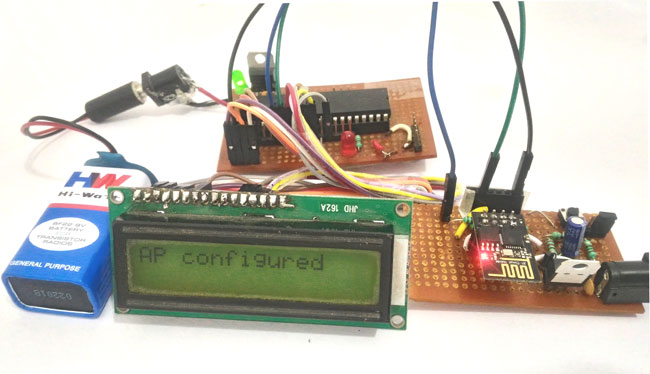
In this article, let us discuss how to interface WIFI module ESP8266 with a PIC microcontroller. So far you might have been using the ESP8266 module as a standalone microcontroller or might have been using it with the Arduino library. But, when it comes to hardcore embedded system projects we should know how to use it with PIC microcontrollers as well. This will help you to customize your projects in design perspective and at the same time also making it cheap.
The ESP8266 modules comes with a default firmware loaded into it, hence we can program the module using AT commands. These commands have to be sent through a serial communication channel. This channel is established between the PIC and the ESP8266 module by using the USART module in the PIC microcontroller. The whole working will be monitored and reported to the user by using a 16x2 LCD display. Hence, this tutorial assumes that you have some basic knowledge about the USART module in PIC, Interfacing LCD with PIC and using AT commands in ESP8266. If you do not then you can fall back to the linked tutorials to learn them beforehand.
Materials Required:
You would need the following hardware to complete this tutorial
- PIC16F877A
- 20MHz crystal oscillator
- 7805
- LM317
- ESP8266
- 16*2 LCD display
- PicKit3 programmer
- Resistors (1K,220ohm,360ohm)
- Capacitors (1uF, 0.1uF, 33pF)
- Jumper wires
- 12V Adapter to power the PIC and ESP module
Hardware:
The complete schematic of the project is shown here below
The schematics consists of two voltage regulator circuits, one is a +5V regulator which is used to power the PIC microcontroller and the other is a 3.3V regulator which powers the ESP8266 module. The +5V is regulated by using a 7805(Linear Voltage Regulator IC). The 3.3V is regulated by using LM317 (Variable Voltage Regulator). The ESP8266 module consumes a lot of current (~800mA) hence if you are designing your own power supply make sure it can source such high current. Also make sure that the ground pins of the PIC and the ESP8266 module is connected together.
So now we know that the PIC operates on +5V and the ESP8266 operates at 3.3V volts. In order to establish a USART communication between these two modules we need have a 5V - 3.3V logic converter circuit as shown in the above figure. This circuit is nothing but a potential divider which simply converts the incoming +5V to 3.3V. This will prevent the 3.3V tolerable RX pin of ESP8266 from getting +5V.
I have made the PIC and ESP modules on two separate perf boards, as shown in these tutorials. This way I can use them universally for more similar projects
You can follow the same, or build your own board in your style or simply connect the above circuit to a breadboard.
Programming the PIC microcontroller:
In order to program the PIC microcontroller to send “AT commands” serially using USART to the ESP8266 module we have to use a library. This library will save you a lot of hassle, like using the ESP8266 instruction modules to check for each and every AT command and then find a way to transmit them to the ESP module. This library is free software originally developed by Camil Staps and later it was improved and modified by Circuit Digest so that it can be used with our PIC16F877A Microcontroller. You can download it here
The library is still under development, but you can use most of the important AT commands in the ESP8266 firmware. If you find any of the command you need is missing, then let me know it in the comment section and I will try to add it for you. This tutorial will explain you all the commands(so far) that can be used by through this library. Further will also guide you to add your own functions to the library.
Functions in ESP8266 Library:
- Initialize_ESP8266(): This function will Initialize the USART module of the PIC to communicate with the ESP8266 module. It sets the baud rate at 115200 and prepares the Rx and Tx pin of PIC for USART communication.
- _esp8266_putch(): This function is used to send a single character serially to the ESP8266 module. For example, _esp8266_putch(‘a’) will send the character a serially to the ESPmodule.
- _esp8266_getch(): This function is used to get a single character from the ESP module. For example if the ESP is printing “OK” and we use char a =_esp8266_getch(). Then the char ‘o’ will be stored in the variable a.
- ESP8266_send_string(): This function is the string version of _esp8266_putch(). It can send one complete string to the ESP8266 module. For example, ESP8266_send_string(“AT/r/n”) will send the command “AT” to the ESP8266 module.
- esp8266_isStarted(): It is used to check if the PIC can communicate with the ESP module. It send the command “AT” and waits for “OK” if received it returns true else it returns false.
- esp8266_restart(): Resets the ESP8266 module and returns true is reset successful and returns false if not successful.
- esp8266_mode(): Used to set the working mode of the ESP8266 module. As we know it can work in three different modes.
|
esp8266_mode(1): |
Station mode |
|
esp8266_mode(2): |
Soft AP mode |
|
esp8266_mode(3): |
Both Station and AP mode |
- esp8266_connect(): Allows you to connect to a wifi signal. For example esp8266_connect(“home”,”12345678”), will allow your module to connect to the wifi signal named home whose password is 12345678.
- esp8266_disconnect(): This function disconnects you module from any wifi connection that was previously connected
- esp8266_ip(): Gets the IP address and returns it. Use this function if you wanna know the IP address of the ESP8266 module.
- esp8266_start(): This function is used to start a TCP or UDP communication. For example esp8266_start("TCP", "192.168.101.110", 80). Will start a TCP network in that IP and port 80.
- esp8266_send(): This function is used to send information to the TCP/UDP network. The HTML script will be sent using this command. Then this script will appear in the IP address in which the communication was established in prior.
- esp8266_config_softAP(): This function is used to configure the softAP. For example esp8266_config_softAP(“office”,”12345678”); will create a Wifi signal named office and the password 12345678 should be used to access it.
- esp8266_get_stationIP(): This function will return you the IP/MAC address of the clients who are connected to your softAP.
Sample Program:
Now that we have understood the functions of each and every command in the library let us look into a small sample program. In this program we will check if the connection between ESP8266 and PIC is successful and then create a WIFI network (SoftAP) with a preferred name and password. The complete program and the simulation of the same will be explained for your understanding.
Again if you have not read our PIC interfacing with LCD and PIC USART tutorial please read the, before proceeding because only then it will make sense to you.
Since we are just getting started to interface PIC with the ESP8266, I have used an LCD to make sure things are working properly.
do
{
Lcd_Set_Cursor(1,1);
Lcd_Print_String("ESP not found");
}while (!esp8266_isStarted()); //wait till the ESP send back "OK"
Lcd_Set_Cursor(1,1);
Lcd_Print_String("ESP is connected");
__delay_ms(1500);
Lcd_Clear();
When we send the “AT” to the ESP8266 module it replies back with a “OK”. This ensures us that the ESP8266 module is connected successfully. The function esp8266_isStarted() is used for the same. We send the signal AT from the PIC and we wait till the ESP module to get alive and send us an OK. If we get an OK we display that the “ESP is connected” on the LCD.
esp8266_mode(2);
Lcd_Set_Cursor(1,1);
Lcd_Print_String("ESP set as AP");
__delay_ms(1500);
Lcd_Clear();
The above lines of code are used to set the ESP module to work in “soft AP” mode. The function esp8266_mode(2); sends the AT commands “AT+CWMODE=3” to the module and waits for the module to respond with “OK”
/*Configure the AP name and Password*/
esp8266_config_softAP("CircuitDigest","619007123");
Lcd_Set_Cursor(1,1);
Lcd_Print_String("AP configured");
__delay_ms(1500);
Lcd_Clear();
/*AP configured*/
This segment of the code is used to configure the softAP. Here we have named the SSID as “CircuitDigest” and the password as “619007123”. To indicate that the process is complete we will wait for the module to respond with “OK” and then print AP configured onto the LCD screen.
That is it now we have interfaced the ESP8266 module with the PIC MCU and have configured the softAP with a name and password of our choice. As usual lets simulate this code and see how it works.
Simulation output:
We are using the Proteus software to simulate the output. The design file for the same can be found in the attachment.
Since we do not have an ESP8266 module in Proteus library we have use the Serial terminal and respond back as a user to the PIC module. The simulation once completed screen will look like below
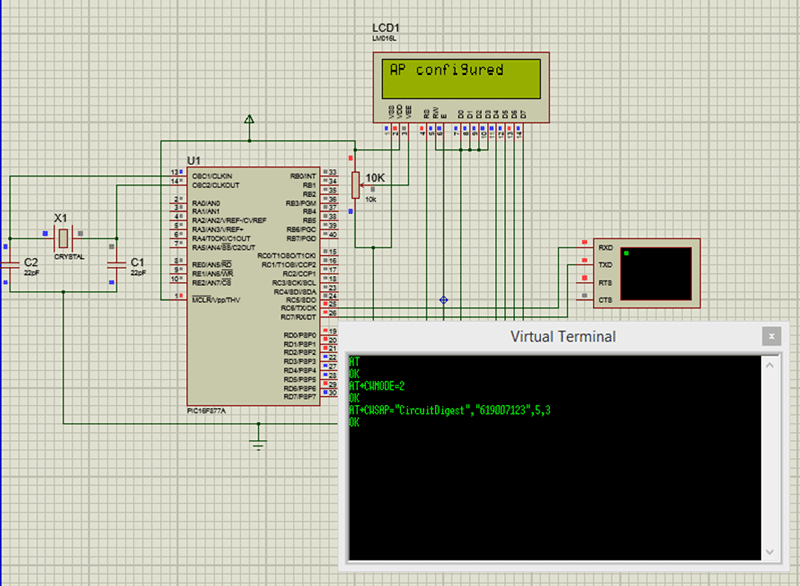
The output of our code is shown in the Virtual terminal. The complete working of the simulation will be explained in the video below.
Output Verification:
Once the program is verified using the simulation, dump it into your PIC microcontroller. Make the connections as shown in the schematics above (Hardware section). You should be able to track your progress through the LCD display.
Once the LCD says that the AP is configured we can check that out using the WIFI settings in Phone or Laptop. My laptop shows the following signal as per our program.
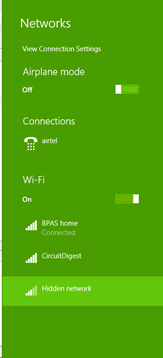
That is it guys we have successfully interfaced the ESP8266 module with the PIC Microcontroller. This is a very basic interface and if you want to do any complicated projects using the ESP8266 you might have to add your own libraries or at least add your own functions. Trust me it is very much easy to do so, I will give a brief insight for the same.
Adding functions to the ESP8266 Library:
Adding your own function will help you to send any “AT” command to the ESP8266 module. To proceed with this you need to read the instruction set documentation of the ESP8266 module. You can directly send any AT command that you find in that instruction set manual. But always remember to append “/r/n” at the end of every AT command. For example if your want to establish multiple connections with your ESP module. Then open the instruction set documentation and find our which AT command will do this job for you. Here the command “AT+CIPMUX=1” will allow you to establish multiple connections with your ESP module.
Now all you have to do is send this “AP+CIPMUX=1” to your ESP8266 module using the serial port. The hardcore way of doing this is by simply using the command
_esp8266_print("AT+CIPMUX=1\r\n"")
This will work but is not the best way of doing it. You have to read back what your ESP8266 responds to your command. In our case it will respond with “OK”. So you have to read the incoming data from ESP8266 module and confirm that it is a “OK”. Also you can make this function where the “1” or “0” can be passed as arguments.
Go ahead and try to make your own functions for the library. But if you need help please fell free to use the comment section and I will help you out.
Complete Project Code
#define _XTAL_FREQ 20000000
#define RS RD2
#define EN RD3
#define D4 RD4
#define D5 RD5
#define D6 RD6
#define D7 RD7
#include <xc.h>
#include "esp8266_functions.h"
#pragma config FOSC = HS // Oscillator Selection bits (HS oscillator)
#pragma config WDTE = OFF // Watchdog Timer Enable bit (WDT disabled)
#pragma config PWRTE = OFF // Power-up Timer Enable bit (PWRT enabled)
#pragma config BOREN = ON // Brown-out Reset Enable bit (BOR enabled)
#pragma config LVP = OFF // Low-Voltage (Single-Supply) In-Circuit Serial Programming Enable bit (RB3 is digital I/O, HV on MCLR must be used for programming)
#pragma config CPD = OFF // Data EEPROM Memory Code Protection bit (Data EEPROM code protection off)
#pragma config WRT = OFF // Flash Program Memory Write Enable bits (Write protection off; all program memory may be written to by EECON control)
#pragma config CP = OFF // Flash Program Memory Code Protection bit (Code protection off)
//****LCD Functions Developed by Circuit Digest.***///
void Lcd_SetBit(char data_bit) //Based on the Hex value Set the Bits of the Data Lines
{
if(data_bit& 1)
D4 = 1;
else
D4 = 0;
if(data_bit& 2)
D5 = 1;
else
D5 = 0;
if(data_bit& 4)
D6 = 1;
else
D6 = 0;
if(data_bit& 8)
D7 = 1;
else
D7 = 0;
}
void Lcd_Cmd(char a)
{
RS = 0;
Lcd_SetBit(a); //Incoming Hex value
EN = 1;
__delay_ms(4);
EN = 0;
}
Lcd_Clear()
{
Lcd_Cmd(0); //Clear the LCD
Lcd_Cmd(1); //Move the curser to first position
}
void Lcd_Set_Cursor(char a, char b)
{
char temp,z,y;
if(a== 1)
{
temp = 0x80 + b - 1; //80H is used to move the curser
z = temp>>4; //Lower 8-bits
y = temp & 0x0F; //Upper 8-bits
Lcd_Cmd(z); //Set Row
Lcd_Cmd(y); //Set Column
}
else if(a== 2)
{
temp = 0xC0 + b - 1;
z = temp>>4; //Lower 8-bits
y = temp & 0x0F; //Upper 8-bits
Lcd_Cmd(z); //Set Row
Lcd_Cmd(y); //Set Column
}
}
void Lcd_Start()
{
Lcd_SetBit(0x00);
for(int i=1065244; i<=0; i--) NOP();
Lcd_Cmd(0x03);
__delay_ms(5);
Lcd_Cmd(0x03);
__delay_ms(11);
Lcd_Cmd(0x03);
Lcd_Cmd(0x02); //02H is used for Return home -> Clears the RAM and initializes the LCD
Lcd_Cmd(0x02); //02H is used for Return home -> Clears the RAM and initializes the LCD
Lcd_Cmd(0x08); //Select Row 1
Lcd_Cmd(0x00); //Clear Row 1 Display
Lcd_Cmd(0x0C); //Select Row 2
Lcd_Cmd(0x00); //Clear Row 2 Display
Lcd_Cmd(0x06);
}
void Lcd_Print_Char(char data) //Send 8-bits through 4-bit mode
{
char Lower_Nibble,Upper_Nibble;
Lower_Nibble = data&0x0F;
Upper_Nibble = data&0xF0;
RS = 1; // => RS = 1
Lcd_SetBit(Upper_Nibble>>4); //Send upper half by shifting by 4
EN = 1;
for(int i=2130483; i<=0; i--) NOP();
EN = 0;
Lcd_SetBit(Lower_Nibble); //Send Lower half
EN = 1;
for(int i=2130483; i<=0; i--) NOP();
EN = 0;
}
void Lcd_Print_String(char *a)
{
int i;
for(i=0;a[i]!='\0';i++)
Lcd_Print_Char(a[i]); //Split the string using pointers and call the Char function
}
//***End of LCD functions***//
void main()
{
TRISD = 0x00;
Lcd_Start();
Initialize_ESP8266() ;
Lcd_Set_Cursor(1,1);
Lcd_Print_String("Circuit Digest");
Lcd_Set_Cursor(2,1);
Lcd_Print_String("ESP5266 with PIC");
__delay_ms(1500);
Lcd_Clear();
/*Check if the ESP_PIC communication is successful*/
do
{
Lcd_Set_Cursor(1,1);
Lcd_Print_String("ESP not found");
}while (!esp8266_isStarted()); //wait till the ESP send back "OK"
Lcd_Set_Cursor(1,1);
Lcd_Print_String("ESP is connected");
__delay_ms(1500);
Lcd_Clear();
/*Yes ESP communication successful*/
/*Put the module in Soft AP mode*/
esp8266_mode(2);
Lcd_Set_Cursor(1,1);
Lcd_Print_String("ESP set as AP");
__delay_ms(1500);
Lcd_Clear();
/*Module set as AP */
/*Configure the AP name and Password*/
esp8266_config_softAP("CircuitDigest","619007123");
Lcd_Set_Cursor(1,1);
Lcd_Print_String("AP configured");
__delay_ms(1500);
/*AP configured*/
while(1)
{
//do nothing
}
}
Comments
Transmit the command AT+CIFSR
Hi Sunad,
In order to get the IP address of your ESP8266 module you have to send a request command to it. The comamand is
AT+CIFSR
You have to send this serially via USART of the PIC MCU. Since this command is not pre-programmed inside the library you have to add it by yourself.
To do this you have to know how to use USART in PIC MCU. If not read the link
https://circuitdigest.com/microcontroller-projects/uart-communication-u…
If you are a beginner and wanna do this soon I would recommend you to try it with Arduino. Once you find the IP address with Arduino you can use the same with PIC later.
HAPPY LEARNING!!
ESP8266 and PIC 18F 46K22
Hi there,
I am wondering if I can use this code to guide me in learning about interfacing the ESP8266 to a PIC 18F46k22. I believe the hardware will be simpler if I use a 3v3 PIC, I can then avoid the level shifting and second power supply. What do you think?
can i have th code written in the esp8266_functions.h
hello can i have th code written in the esp8266_functions.h
Yes its given already
Hi mohammad,
The code inside the esp8266_functions.h is already given.https://circuitdigest.com/sites/default/files/inlineimages/ESP8266_PIC%20librarey.zip
I am pasting the link again for you!
hello can i contact you to
hello can i contact you to know some detail
hi is esp8266_functions.h
hi is esp8266_functions.h same as esp8266.h (https://circuitdigest.com/sites/default/files/inlineimages/ESP8266_PIC%20librarey.zip) ? because in the file attached, the esp8266_config_SoftAP doesn't have its own function in the library. its not in the header file thus I cant even compile it. what should I do with esP8266_config_SoftAP?
Hi Sylvia,
Hi Sylvia,
I apologies for the confusion.
Yes the file esp8266_functions.h is same as esp8266.h
You can the required files here https://github.com/Aswinth-raj/PIC_ESP8266-Sending-mail
Thanks
Hello can i have the code
Hello can i have the code written in the xc.h
the code is available but file is not here
it show error for xc.h header not avaiable
plz, can the library esp8266
plz, can the library esp8266.c be compiled with any compiler?? because i'm trying to compile this with ccs compiler and i'm having troubles. the compiler open another file named stdbool.h and print the error #device required before the line "#if defined(FALSE)". plz help.
interfacing it with pic16f887
hello sir, I am interfacing the esp8266 with pic16f887 also i dont have an XC8 compiler so I'm creating each and every function. The problem I am facing is that how to use this module to get ip address also if I get it how to diplay the content on the webpage of that ip address...
please help me....
First of all, thank you very
First of all, thank you very much for the tutorial.
But I wanted to point out that some functions listed here are missing in the library, such as esp8266_config_softAP.
Hi thanks for pointing it out.
Hi Dani,
Thanks for pointing it out. You can download the complete code from my github page here : https://github.com/Aswinth-raj/PIC_ESP8266-Sending-mail/archive/master.zip
Thanks!!
Same concept is applicable for all MCU
Hi Lakshmi,
Yes the same code can be used however with few modifications on the USART sections.
Hi Mr Raj,
Hi Mr Raj,
I can't compile code with xc8 v1.42 and Pic16f877a, i tried with pic18 PIC18F4550 also but same with a lot of error
Pls guide how to use your code also CamilStaps Library for Pic16f877a, (CamilStaps commented this lib for Pic18)
Thank You !
hello everybody
hello everybody
i want to connect 16f887 with esp...it's so difficult, i'm finding it. can you help me?
hello i wanna control led
hello i wanna control led through mobile app or web server using pic and esp8266, with the above code what should we add to control led through wifi..
Can i use this same ESP8266 library for 32Bit controller.
Hi every one,
I need help can i use this ESP8266 library for 32 bit controller which is ARM cortex M4 series. I am using eclipse and GCC compiler for developing. But for WiFi i am trying to interface ESP8266 with ARM cortex M4 CPU. It it possible and will be work with my GCC compiler. if not can you give dome useful tutorial and their library for same.
Thanks....
Its a big work around. Will
Its a big work around. Will try in future though
_esp8266_waitFor() wait forerver
Hello B.Aswinth Raj and Everyone,
I'm follow your guide and success to send somethings from outside to esp8266 to PIC16f877a. i capture it in IRS.
But now i'm stuck with _esp8266_waitFor() if i dont send any things from outside to esp chip, PIC stop operation there of course, and other code after that (in main loop) pending. I know _esp8266_waitFor() have that limitation.
How can i go over this stop, i think of multithread but it is another difficult story.
Thanks for your nice tutorials and your advice!
Actually this code does
Actually this code does suffer from this draw back. Multithreading would sure be an overkill, you figure out a way something like the millis() used in Arduino. You can use PIC timers to get this done.
Multithread with ESP
Thank B.Aswinth Raj,
I'm begining with Multithread, try solution same millis() as you advice but right time to add sprintf() to convert num to string (in ISR), ESP seem disconnect with PIC, and LCD show incorrect character. Baud rate is 115200, still work if without code use sprintf. I use pic16f877a, OSC 20mhz.
Could you guide me how to debug or any advice. Thank You again!
esp8266 with timer
Hello Mr B.Aswinth Raj,
I make a clock by timer0 in isr and and convert time to string to show in LCD, it's ok. But when i combine it clock to ESP code i have trouble that after ESP connected for initialisation (return OK after At command), ESP don't return any more reply after some first command from PIC (i see in terminal connect paranelly with PIC to ESP tx pin), but this code is ok with simulation Proteus (i reply to pic instead of ESP).
I did not yet find issue, Pls help advice.
Thank B.Aswinth Raj a lot!
Can I do this with a NODEMCU
Can I do this with a NODEMCU flashed ESP8266?
insertion of library
your tutorial help me alot thnx.. i am facing some problem ''Error [141] C:\Users\hp\Documents\Test_skills\lcdd.c; 10.30 can't open include file "esp8266_functions.h": No such file or directory''.
please guide me how to add ESP library
Can we connect ESP8266 to
Can we connect ESP8266 to dsPIC33 series? Will this code work in that?
Any PIC that supports USART
Any PIC that supports USART can be interfaced with ESP8266. The code will not work as such, but the concept will remain the same
What so you mean by different
What so you mean by different frequencies? do you mean baud rate? Here the PIC's registers are set to work in same baud rate as ESP8266
How can I interface the ESP8266-12F to other MCU
hI, your work is very encouraging and insightful.My question is am working on a senior design using FRDMK-64F board but am having issues not been able to interface the ESP8266-12F wifi module. Please how can I go about it.
library installation
i have downloaded the library . how can i link that to the main file,,, is #include just enough,,,,, how to do that in mplab x ide.
Is this a complete project? I
Is this a complete project? I had download all the library file but having error on esp8266.h while compiling
i dont see the attachment,
i dont see the attachment, can you upload it, please
How can upload sensor
How can upload sensor readings (datas) to cloud using ESP8266
Can you tell me please? How
Can you tell me please? How to get IP of ESP? I'm try to get IP and show in LCD 16x02 but it is wrong.
I use code:
esp8266_ip(IP);
sprintf(str,"%c",IP);
LCD_goto(1,1);
LCD_Puts(IP);
__delay_ms(2000);
LCD_Clear();
Hi @B.Aswinth Raj , you can
Hi @B.Aswinth Raj , you can reply for me?
esp library
where i get definition of functions used in esp wifi module like initialize_ESP8266(); get_char();
etc
pic16f877a and esp8266
hi .. when i try to build the code this line is being referred to(bit esp8266_isStarted(void); // Check if the module is started (AT))
and the error says (66 436 Function must not have return value of bit or sbit type esp8266_functions.h)
and it took me so long to read "ok" from the esp but no luck ...what is your advice??
thanks in advance
cant understand what your
cant understand what your problem is. Do you get an ok now?
PIC16F877A+ESP8266-01 send data to another device
Hi,
Thanks for such a wonderful article.
I need to send some data from this system(PIC16F877A+ESP8266-01) to another device on the same Wifi network having another IP Address of the same class.
Can you guide me, how to send one packet of information from this system AND receive that packet of information on the other device?
An example code (or a link to such an article) will be of great help.
Thank You in advance.
Thanks for such a wonderful article.
Hi
I am a gagandeep singh from Punjab. I facing problem with this code. Actully I download library and add this with mine code.and and when i call " (!esp8266_isStarted()); " this function, it not receive "ok". and my code not execute after ""ESP is Not Found"..
please solve my this ploblem..
Hi Gagandeep
Hi Gagandeep
I have the same problem. Did you manage to solve it? What did you do?
Thanks in advanced
Linda
compatible with mikro c
can we use this library for mikro c compiler?
Proteus design project
Hi,
Are you able to share the proteus design project? It is not present in the attached ZIP file. Only the header and code files found. :( It is a really interesting project so thank you :)
Interfacing ESP8266 with PIC16F877A Microcontroller
Hi Aswinth Raj
The esp8266_PIC library does work on my mplab xc8 v5.0.
I've been trying it. More of the subrounite is the library gives me error. I don't know if it mplab version I'm using. Please assist me.
_esp8266_waitResponse()
Hi Aswinth
Now I can compile. Atleast some positive move.
On proteus virtual terminal when I put "OK", I think the PIC doesn't take it because the lcd display doesn't display "ESP is connected" and I think this is because of "_esp8266_waitResponse()" subroutine. When I start simulation, the lcd display shows "ESP not found" and on virtual terminal the PIC sends the "AT",but when I put "OK" the next step doesn't happen. Please assist.
Thank you,
Linda
Did you turn on Echo on the
Did you turn on Echo on the virtual terminal of the simulation?
Yes its ON. I right clicked
Yes its ON. I right clicked on the virtual terminal window and enabled the ECHO option.
Project issues
Hi there the proteus simulation is not working for this project, only displaying ESP not found, please any help?
Did you send OK form the
Did you send OK form the virtual window?
When I run the simulation.
When I run the simulation. The PIC sends this command "AT" and wait for an "OK". I write the "OK" on the virtual terminal but nothing happens. It doesn't got to "ESP is connected".
I suspect that the "_esp8266
I suspect that the "_esp8266_waitResponse" is not working fine. I'm using the PIC18F46K22.
There are chances since the
There are chances since the clock frequency is different
The librarey was built with
The librarey was built with an intention on PIC16F877A only. Its been a along time and I no longer update it. So you have to make the changes required to adapt for your MCU
Library is broken. What to do to fix it
The library won't compile. See the errors in the following posts. Please advise.
esp8266_functions.h build error
hi raj
esp8266_functions.h build error..please help me
Has anyone come up with a fix for this?
If someone has come up with a fix for this, please post it here.
Thank you.
hola, como estas? para los
hola, como estas? para los ultimos compiladores tenes que escribirlo de esta manera:
"bit" por " __bit".
"inline" por "__inline"
tiene igual varios errores mas que son faciles de corregir que lo veras cuando lo compiles, lo que te pase te soluciona los errores que mencionas.
Por otro lado te recomiendo que siempre leas la ultima manual de mplab xc8 me paro por experiencias que cambias cosas y si tenes un programa hecho en un version antigua no te va a funcionas.
Hi how are you? for the
Hi how are you? for the latest compilers you have to write it this way:
"bit" for "__bit".
"inline" by "__inline"
It also has several more errors that are easy to correct that you will see when you compile it, what happens to you will solve the errors you mention.
On the other hand, I recommend that you always read the latest manual of mplab xc8. I stop for experiences that change things and if you have a program made in an old version it will not work for you.
Schematic 3.3V Power Supply Error.
Hi.
I think there is a error in the schematic drawing.
Where the 3.3V Power Supply Vin and Vout is switch around.
Vin should be the 12V and Vout the 3.3V.
/Stig Allan
Receiving web page data using ESP8266
I have write the receiving code but in the store_in option alwais comes with an error
esp8266_start(ESP8266_TCP, "localhost", 80);
Lcd_Set_Cursor(1,1);
Lcd_Print_String("Connected to Host.");
__delay_ms(1500);
esp8266_receive("ABCDEFGH",160, true);
what is the error in here
Getting errors
Don't know if I am including the library properly, Program won't compile. Keeps getting errors from the library.
Ei: In file included from main.c:19:
./ESP8266_functions.h:66:1: error: unknown type name 'bit'
bit esp8266_isStarted(void); // Check if the module is started (AT)
added the library from the project properties tab.
Correct?
Thanks
^
hello, Can you help me
I can't copmlile this project because i have some errors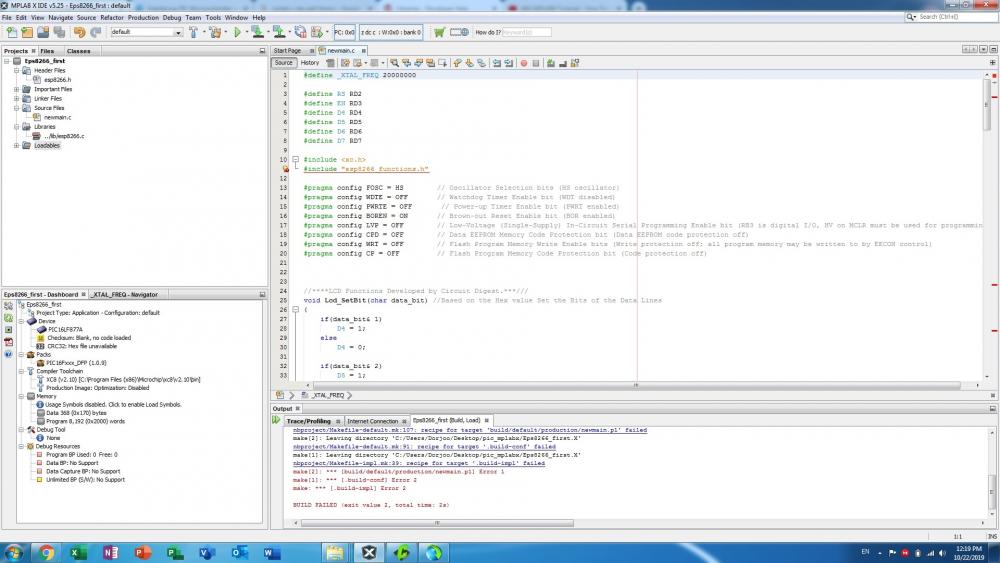
Check letters and app
Please if i do this code can i send assume letter "O"
And use
If _esp8266_getch("O"); { RB1=1;}
This will check letter and turn on led or no ?
And what app in mobile phone that I can use it
interconecting esp8266
Hola, Agradezco los aportes recibidos en este articulo.
Descargo la libreria pero veo que le faltan metodos como por ejemplo Initialize_ESP8266 (). y demás.Por lo tanto quisiera recibir la biblioteca completa.Les agradezco mucho
Can u send me a esp8266…
Can u send me a esp8266_functions.h file or give me a link for download please!
dimaryhlickii@mail.ru
can please tell me how to…
can please tell me how to store a sensor data in firebase realtime database using PIC microcontroller and wifi module.
Thank you for uploading this…
Thank you for uploading this library. This is a very useful and nice article to read.
In my application, I require interfacing ESP32-C3 module with PIC18F microcontroller. Both ESP32-C3 modules will be interfaced with PIC18F and implement BLE services for pairing, command communications with host MCU and data transfer between two modules. Communication between host PIC18F and ESP32-C3 will be via UART using AT-Commands.
Can you please provide or link to similar AT parser library that I can use with XC8?
Thank you








please can u tell me what parameter should be passed in function esp8266_ip() so that i can get the ip adress back