Digital Electronics
|
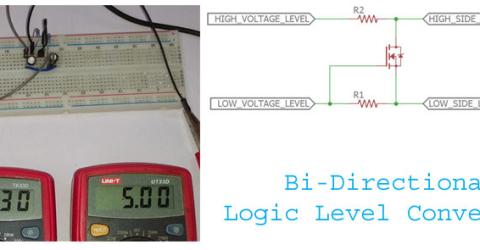
Bi-Directional Logic Level converter using MOSFET Back in the ENIAC era, computers were more analog in nature and used very few digital ICs. Today an average Joe’s computer… |
|
One-Gate Logic with Single Power Supply Supporting Low Voltage Operation Toshiba announced the release of the new 31 single power supply one-gate logic device series ‘7UL1G’ and ‘7UL1T’. Both… |

|
Missing Pulse Detector Circuit When a signal goes through a sudden change from base value to higher value and again comes to base value from higher value… |
|
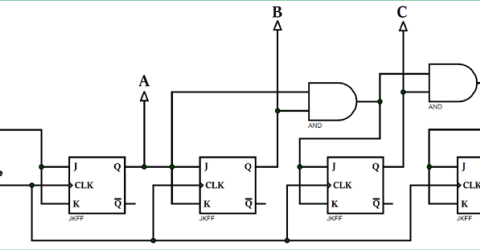
Synchronous CounterWhat is a Counter?
A counter is a device which can count any particular event on the basis of how many times the particular… |
|
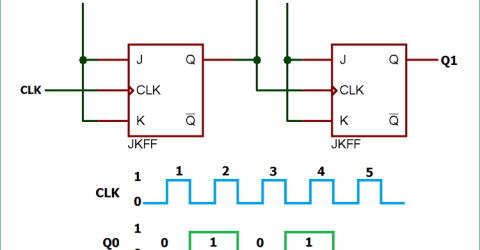
Asynchronous Counter An asynchronous counter (or ripple counter) is a sequential digital circuit in which the outputs of flip-flops are connected in series, so that… |
|
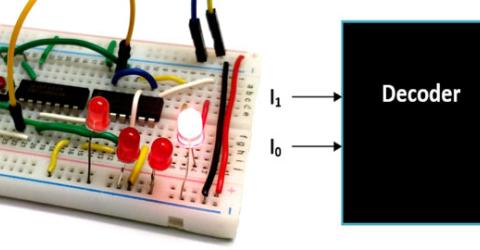
Binary Decoders Decoder is type of combinational Circuit which decodes a small bit value into large bit value. It is normally used in… |
|
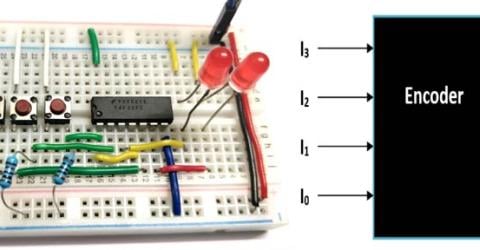
Binary Encoders Encoders, as the name suggest, encodes a larger bit of information into a smaller bit value. There are many types of… |
|
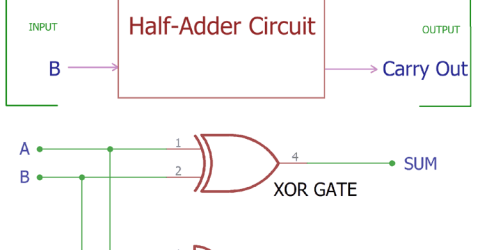
Half Adder Circuit and its Construction Computers use binary numbers 0 and 1. An adder circuit uses these binary numbers and calculates the addition. A binary adder… |

|
Different Types of Shift Registers and its Applications with Examples What is Shift Register:
Shift Registers are sequential logic circuits, capable of storage and transfer of data. They are made… |
|
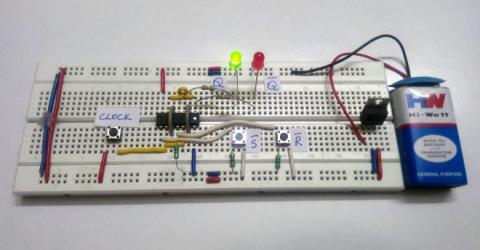
SR Flip-Flop with NAND Gates: Circuit, Truth Table and Working The SR flip flop using NAND gate truth table is a basic sequential logic circuit that holds one bit of digital information. This extensive guide… |

