
The era of automation has begun already. Most of the things that we use now can be automated. To design automated devices first we need to know about the sensors, these are the modules/devices which are helpful in making things done without human intervention. Even the mobiles or smartphones which we daily use will have some sensors like hall sensor, proximity sensor, accelerometer, touch screen, microphone etc. These sensor acts as eyes, ears, nose of any electrical equipment which senses the parameters in outside world and give readings to devices or Microcontroller.
What is a sensor?
The sensor can be defined as a device which can be used to sense/detect the physical quantity like force, pressure, strain, light etc and then convert it into desired output like the electrical signal to measure the applied physical quantity. In few cases, a sensor alone may not be sufficient to analyze the obtained signal. In those cases, a signal conditioning unit is used in order to maintain sensor’s output voltage levels in the desired range with respect to the end device that we use.
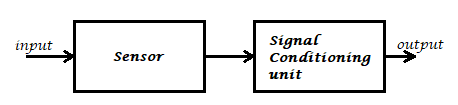
In signal conditioning unit, the output of the sensor may be amplified, filtered or modified to the desired output voltage. For example, if we consider a microphone it detects the audio signal and converts to the output voltage (is in terms of millivolts) which becomes hard to drive an output circuit. So, a signal conditioning unit (an amplifier) is used to increase the signal strength. But the signal conditioning may not be necessary for all the sensors like photodiode, LDR etc.
Most of the sensors can’t work independently. So, sufficient input voltage should be applied to it. Various sensors have different operating ranges which should be considered while working with it else the sensor may get damaged permanently.
Types of Sensors:
Let us see the various different types of sensors that are available in the market and discuss their functionality, working, applications etc. We will discuss various sensors like:
- Light Sensor
- IR Sensor (IR Transmitter / IR LED)
- Photodiode (IR Receiver)
- Light Dependent Resistor
- Temperature Sensor
- Thermistor
- Thermocouple
- Pressure/Force/Weight Sensor
- Strain Gauge (Pressure Sensor)
- Load Cells (Weight Sensor)
- Position Sensor
- Potentiometer
- Encoder
- Hall Sensor (Detect Magnetic Field)
- Flex Sensor
- Sound Sensor
- Microphone
- Ultrasonic Sensor
- Touch Sensor
- PIR Sensor
- Tilt Sensor
- Accelerometer
- Gas Sensor
We need to select the desired sensor based on our project or application. As said earlier in order to make them work proper voltage should be applied based on their specifications.
Now let us see the working principle of these different types of sensors and where it can be seen in our day to day life or its application.
IR LED:
It is also called as IR Transmitter. It is used to emit Infrared rays. The range of these frequencies are greater than the microwave frequencies (i.e. >300GHz to few hundreds of THz). The rays generated by an infrared LED can be sensed by Photodiode explained below. The pair of IR LED and photodiode is called IR Sensor. Here is how an IR sensor works.

Photo Diode (Light Sensor):
It is a semiconductor device which is used to detect the light rays and mostly used as IR Receiver. Its construction is similar to the normal PN junction diode but the working principle differs from it. As we know a PN junction allows small leakage currents when it is reverse biased so, this property is used to detect the light rays. A photodiode is constructed such that light rays should fall on the PN junction which makes the leakage current increase based on the intensity of the light that we have applied. So, in this way, a photodiode can be used to sense the light rays and maintain the current through the circuit. Check here the working of Photodiode with IR sensor.
Using a photodiode we can build a basic automatic street lamp which glows when the sunlight intensity decreases. But the photodiode works even if a small amount of light falls on it so, care should be taken.

LDR (Light Dependent Resistor):
As the name itself specifies that the resistor that depends upon the light intensity. It works on the principle of photoconductivity which means the conduction due to the light. It is generally made up of Cadmium sulfide. When light falls on the LDR, its resistance decreases and acts similar to a conductor and when no light falls on it, its resistance is almost in the range of MΩ or ideally it acts as an open circuit. One note should be considered with LDR is that it won’t respond if the light is not exactly focused on its surface.

With a proper circuitry using a transistor it can be used to detect the availability of light. A voltage divider biased transistor with R2 (resistor between base and emitter) replaced with an LDR can work as a light detector. Check here the various circuits based on LDR.
Thermistor (Temperature Sensor):
A thermistor can be used to detect the variation in temperature. It has a negative temperature coefficient that means when the temperature increases the resistance decreases. So, the thermistor’s resistance can be varied with the rise in temperature which causes more current flow through it. This change in current flow can be used to determine the amount of change in temperature. An application for thermistor is, it is used to detect the rise in temperature and control the leakage current in a transistor circuit which helps in maintaining its stability. Here is one simple application for Thermistor to control the DC fan automatically.
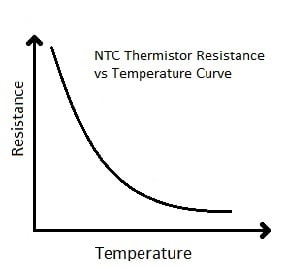

Thermocouple (Temperature Sensor):
Another component that can detect the variation in temperature is a thermocouple. In its construction, two different metals are joined together to form a junction. Its main principle is when the junction of two different metals are heated or exposed to high temperatures a potential across their terminals varies. So, the varying potential can be further used to measure the amount of change in temperature.
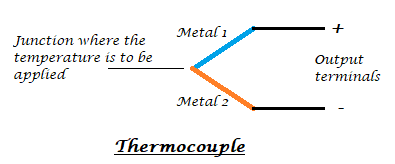
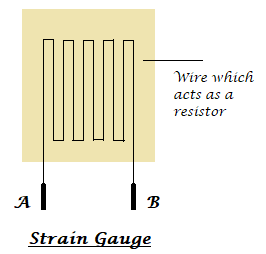
Strain Gauge (Pressure/Force Sensor):
A strain gauge is used to detect pressure when a load is applied. It works on the principle of resistance, we know that the resistance is directly proportional to the length of the wire and is inversely proportional to its cross-sectional area (R=ρl/a). The same principle can be used here to measure the load. On a flexible board, a wire is arranged in a zig-zag manner as shown in the figure below. So, when the pressure is applied to that particular board, it bends in a direction causing the change in overall length and cross-sectional area of the wire. This leads to change in resistance of the wire. The resistance thus obtained is very minute (few ohms) which can be determined with the help of the Wheatstone bridge. The strain gauge is placed in one of the four arms in a bridge with the remaining values unchanged. Therefore, when the pressure is applied to it as the resistance changes the current passing through the bridge varies and pressure can be calculated.
Strain gauges are majorly used to calculate the amount of pressure that an airplane wing can withstand and it is also used to measure the number of vehicles allowable on a particular road etc.
Load Cell (Weight Sensor):
Load cells are similar to strain gauges which measure the physical quantity like force and give the output in form of electrical signals. When some tension is applied on the load cell it structure varies causing the change in resistance and finally, its value can be calibrated using a Wheatstone bridge. Here is the project on how to measure weight using Load cell.

Potentiometer:
A potentiometer is used to detect the position. It generally has various ranges of resistors connected to different poles of the switch. A potentiometer can be either rotary or linear type. In rotary type, a wiper is connected to a long shaft which can be rotated. When the shaft has rotated the position of the wiper alters such that the resultant resistance varies causing the change in the output voltage. Thus the output can be calibrated to detect the change its position.

Encoder:
To detect the change in the position an encoder can also be used. It has a circular rotatable disk-like structure with specific openings in between such that when the IR rays or light rays pass through it only a few light rays get detected. Further, these rays are encoded into a digital data (in terms of binary) which represents the specific position.

Hall Sensor:
The name itself states that it is the sensor which works on the Hall Effect. It can be defined as when a magnetic field is brought close to the current carrying conductor (perpendicular to the direction of the electric field) then a potential difference is developed across the given conductor. Using this property a Hall sensor is used to detect the magnetic field and gives output in terms of voltage. Care should be taken that the Hall sensor can detect only one pole of the magnet.

The hall sensor is used in few smartphones which are helpful in turning off the screen when the flap cover (which has a magnet in it) is closed onto the screen. Here is one practical application of Hall Effect sensor in Door Alarm.
Flex Sensor:
A FLEX sensor is a transducer which changes its resistance when its shape is changed or when it is bent. A FLEX sensor is 2.2 inches long or of finger length. It is shown in the figure. Simply speaking the sensor terminal resistance increases when it’s bent. This change in resistance can do no good unless we can read them. The controller at hand can only read the changes in voltage and nothing less, for this, we are going to use voltage divider circuit, with that we can derive the resistance change as a voltage change. Learn here about how to use Flex Sensor.

Microphone (Sound Sensor):
Microphone can be seen on all the smartphones or mobiles. It can detect the audio signal and convert them into small voltage (mV) electrical signals. A microphone can be of many types like condenser microphone, crystal microphone, carbon microphone etc. each type of microphone work on the properties like capacitance, piezoelectric effect, resistance respectively. Let us see the operation of a crystal microphone which works on the piezoelectric effect. A bimorph crystal is used which under pressure or vibrations produces proportional alternating voltage. A diaphragm is connected to the crystal through a drive pin such that when the sound signal hits the diaphragm it moves to and fro, this movement changes the position of the drive pin which causes vibrations in the crystal thus an alternating voltage is generated with respect to the applied sound signal. The obtained voltage is fed to an amplifier in order to increase the overall strength of the signal. Here are various circuits based on Microphone.

You can also convert the Microphone value in Decibels using some microcontroller like Arduino.
Ultrasonic sensor:
Ultrasonic means nothing but the range of the frequencies. Its range is greater than audible range (>20 kHz) so even it is switched on we can’t sense these sound signals. Only specific speakers and receivers can sense those ultrasonic waves. This ultrasonic sensor is used to calculate the distance between the ultrasonic transmitter and the target and also used to measure the velocity of the target.
Ultrasonic sensor HC-SR04 can be used to measure distance in the range of 2cm-400cm with an accuracy of 3mm. Let’s see how this module works. The HCSR04 module generates a sound vibration in ultrasonic range when we make the ‘Trigger’ pin high for about 10us which will send an 8 cycle sonic burst at the speed of sound and after striking the object, it will be received by the Echo pin. Depending on the time taken by sound vibration to get back, it provides the appropriate pulse output. We can calculate the distance of the object based on the time taken by the ultrasonic wave to return back to the sensor. Learn more about Ultrasonic sensor here.

There are many applications with the ultrasonic sensor. We can make use of it avoid obstacles for the automated cars, moving robots etc. The same principle will be used in the RADAR for detecting the intruder missiles and airplanes. A mosquito can sense the ultrasonic sounds. So, ultrasonic waves can be used as mosquito repellent.
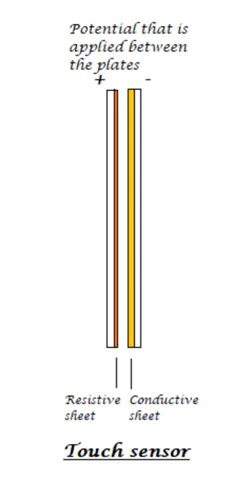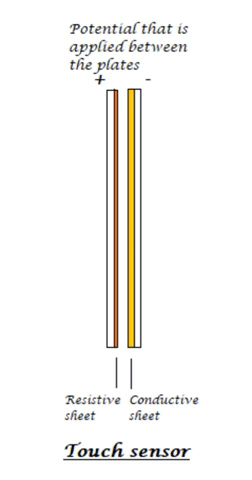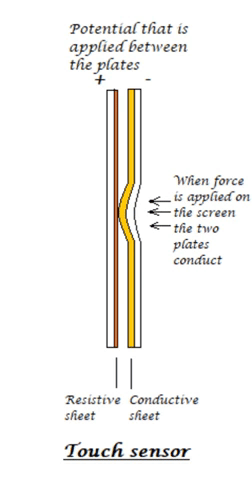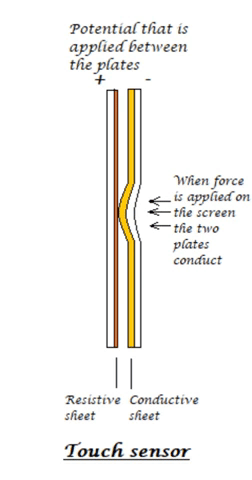
Touch Sensor:
In this generation, we can say that almost all are using smartphones which have widescreen that too a screen which can sense our touch. So, let’s see how this touchscreen works. Basically, there are two types of touch sensors resistive based and a capacitive based touch screens. Let’s know about working of these sensors briefly.
The resistive touchscreen has a resistive sheet at the base and a conductive sheet under the screen both of these are separated by an air gap with a small voltage applied to the sheets. When we press or touch the screen the conductive sheet touches the resistive sheet at that point causing current flow at that particular point, the software senses the location and relevant action is performed.
Whereas capacitive touch works on the electrostatic charge that is available on our body. The screen is already charged with s the all electric field. When we touch the screen a close circuit forms due to electrostatic charge that flow through our body. Further, software decides the location and the action to be performed. We can observe that capacitive touch screen won’t work when wear hand gloves because there won’t be conduction between the finger(s) and the screen.
PIR sensor:
PIR sensor stands for Passive Infrared sensor. These are used to detect the motion of humans, animals or things. We know that infrared rays have a property of reflection. When an infrared ray hits an object, depending upon the temperature of the target the infrared ray properties changes, this received signal determines the motion of the objects or the living beings. Even if the shape of the object alters, the properties of the reflected infrared rays can differentiate the objects precisely. Here is the complete working or PIR sensor.

Accelerometer (Tilt Sensor):
An accelerometer sensor can sense the tilt or movement of it in a particular direction. It works based on the acceleration force caused due to the earth’s gravity. The tiny internal parts of it are such sensitive that those will react to a small external change in position. It has a piezoelectric crystal when tilted causes disturbance in the crystal and generates potential which determines the exact position with respect to X, Y and Z axis.
These are commonly seen in mobiles and laptops in order to avoid breakage of processors leads. When the device falls the accelerometer detects the falling condition and does respective action based on the software. Here are some projects using Accelerometer.
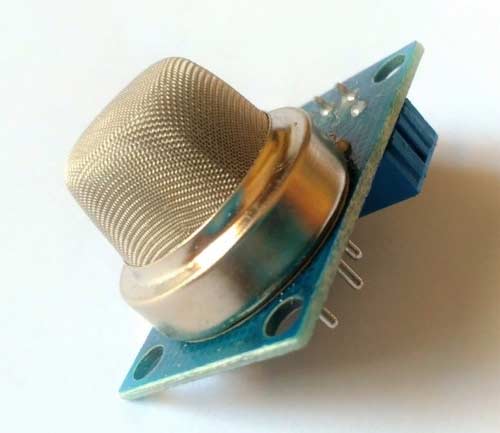
Gas sensor:
In industrial applications gas sensors plays a major role in detecting the gas leakage. If no such device is installed in such areas it ultimately leads to an unbelievable disaster. These gas sensors are classified into various types based on the type of gas that to be detected. Let’s see how this sensor works. Underneath a metal sheet there exists a sensing element which is connected to the terminals where a current is applied to it. When the gas particles hit the sensing element, it leads to a chemical reaction such that the resistance of the elements varies and current through it also alters which finally can detect the gas.

So finally, we can conclude that sensors are not only used to make our work simple to measure the physical quantities, making the devices automated but also used to help living beings with disasters.






I knew most of them, but very helpfull to have info avilable when making small circuits.