_hand_landmarks[handNo]
for id, lm in enumerate(myHand.landmark):
# print(id, lm)
h, w, c = img.shape
cx, cy = int(lm.x * w), int(lm.y * h)
# print(id, cx, cy)
lmList.append([id, cx, cy])
if draw:
cv2.circle(img, (cx, cy), 5, (255, 0, 255), cv2.FILLED)
return lmList
def main():
pTime = 0
cTime = 0
cap = cv2.VideoCapture(0)
detector = handDetector()
while True:
success, img = cap.read()
img = detector.findHands(img)
lmList = detector.findPosition(img)
if len(lmList) != 0:
print(lmList[4])
cTime = time.time()
fps = 1 / (cTime - pTime)
pTime = cTime
cv2.putText(img, str(int(fps)), (10, 70), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_PLAIN, 3,
(255, 0, 255), 3)
cv2.imshow("Image", img)
cv2.waitKey(1)
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()