The 5 band resistance colour code calculator gives better accuracy than the normal 4-band resistors. With three significant digits and tight tolerances of ± 0.05% to ± 2%. Whether you are using the 5 band colour code resistor calculator for determining a precision instrumentation project or any other electronics project, our 5 band resistor color code calculator will obtain you exact resistance values and tolerances in seconds.
Our resistor color coding 5 band produces accurate resistance calculations for professional electronics applications. Our five color resistor calculator will perform calculations for resistance values from 10 ohms to 10M ohms with high accuracy. Simply select the colors from each band in the calculator above to instantly determine resistance values and tolerance specifications. Our 5-band resistance calculator excels at determining precise values across the most commonly used resistance ranges.
How To Calculate Resistor Color Code Values?
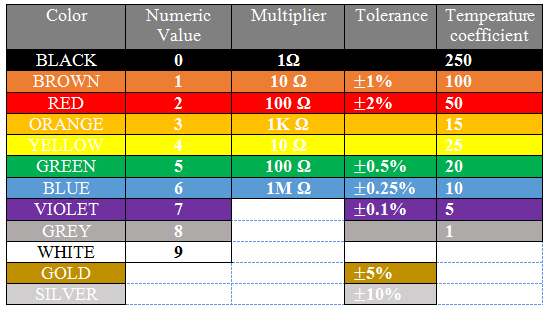
Calculating 5-band resistor values requires understanding the enhanced precision system. The first three bands represent significant digits, the fourth band is the multiplier, and the fifth band indicates tolerance. This system provides greater accuracy than 4-band resistors, making them essential for precision electronics. Use the resistor color code chart below to see the step-by-step calculation process.
Why Choose a 5-Band Resistance Colour Code Calculator?
5-band resistors are designed for precision applications where accuracy matters. With three significant digits instead of two, they offer resistance values with 1% precision, making them ideal for sensitive analog circuits, measurement equipment, and high-frequency applications.
Key Advantages of 5-Band Resistors
- Higher precision - ±1% to ±2% tolerance compared to ±5% standard tolerance
- Better temperature stability - Enhanced performance across varying operating conditions
- More precise resistance values - Three significant digits provide exact component specifications
- Improved performance in critical circuits - Essential for measurement equipment and precision applications
For general applications with standard tolerance requirements, our 4-band resistor calculator may be more suitable.
Calculating Resistor Color Coding 5 Band

![]()
Where,
‘a’ represents the 1st significant digit, which is the first band color of the resistor.
‘b’ represents the 2nd significant digit, which is the second band color of the resistor.
‘c’ represents the 3rd significant digit, which is the third band color of the resistor.
‘d’ represents the 4th significant digit, which is the fourth band color of the resistor, and this is the multiplier value used in the formula.
‘e’ represents the 5th significant digit, which is the fifth band color of the resistor, and this is the tolerance value of the resistor.
|
5-Band |
Name |
Description |
|
1st Band |
a |
1st significant digit |
|
2nd Band |
b |
2ndsignificant digit |
|
3rd Band |
c |
3rdsignificant digit |
|
4th Band |
d |
Multiplier |
|
5th Band |
e |
Tolerance |
Let’s take an example of a 5-band resistor with the colors given in the above image (brown, green, red, black, and gold).
So, according to the formula, the resistance will be: 152 * 1 = 152 Ohms with 5% tolerance.
Step-by-Step 5-Band Resistor Calculation Example
Let's calculate a 5-band resistor with the colors: Brown, Green, Red, Black, Gold
Step 1⇒ First band (Brown) = 1
Step 2⇒ Second band (Green) = 5
Step 3⇒ Third band (Red) = 2
Step 4⇒Fourth band (Black) = ×1 (multiplier)
Step 5⇒Fifth band (Gold) = ±5% (tolerance)
Calculation: (1×100 + 5×10 + 2) × 1 = (100 + 50 + 2) × 1 = 152 Ohms with ±5% tolerance
This means the actual resistance value can range from 144.4Ω to 159.6Ω (152Ω ± 5%). The third significant digit (2) provides the extra precision that 4-band resistors cannot offer.
Precision Applications for 5 Band Resistor Color Code Calculator Online
5-band resistors are essential in applications where precision and stability are critical. Their tight tolerances and accurate resistance values make them the preferred choice for professional electronics and measurement equipment.
Professional Applications Using 5 Band Resistance Calculator
∗ Precision Measurement Circuits: Multimeters, oscilloscopes, and laboratory equipment requiring accurate voltage/current sensing.
∗ Audio Equipment: High-fidelity amplifiers and professional audio gear where precision affects sound quality.
∗ Medical Devices: Patient monitoring equipment and diagnostic instruments require reliable measurements.
∗ Instrumentation: Data acquisition systems and sensor interface circuits - use our LM317 calculator for precision voltage regulation.
∗ RF Circuits: High-frequency applications where component tolerance affects performance.
Precision Resistor Network Calculations
When combining multiple 5-band resistors in precision circuits, accurate calculations are crucial. Use our series resistor calculator or parallel resistor calculator to determine exact total resistance values while maintaining precision tolerances.
5 Band Capacitor Color Code Calculator Alternative
However, while our tool is designed to help with the 5 band resistance colour code calculator functionality, when looking at capacitor color coding, it uses different standards. Capacitor calculations should be using specialized capacitor calculators, and the conventional color coding system for capacitors differs substantially. However, the concepts of precision remain similar for high-precision electronic components.
5-Band Resistor Calculator FAQ
⇥ When should I use 5-band resistors instead of 4-band?
Use 5-band resistors for precision applications requiring ±1% or ±2% tolerance. They're essential in measurement equipment, audio circuits, and instrumentation. For general circuits where ±5% tolerance is acceptable, 4-band resistors are more cost-effective.
⇥ What's the difference between 5-band and 6-band resistors?
6-band resistors include an additional temperature coefficient band, indicating how resistance changes with temperature. Use our 6-band resistor calculator for applications requiring temperature stability specifications.
⇥ How do I identify if a resistor is 5-band or 4-band?
Count the colored bands on the resistor body. 5-band resistors have five distinct colored bands, while 4-band resistors have four. The tolerance band (usually gold, silver, or another color) is typically spaced slightly apart from the other bands.
⇥ Can I substitute a 5-band resistor with a 4-band resistor?
You can substitute if the circuit can tolerate the lower precision of 4-band resistors (±5% vs ±1-2%). However, precision circuits may not function correctly with the reduced accuracy. Use our resistor wattage calculator to ensure power ratings are also compatible.
⇥ What does the tolerance percentage mean in practical terms?
Tolerance indicates the maximum deviation from the stated resistance value. A 1000Ω resistor with ±1% tolerance can measure between 990Ω and 1010Ω. For ±2% tolerance, the range would be 980Ω to 1020Ω. Tighter tolerances provide more predictable circuit behavior.
Update: This calculator was last updated in May 2025 to support the latest mobile devices and iPhone screens. If you are facing any problems in using our electronics calculators or have any suggestions, kindly contact us.
Related Electronics Calculators You Might Find Useful
If you're working with resistors and circuit components, here are three additional calculators to make your design process smoother and more accurate:
Resistors in Parallel Calculator
This parallel resistance calculator calculates the total resistance value for all the resistors connected in parallel.
The Hex Calculator is a powerful online tool used to perform addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division on two hexadecimal numbers. This hex calculator online provides step-by-step solutions for all hexadecimal arithmetic operations, making it perfect for programmers, students, and digital electronics enthusiasts.
Use our free online voltage divider calculator to calculate output voltage, input voltage, or resistor values. This resistor divider calculator works with any voltage divider circuit and provides instant results using the standard voltage divider formula.