In this project, we upgraded LiteWing, an ESP32-based development drone by adding a lightweight Bluetooth speaker system to extend its capabilities beyond flight. By adding a simple Bluetooth audio setup, the drone can now deliver real-time announcements, voice messages, or music directly from the air without requiring any additional coding. The entire system works through a standard Bluetooth connection, making it easy to set up, practical for demonstrations, events, and experimental applications while also being fun.
If you want to learn how to make a DIY Bluetooth speaker, check out the article titled “Build a Compact and Portable DIY Bluetooth Speaker.” By combining wireless communication and lightweight audio hardware, this setup makes it possible to use the drone announcements, campus activities, safety alerts, and creative applications. Our collection of DIY drone projects focuses on building programmable and sensor-equipped drones using microcontrollers such as ESP32 and related technologies.
Drone with Loudspeaker: Add a Bluetooth Speaker System to the LiteWing ESP32 Drone
A beginner-friendly, step-by-step guide to build a loudspeaker drone for real-time aerial announcements, voice alerts, and Bluetooth audio streaming powered by the LiteWing ESP32 platform.
- Pair the JDY-62 Bluetooth module as a Bluetooth audio receiver.
- Feed the audio signal into the PAM8403 amplifier.
- Drive the 2W 8Ω speaker for audible aerial playback.
- Power everything via a 3.7V–5V boost converter from the drone's VBUS pin.
- Pair your smartphone → stream audio → fly and announce. No code needed.
LiteWing ESP32 Drone Bluetooth Speaker Explanation and Demo Video
Overview of Drones with added Loudspeaker Systems
The drone is an unmanned aerial vehicle integrated with a loudspeaker system, allowing it to transmit live voice announcements, music, and various audio alerts during flight operations.
A drone that has an integrated wireless sound system has all of these components built right into the frame of the craft itself, providing a mobile public address system from any location within the drone’s flight range. This technology can easily be used in areas where traditional ground-level sound systems may not be able to reach their intended audience effectively.
Components Required for the Bluetooth Speaker Drone
To add a drone speaker system to the LiteWing drone, a few basic hardware components are needed. These parts help in receiving wireless audio, amplifying the sound, and supplying proper power to the system. The list below shows all the components used in this project and their purpose.
| Component | Function |
| LiteWing Drone | Receives wireless audio data via Bluetooth from a mobile device |
| PAM8403 Audio Amplifier | Amplifies low-power audio signals to drive the external speaker |
| 2-Watt 8Ω Speaker | Outputs audio for real-time announcements and voice playback |
| 3.7V to 5V Boost Converter | Steps up battery voltage to provide stable power supply for the audio system components |
| Wires | Used to connect the Bluetooth module, amplifier, boost converter, and speaker together |
Hardware Setup and Wiring Guide
The hardware setup involves connecting the drone with a Bluetooth speaker, audio amplifier, speaker, and boost converter to the LiteWing drone. Proper wiring and power connections are important to ensure stable audio output and safe operation during flight. In this section, we will explain how each component is connected and how the overall system is assembled, as shown in the image below.
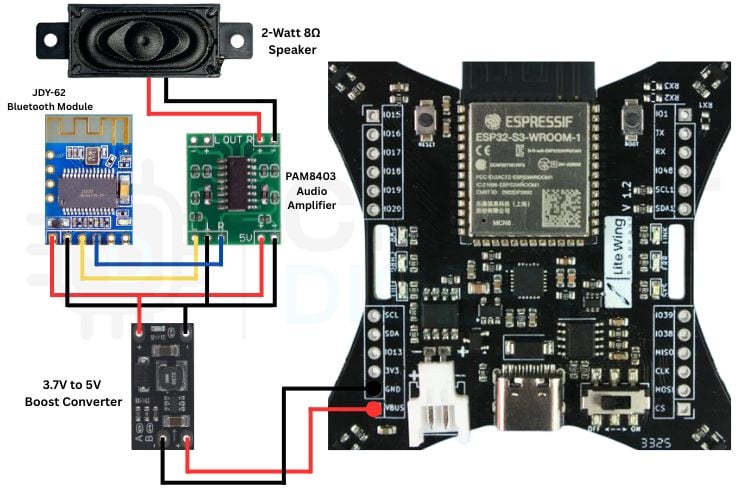
The image shows the hardware connections for integrating a BLE speaker system with the LiteWing drone.
Key Wiring Points at a Glance
- The JDY-62 Bluetooth module connects to the PAM8403 amplifier, which then drives the 2W speaker. In this connection, the red and black wires are used for the power supply, while the yellow wire carries the audio signal and is connected to the right audio input of the amplifier.
- A 3.7V to 5V boost converter powers the amplifier and speaker to ensure a stable voltage.
- All components are connected to the LiteWing ESP32 drone through the GND and VBUS pins for power.
This setup allows the drone to receive audio via Bluetooth and play it through the speaker while flying.
How the LiteWing Bluetooth Speaker Drone System Works
The LiteWing drone with Bluetooth speaker system works by combining wireless communication, audio processing, and flight control to create an interactive aerial platform. Here’s how it functions step by step:
Wireless Audio Reception
The JDY-62 Bluetooth module acts as the audio receiver. When paired with a mobile device, it receives audio signals wirelessly using Bluetooth. This allows you to stream drone announcements, music, or voice messages directly to the drone while it is flying.
Audio Amplification
The low-power audio signal received from the JDY-62 module is not strong enough to drive a speaker directly. The PAM8403 audio amplifier boosts this signal, ensuring that the output sound is loud and clear for real-time announcements.
Power Supply Management
The drone’s battery voltage (typically 3.7V) is stepped up to a stable 5V using the boost converter. The VIN+ of the boost converter is connected to the VBUS of the drone, ensuring that both the Bluetooth module and the amplifier receive consistent power for uninterrupted operation, even while the drone is flying.
Audio Output
The amplified signal is sent to the 2-Watt 8Ω speaker mounted on the drone. The speaker plays the received audio clearly, allowing the drone to deliver announcements, alerts, or interactive messages from the air. In real-world testing, the drone speaker is clearly audible at typical low-altitude flight heights, making this an effective solution for short-range aerial drone announcement applications such as event broadcasts and safety alerts.
Integration with the Drone
The entire audio system is lightweight and carefully integrated with the LiteWing drone with a loudspeaker. Wires connect the Bluetooth module, amplifier, and speaker, while the ESP32 flight controller continues to manage drone navigation. This ensures that the drone can fly normally while also functioning as a flying audio communication platform.
Working Demonstration
In the working video, you can see the LiteWing drone flying while playing audio in real time through the Bluetooth speaker system. It clearly shows how the drone connects to a mobile phone via Bluetooth and broadcasts voice messages from the air. This video gives a practical view of the setup in action and helps you understand how the system performs.
In our article DIY Gesture Control Drone using Python with LiteWing and ESP32, we built a gesture-controlled system ourselves using an ESP32 and MPU6050 sensor to wirelessly control a LiteWing drone via Bluetooth and Python, and you can try it yourself if you're passionate about innovative DIY tech projects.
Real-World Applications of a Loudspeaker Drone
The ability to broadcast audio from the air makes a loudspeaker drone uniquely versatile across a wide range of industries and use cases. Here are the primary applications of this drone announcement platform:
- Event announcements and public messaging
- Safety alerts and emergency notifications
- Tour guidance and interactive experiences
- Advertising and promotional campaigns
- Search and rescue communication
- Educational demonstrations
- Creative content and entertainment
Troubleshooting Drone Restarting Issue
Connect the VIN+ of the boost converter to the drone’s VBUS pin instead of the 3.3V pin to prevent restarting problems. This is necessary because the 3.3V power line cannot supply enough current for the boost converter and audio components, which causes the drone to reboot. The VBUS pin provides a more stable and higher current power supply, allowing the system to operate smoothly.
| Symptom | Likely Cause | Solution |
| Drone resets on power-up | Insufficient current from 3.3V pin | Move boost converter VIN+ to VBUS pin |
| No audio output | JDY-62 not paired / wrong audio channel | Re-pair device; confirm yellow wire is on R+ input of PAM8403 |
| Drone unstable or drifting | Added weight unbalanced on frame | Redistribute speaker and module mass symmetrically; keep total added weight under 25 g |
Frequently Asked Questions: Drone with Loudspeaker
⇥ 1. How much weight can the LiteWing drone lift?
The LiteWing drone can typically lift around 20 to 30 grams of additional payload, depending on battery and motor performance. For stable flight, it is recommended to keep the added weight as low as possible.
⇥ 2. Is a boost converter mandatory for this setup?
Yes, a boost converter is recommended because the drone battery provides around 3.7V, while the Bluetooth module and amplifier require a stable 5V supply for reliable operation.
⇥ 3. Can I use a different Bluetooth module instead of JDY-62?
Yes, you can use other Bluetooth audio receiver modules, but make sure they support audio output, work on low power, and are lightweight to avoid affecting the drone’s flight performance.
⇥ 4. Do I need to write any code to use the Bluetooth speaker system
No, coding is not required. The system works directly through Bluetooth pairing, allowing audio to be streamed from a mobile device without any programming.
⇥ 5. What precautions should be taken while adding extra hardware?
Keep the added components lightweight, use proper soldering to make strong and reliable connections, ensure a stable power supply, and avoid blocking the propellers or airflow to maintain safe and stable flight.
⇥ 6. What Module Is The Best For A Drone Speaker?
The excellent Bluetooth audio modules available make them ideal choices for drone speakers, as they typically offer wireless audio streaming, very low power draw (3.3 to 5V) and very lightweight (important for maintaining flight performance). All Bluetooth audio modules provide standard analogue audio outputs, allow for Bluetooth pairing, and draw less than 100mA in their operating mode, so any one of these will work with your Bluetooth speaker build.
⇥ 7. What Amplifier Should Be Used For A Drone Speaker?
The PAM8403 Class D stereo amplifier would be the best option to power a drone speaker. It will operate on 5V power, has excellent power efficiency (Class D), has a weight of only a few grams, and provides 3W per channel (more than enough to power a two watt 8Ω speaker at outdoor listening levels). It also has a low idle current; therefore, this will help reduce the overall impact of the amplifier on a drone's flight time.
Related Tutorial: Similar to LiteWing ESP32 Drone
This series shows how to set up the LiteWing ESP32 DIY drone with Betaflight, control it using Python, and enable height hold for stable hovering, perfect for beginners and makers.
How to Connect the LiteWing ESP32 Drone to Betaflight
This project shows how to connect and configure the LiteWing ESP32 drone with Betaflight firmware. By flashing Betaflight on the ESP32 and setting up motors, IMU, receiver, and flight modes, you can convert a small DIY drone into a fully tunable FPV-style flight controller for stable and customizable flight performance.
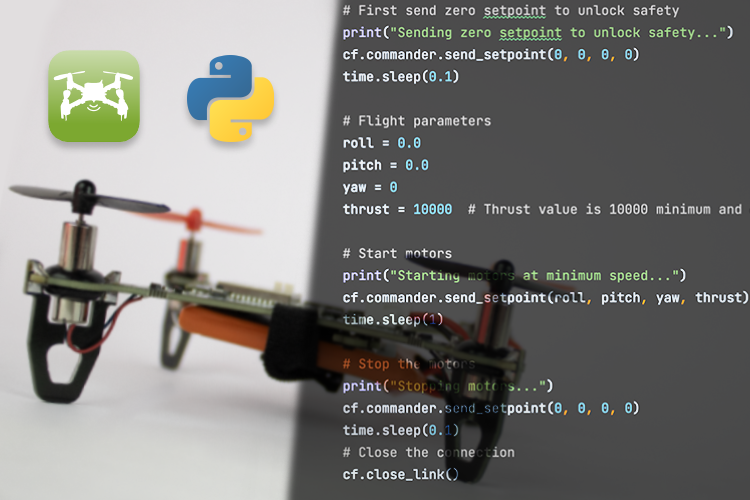
How to Program the LiteWing Drone using Python with Crazyflie Cflib Python SDK
This guide shows how to program the LiteWing ESP32 DIY Drone Kit for Makers and Developers Q20 C2 using Python with the Crazyflie cflib SDK over Wi-Fi. It explains how to install the Python SDK, connect to the drone via UDP, and write a simple script to arm the drone and spin the motors using Python commands.
How to Use Height Hold Mode in LiteWing ESP32 Drone?
This guide explains how to add and use height hold mode on the LiteWing ESP32 drone using a VL53L1X Time-of-Flight (ToF) distance sensor. It shows how attaching the sensor and activating height hold lets the drone automatically maintain a set altitude for stable hovering and easier flight control.