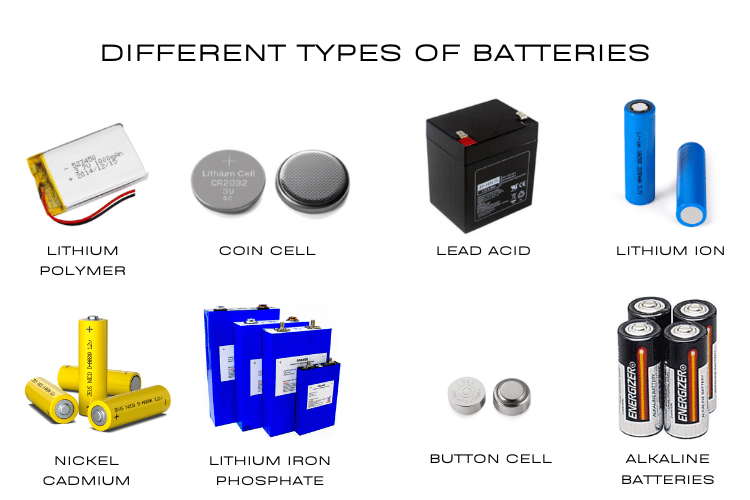
Battery types are fundamental to understanding modern electronics and electrical systems. Whether you're a student learning about electrochemistry or an engineer working on your next electronics project, understanding the different types of batteries and their applications is essential. This comprehensive guide covers over 50 battery types, from basic primary batteries like alkaline cells to advanced secondary batteries like lithium-ion, helping you to understand battery chemistry, characteristics, and practical applications. We have previously used many types of batteries here in CircuitDigest to build a wide range of electronics projects, and we will also share our experience along the way.
We'll explore how batteries work, compare primary vs secondary batteries, examine specific battery chemistries including NiMH, lead-acid, and various lithium-ion types, and provide practical guidance for selecting the right battery for your application. Whether you need batteries for consumer electronics, electric vehicles, or industrial applications, this guide will help you make informed decisions.
Table of Contents
- Quick Guide to Battery Types
- What is a Battery? Definition and Basic Principles
- Battery Components and How They Work
- Types of Batteries: Primary vs Secondary Classification
- Primary Batteries
- Secondary Batteries
- 1. Nickel-Cadmium Batteries
- 2. Nickel-Metal Hydride Batteries
- 3. Lead-Acid Batteries
- 4. Lithium-ion Batteries
- Battery Sizes and Form Factors
- Battery Applications by Type
- Selecting the right battery for your application
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Comprehensive List of Battery Types
- └ Primary (Non-rechargeable) Battery Types
- └ Secondary (Rechargeable) Battery Types
- Latest Trends in Battery Technology (2025)
- Future Battery Technologies Beyond 2025
Quick Guide to Battery Types
Quick Reference: Most Common Battery Types, Uses and Key Advantages.
What is a Battery? Definition and Basic Principles
Battery definition in simple terms: A battery is an electrochemical device that converts stored chemical energy into electrical energy through oxidation-reduction reactions. More specifically, a battery consists of one or more electrochemical cells that generate an electric current when connected to an external circuit.
How do batteries work? Simple put, when a battery is connected to a circuit, chemical reactions occur at the electrodes, causing electrons to flow from the negative terminal (anode) to the positive terminal (cathode) through the external circuit. This electron flow creates the electric current that powers our devices.
Key battery principles every student and engineer should understand:
- Energy storage: Batteries store electrical energy in chemical form for later use
- DC power only: Batteries can only store and provide direct current (DC), not alternating current (AC)
- Energy conversion: Chemical energy converts to electrical energy during discharge
- Voltage Rating: Based on the type of battery, the voltage rating of a single cell of the battery various. The voltage is normally mentioned as nominal voltage it when its fully charge its reaches the maximum voltage of the battery and when fully discharged it reaches minimum voltage of the battery
- Ah Rating: how much power can be delivered by a battery is answered using its ah rating, for example a 10Ah battery can provide 10A for 1 hour or 5A for 2 hours
- C Rating: The maximum power that can be delivered by a battery is called C rating, For example a 2Ah cells with 5C rating can give a maximum output current of (5*2) 10A.
Understanding battery fundamentals is crucial for applications ranging from small consumer electronics to large-scale energy storage systems and electric vehicles. The specific battery chemistry and construction determine characteristics like voltage, capacity, cycle life, and safety.
Battery Components and How They Work
Understanding battery components is essential for grasping how different battery types function. Every battery cell contains three fundamental components that work together to produce electricity:
- The Anode (Negative Electrode) - where oxidation occurs, releasing electrons
- The Cathode (Positive Electrode) - where reduction occurs, accepting electrons
- The Electrolyte - ionic conductor that allows ion flow between electrodes
How battery components interact: The anode releases electrons to the external circuit, creating a potential difference between electrodes. The electrolyte prevents direct electron flow between electrodes while allowing ions to move internally, completing the circuit. When connected to a load, electrons flow from anode to cathode through the external circuit, powering the connected device.
By changing the electrode materials and electrolyte composition, manufacturers create different battery chemistries with unique characteristics. For example, alkaline batteries use zinc and manganese dioxide electrodes with alkaline electrolyte, while lithium-ion batteries use lithium-based compounds with organic electrolytes.
Advanced Battery Components in Modern Cells
Modern battery designs incorporate additional components beyond the basic three:
- Separators: Prevent physical contact between electrodes
- Current collectors: Conduct electricity efficiently
- Battery Management Systems (BMS): Monitor and control battery operation
- Thermal management systems: Regulate battery temperature
Types of Batteries: Primary vs Secondary Classification
Battery classification helps students and engineers understand which battery type suits specific applications. While there are many different types of batteries based on chemistry, size, and form factor, all batteries fall into two fundamental categories based on their rechargeability:
- Primary Batteries (Non-rechargeable, single-use)
- Secondary Batteries (Rechargeable, multiple-use)
This primary vs secondary battery distinction is crucial for understanding battery applications, cost considerations, and environmental impact. Let's explore the key differences between primary cells and secondary cells to help you choose the right battery type for your specific needs.
Primary Batteries
Primary batteries are non-rechargeable batteries that cannot be recharged once depleted. Primary batteries use electrochemical cells whose electrochemical reactions are irreversible.
Primary batteries exist in different forms, ranging from coin cells to AA batteries. They are commonly used in standalone applications where charging is impractical or impossible. A good example of which is in military grade devices and battery-powered equipment. It will be impractical to use rechargeable batteries as recharging a battery will be the last thing in the mind of the soldiers. Primary batteries always have high specific energy, and the systems in which they are used are always designed to consume low amount of power to enable the batteryto last as long as possible.

Some other examples of devices using primary batteries include; Pace makers, Animal trackers, Wrist watches, remote controls and children toys to mention a few.
The most popular type of primary batteries are alkaline batteries with a market share of 80% among the primary battery market. These batteries have a typical voltage of 1.5V and a shelf life of 5-10 years. They also have a high specific energy and are environmentally friendly, cost-effective and do not leak even when fully discharged. They can be stored for several years, have a good safety record and can be carried on an aircraft without being subject to UN Transport and other regulations. The only downside to alkaline batteries is the low load current, which limits its use to devices with low current requirements like remote controls, flashlights and portable entertainment devices. Other types of commonly used primary batteries include Zinc-Carbon batteries, Lithium batteries, mercury batteries, Silver-Oxide batteries, Zinc-air batteries and Zinc-Chloride batteries.
Secondary Batteries
Secondary batteries are batteries with electrochemical cells whose chemical reactions can be reversed by applying a certain voltage to the battery in the reversed direction. Also referred to as rechargeable batteries, secondary cells unlike primary cells can be recharged after the energy on the battery has been used up. This recharging capability makes secondary batteries ideal for high-drain applications and scenarios where replacing batteries frequently would be expensive or impractical.
They are typically used in high drain applications and other scenarios where it will be either too expensive or impracticable to use single charge batteries. Small capacity secondary batteries are used to power portable electronic devices like mobile phones, and other gadgets and appliances while heavy-duty batteries are used in powering diverse electric vehicles and other high drain applications like load levelling in electricity generation. They are also used as standalone power sources alongside Inverters to supply electricity. Although the initial cost of acquiring rechargeable batteries is always a whole lot higher than that of primary batteries but they are the most cost-effective over the long-term. If you are interested in Electric vehicle batteries you can check out this article on Electric Car batteries to know more.
Secondary batteries can be further classified into several other types based on their chemistry. This is very important because the chemistry determines some of the attributes of the battery including its specific energy, cycle life, shelf life, and price to mention a few.
The following are the different types of rechargeable batteries that are commonly used.
- Nickel Cadmium(Ni-Cd)
- Nickel-Metal Hydride(Ni-MH)
- Lead-Acid
- Lithium-ion(Li-ion)
- Lithium iron phosphate(LiFePO4)
- Lithium Nickel Manganese Cobalt Oxide (NMC)
- Lithium Nickel Cobalt Aluminum Oxide (NCA)
- Lithium Cobalt Oxide (LCO)
- Lithium Manganese Oxide (LMO)
- Lithium Titanate (LTO)
1. Nickel-Cadmium Batteries
The nickel–cadmium battery (NiCd battery or NiCad battery) is a type of rechargeable battery which is developed using nickel oxide hydroxide and metallic cadmium as electrodes. Ni-Cd batteries excel at maintaining voltage and holding charge when not in use. However, NI-Cd batteries easily fall a victim of the dreaded “memory” effect when a partially charged battery is recharged, lowering the future capacity of the battery.

In comparison with other types of rechargeable cells, Ni-Cd batteries offer good life cycle and performance at low temperatures with a fair capacity but their most significant advantage will be their ability to deliver their full rated capacity at high discharge rates. They are available in different sizes including the sizes used for alkaline batteries, AAA to D. Ni-Cd cells are used individual or assembled in packs of two or more cells. The small packs are used in portable devices, electronics and toys while the bigger ones find application in aircraft starting batteries, Electric vehicles and standby power supply.
Some of the properties of Nickel-Cadmium batteries are listed below.
- Specific Energy: 40-60W-h/kg
- Energy Density: 50-150 W-h/L
- Specific Power: 150W/kg
- Charge/discharge efficiency: 70-90%
- Self-discharge rate: 10%/month
- Cycle durability/life: 2000cycles
2. Nickel-Metal Hydride Batteries
Nickel metal hydride (Ni-MH) is another type of chemical configuration used for rechargeable batteries. The chemical reaction at the positive electrode of batteries is similar to that of the nickel–cadmium cell (NiCd), with both battery type using the same nickel oxide hydroxide (NiOOH). However, the negative electrodes in Nickel-Metal Hydride use a hydrogen-absorbing alloy instead of cadmium which is used in NiCd batteries
.
NiMH batteries find application in high drain devices because of their high capacity and energy density. A NiMH battery can possess two to three times the capacity of a NiCd battery of the same size, and its energy density can approach that of a lithium-ion battery. Unlike the NiCd chemistry, batteries based on the NiMH chemistry are not susceptible to the “memory” effect that NiCads experience.
Specifications of Nickel-Metal Hydride batteries:
- Specific Energy: 60-120 Wh/kg
- Energy Density: 140-300 Wh/L
- Specific Power: 250-1000 W/kg
- Charge/discharge efficiency: 66-92%
- Self-discharge rate: 1.3-2.9%/month at 20°C
- Cycle Durability: 180-2000 cycles
3. Lead-Acid Batteries
Lead-acid batteries are a low-cost reliable power workhorse used in heavy-duty applications. They are usually very large and because of their weight, they’re always used in non-portable applications such as solar-panel energy storage, vehicle ignition and lights, backup power and load levelling in power generation/distribution. The lead-acid is the oldest type of rechargeable battery and still very relevant and important into today’s world. Lead-acid batteries have very low energy to volume and energy to weight ratios but it has a relatively large power to weight ratio and as a result, can supply huge surge currents when needed. These attributes alongside its low cost make these batteries attractive for use in several high current applications like powering automobile starter motors and for storage in backup power supplies. You can also check out the article on Lead Acid Battery working if you want to know more about the different types of Lead-acid batteries, its construction and applications.

4. Lithium-ion Batteries
Lithium-ion batteries are the most popular type of rechargeable battery technology today. There are many different lithium battery types and lithium-ion battery chemistries, each optimized for specific applications. From smartphones to electric vehicles, lithium battery technology dominates modern portable power applications due to its high energy density and cycle life.

Lithium-ion batteries are a type of rechargeable battery in which lithium ions from the negative electrode migrate to the positive electrode during discharge and migrate back to the negative electrode when the battery is being charged. Li-ion batteries use an intercalated lithium compound as one electrode material, compared to the metallic lithium used in non-rechargeable lithium batteries.
Lithium-ion batteries generally possess high energy density, little or no memory effect and low self-discharge compared to other battery types. Their chemistry alongside performance and cost vary across different use cases, for example, Li-ion batteries used in handheld electronic devices are usually based on lithium cobalt oxide (LiCoO2) which provides high energy density and low safety risks when damaged while Li-ion batteries based on Lithium iron phosphate which offer a lower energy density are safer due to a reduced likelihood of unfortunate events happening are widely used in powering electric tools and medical equipment. Lithium-ion batteries offer the best performance to weight ratio with the lithium sulphur battery offering the highest ratio.
Some of the attributes of lithium-ion batteries are listed below;
- Specific Energy: 100: 265W-h/kg
- Energy Density: 250: 693 W-h/L
- Specific Power: 250: 340 W/kg
- Charge/discharge percentage: 80-90%
- Cycle Durability: 400: 1200 cycles
- Nominal cell voltage: NMC 3.6/3.85V
Within the Li-ion batteries, there are several types depending on the battery chemistry used. Here are some of the most popular Li-Ion battery types.
Battery Chemistry Comparison Chart
| NiCd | 40-60 | 2000 | Low |
| NiMH | 60-120 | 500-1000 | Medium |
| Lead-Acid | 30-50 | 200-300 | Very Low |
| Li-ion | 100-265 | 500-1500 | High |
| LiFePO4 | 90-120 | 2000-5000 | Medium-High |
a. Lithium Iron Phosphate Batteries
Due to the use of iron and phosphate in manufacturing, LiFePO4 batteries are cheaper to make than the common Li-Ion variants. However, they offer lesser specific energy comparatively. Additionally, LiFePO4 batteries are considered one of the safest types of rechargeable Lithium batteries and have a long lifespan. Nowadays they are very popular among to use with power backup systems due to their low price and safety.
b. Lithium Nickel Manganese Cobalt Oxide (NMC)
In an NMC battery the cathodes typically contain large proportions of nickel, which increases the battery energy density. However, this high nickel content makes the battery highly unstable and dangerous. To make the NMC batteries more thermally stable and safe, manganese and cobalt are added. Depending on on the exact chemical composition, there are several sub-types within the NMC batteries, like NMC811, NMC532 and NMC622 etc.
c. Lithium Nickel Cobalt Aluminum Oxide (NCA)
NCA shares similar battery chemistry with the NMC type. But instead of manganese, aluminium is used as a stability agent. Compared to other Li-ion batteries, NCA batteries and typically more expensive and less safe.
d. Lithium Cobalt Oxide (LCO)
When compared to other Li-ion batteries, LCO batteries offer high energy density. But it also comes with some drawbacks such as relatively shorter battery life, low thermal stability, limited specific power etc. But since they pack higher energy they are a very popular choice for applications such as smartphones, laptops and other electronic gadgets, where a low amount of power for a longer duration is needed.
e. Lithium Manganese Oxide (LMO)
The Lithium Manganese Oxide (LMO) offers faster charging and discharging capabilities along with higher stability. They can provide much higher current for shorter durations, than other types of batteries. They are even used in combination with NMC chemistry in EVs, due to their higher current capability.
e. Lithium Titanate (LTO)
Unlike the other chemistries above, where the cathode composition makes the difference, LTO batteries use a unique anode surface made of lithium and titanium oxides. These batteries exhibit excellent safety and performance under extreme temperatures but have low capacity and are relatively expensive, limiting their use at scale.
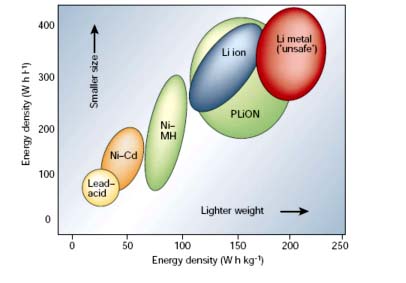
Each of these batteries has its area of best fit and the image below is to help choose between them. You can also check out our article to learn more about li-ion batteries.
Battery Sizes and Form Factors
Battery Applications by Type
Understanding battery applications helps in selecting the right battery type for specific devices and systems. Different battery chemistries excel in different applications based on their characteristics.
| Consumer Electronics | Alkaline, Li-ion | Cost-effective, high energy density |
| Electric Vehicles | Li-ion (NMC, LFP) | High energy density, fast charging |
| Automotive Starting | Lead-acid | High current capability, low cost |
| Solar Energy Storage | LiFePO4, Lead-acid | Long cycle life, deep discharge |
| Power Tools | Li-ion, NiMH | High power output, durability |
| Medical Devices | Lithium primary, Li-ion | Reliability, long life, safety |
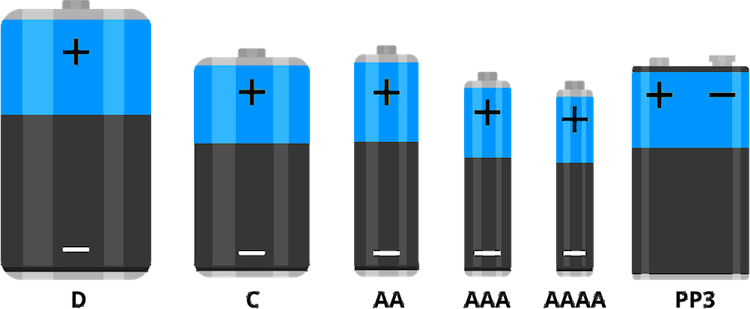
As we know about different batteries based on their chemistry, now let's look into the different battery sizes or packages. Since covering all available packages is difficult and unnecessary we are going to look at the most commonly used battery types. To start with let's look at the different types of primary batteries we use. The image below shows the different non-rechargeable battery types we use every day. The bigger brothers D and C-type batteries are normally used in devices such as radios, cassette players, toys, and flashlights. The AA, AAA, and AAAA were commonly used in devices such as alarm clocks, portable electronics, remote controls, etc. The PP3 or 6F22 batteries are mostly used in industrial test equipment such as multimeters, cable testers, etc.
Another type of battery we use is the one commonly known as the coin battery. they are small in size and look like a coin or a button. they are most commonly used in devices with very low power consumption such as watches, calculators and car keys. you can also find them in most devices with an RTC in it. They are used in such devices only to provide backup power to RTC chips for timekeeping. Here are some of the most commonly used coin batteries.

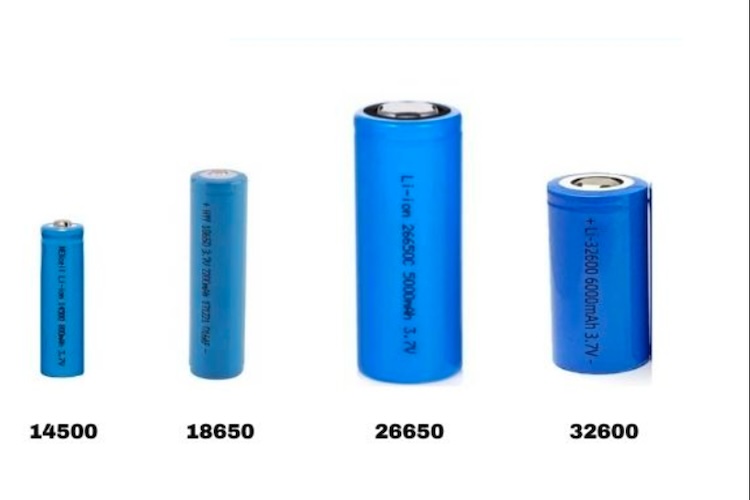
Now if we look at the rechargeable batteries they are available in a ton of different package types. Here we are going to look at the different cylindrical rechargeable battery packages. the NiMH and NiCd batteries are available in common AAA or AA packages, while the Lithium-ion batteries come in their own specific package types. The most common type is the 18650 battery. which can be found in many rechargeable gadgets on the market. Most lithium-ion cylindrical packages are named in such a numeric scheme, in which the first two numbers denote the diameter while the second and third numbers indicate the length. For example, the 18650 battery will be 65mm in length and will have a diameter of 18mm. The below image shows the most popular lithium-iron battery packages.

Emerging Battery Form Factors
As of the day of updating this article in 2025, there are many new promising battery form factors that are current emerging. Even though these batteries have not made into the market, it is worth mentioning them below
- Flexible batteries
- Printed batteries
- Structural batteries
- Nano batteries
Selecting the right battery for your application
How to choose the right battery depends on your specific application requirements. Whether you're designing a portable device, building an IoT project, or selecting batteries for consumer products, following a systematic approach ensures optimal performance and cost-effectiveness.
Battery selection process: Start by defining your power requirements (voltage, current, runtime), then consider environmental factors (temperature, size constraints), and finally evaluate cost and availability. Here are the key factors to consider:
One of the main problems hindering technology revolutions like IoT is power, battery life affects the successful deployment of devices that require long battery life and even though several power management techniques are being adopted to make the battery last longer, a compatible battery must still be selected to achieve the desired outcome.
Below are some factors to consider when selecting the right type of battery for your project.
1. Energy Density: The energy density is the total amount of energy that can be stored per unit mass or volume. This determines how long your device stays on before it needs a recharge.
2. Power Density: Maximum rate of energy discharge per unit mass or volume. Low power: laptop, i-pod. High power: power tools.
3. Safety: It is important to consider the temperature at which the device you are building will work. At high temperatures, certain battery components will breakdown and can undergo exothermic reactions. High temperatures generally reduces the performance of most batteries.
4. Life cycle durability: The stability of energy density and power density of a battery with repeated cycling (charging and discharging) is needed for the long battery life required by most applications.
5. Cost: Cost is an important part of any engineering decisions you will be making. It is important that the cost of your battery choice is commensurate with its performance and will not increase the overall cost of the project abnormally.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the different types of batteries?
The different types of batteries include primary batteries (alkaline, zinc-carbon, lithium primary) and secondary batteries (lithium-ion, NiMH, lead-acid, NiCd). Each type has specific applications: alkaline for consumer electronics, lithium-ion for mobile devices, lead-acid for vehicles, and NiMH for power tools.
What type of battery lasts the longest?
Lithium primary batteries last the longest with 10-15 years shelf life. For rechargeable batteries, LiFePO4 batteries last longest with 2000-5000 charge cycles. Lead-acid batteries typically last 3-5 years, while lithium-ion batteries last 2-3 years with daily use.
Which battery is best for high-power applications?
For high-power applications, lithium-ion batteries (especially NMC and LTO chemistries) are best due to high power density. Lead-acid batteries work well for high-current automotive applications, while NiMH batteries are good for power tools requiring moderate high-power output.
What is the difference between primary and secondary batteries?
Primary batteries are single-use and cannot be recharged (alkaline, zinc-carbon). Secondary batteries are rechargeable and can be used hundreds of times (lithium-ion, NiMH, lead-acid). Primary batteries have lower upfront cost but higher long-term cost for frequent use applications.
What is the most common type of battery?
For primary batteries, alkaline batteries are most common in consumer electronics. For rechargeable batteries, lithium-ion dominates the market, particularly in mobile devices and electric vehicles.
Which battery is best for high-power applications?
For high-power applications:
- Portable devices: Li-ion (NMC or LiPO)
- Electric vehicles: NMC, NCA, or LFP
- Grid storage: LFP or Flow batteries
- Industrial: LTO or advanced Lead-acid
Comprehensive List of Battery Types
Primary (Non-rechargeable) Battery Types
- Zinc-Carbon Batteries
- Leclanché cell
- Zinc chloride cell
- Alkaline Batteries
- Alkaline-manganese dioxide
- Alkaline-zinc/air
- Lithium Primary Batteries
- Lithium-Manganese Dioxide (Li-MnO2)
- Lithium-Carbon Monofluoride (Li-CFx)
- Lithium-Thionyl Chloride (Li-SOCl2)
- Lithium-Sulfur Dioxide (Li-SO2)
- Lithium-Iron Disulfide (Li-FeS2)
- Lithium-Iodine (Li-I2)
- Lithium-Silver Vanadium Oxide (Li-SVO)
- Mercury Batteries (Historical)
- Mercury oxide-zinc
- Mercury oxide-cadmium
- Silver-based Batteries
- Silver-Oxide
- Silver-Zinc
- Silver-Cadmium
- Other Primary Types
- Zinc-Air
- Magnesium
- Nickel Oxyhydroxide
- Sodium-based primary cells
Secondary (Rechargeable) Battery Types
- Lead-Acid Variations
- Flooded Lead Acid
- Valve Regulated Lead Acid (VRLA)
- Absorbed Glass Mat (AGM)
- Gel Cell
- Enhanced Flooded Battery (EFB)
- Advanced Lead-Carbon
- Nickel-based Batteries
- Nickel-Cadmium (NiCd)
- Nickel-Metal Hydride (NiMH)
- Nickel-Zinc (NiZn)
- Nickel-Iron (NiFe)
- Nickel-Hydrogen (NiH2)
- Lithium-ion Variants
- Lithium Cobalt Oxide (LCO)
- Lithium Manganese Oxide (LMO)
- Lithium Iron Phosphate (LFP/LiFePO4)
- Lithium Nickel Manganese Cobalt Oxide (NMC)
- Lithium Nickel Cobalt Aluminum Oxide (NCA)
- Lithium Titanate (LTO)
- Lithium Polymer (Li-Po)
- Lithium Sulfur (Li-S)
- Lithium Air (Li-air)
- Lithium Metal (Li-metal)
- Sodium-based Batteries
- Sodium-ion (Na-ion)
- Sodium-sulfur (NaS)
- Sodium-nickel chloride (ZEBRA)
- Flow Batteries
- Vanadium Redox Flow
- Zinc-Bromine Flow
- Iron-Chromium Flow
- Polysulfide Bromide Flow
- Zinc-Cerium Flow
- Organic Flow
- Metal-Air Rechargeable
- Zinc-Air Rechargeable
- Aluminum-Air
- Iron-Air
- Lithium-Air
- Emerging Technologies
- Solid-State Batteries
- Lithium Ceramic
- Glass Battery
- Polymer-based
- Graphene Batteries
- Dual-Carbon Batteries
- Aluminum-ion
- Magnesium-ion
- Calcium-ion
- Potassium-ion
- Glass Batteries
- Sand Batteries
- Structural Batteries
- Bio Batteries
- Nuclear Batteries
- Atomic Batteries
- Radioisotope Thermoelectric Generators (RTGs)
- Solid-State Batteries
- Hybrid Battery Systems
- Lithium-Ion Capacitors
- Lead-Carbon Hybrids
- Aqueous Hybrid Ion
This comprehensive list includes both commercially available and experimental battery technologies. While some of these battery types are widely used, others are still in the research and development phases or have specialized applications.
Latest Trends in Battery Technology (2025)
The battery technology landscape in 2025 is experiencing unprecedented innovation, with several breakthrough technologies moving from laboratories to commercial production. Here are the most significant developments reshaping the industry:
1. Solid-State Batteries: The Commercial Reality
Solid-state battery technology has finally reached the commercialization threshold in 2025. Unlike traditional lithium-ion batteries that use liquid electrolytes, solid-state batteries use solid electrolytes, offering several critical advantages:
- Higher energy density: Up to 400 Wh/kg compared to 250-300 Wh/kg for conventional Li-ion
- Enhanced safety: Solid electrolytes are non-flammable and reduce fire risk
- Longer lifespan: Over 1,000 cycles while maintaining 95% capacity
- Faster charging: Capability for 10-80% charging in under 10 minutes
Commercial developments in 2025: Toyota and Idemitsu are targeting commercial production by 2027-2028, with Toyota claiming breakthrough durability solutions for cracking issues . Mercedes-Benz has already begun testing the world's first production EV powered by solid-state batteries, achieving over 621 miles of driving range . Nissan is constructing a pilot factory in Yokohama with plans to produce the first batch of solid-state batteries in 2025 .
2. Sodium-Ion Batteries: The Cost-Effective Alternative
Sodium-ion battery technology has emerged as a commercially viable alternative to lithium-ion batteries in 2025, particularly for applications where cost is more critical than energy density.
Key advantages of sodium-ion batteries:
- Abundant raw materials: Sodium is widely available and inexpensive
- Excellent cold weather performance: Normal discharge at temperatures as low as -40°C
- Enhanced safety: Better thermal stability than lithium-ion
- Cost competitive: Expected to match LiFePO4 battery costs by 2025
Commercial progress in 2025: CATL announced its second-generation sodium-ion batteries with energy density exceeding 200 Wh/kg, launching in 2025 with mass production expected by 2027 . BYD's sodium-ion batteries are already on track to be cost-competitive with lithium iron phosphate batteries in 2025 . These batteries are being deployed in electric vehicles and energy storage systems.
3. Semi-Solid State Batteries: The Bridge Technology
Semi-solid state batteries represent a transitional technology that combines liquid and solid electrolyte elements, offering improvements over traditional lithium-ion while being easier to manufacture than full solid-state batteries.
Characteristics of semi-solid state batteries:
- Energy density: Up to 350 Wh/kg
- Improved safety: Better thermal stability than liquid electrolyte systems
- Manufacturing compatibility: Can use existing production lines with modifications
- Cost effective: Lower production costs compared to full solid-state
4. Aluminum-Air Batteries: High Energy Density Solution
Aluminum-air battery technology is gaining momentum for specific applications requiring extremely high energy density and long-term storage.
Aluminum-air battery advantages:
- Exceptional energy density: Up to 8.1 kWh/kg theoretical capacity
- Lightweight design: Significantly lighter than lithium-ion equivalents
- Environmentally friendly: Non-toxic materials and recyclable aluminum
- Long shelf life: Minimal self-discharge rates
Current applications and development: The aluminum-air battery market is valued at $11.93 billion in 2024 and expected to reach $20.11 billion by 2037 . These batteries are being tested for electric vehicles, military applications, and grid-scale energy storage systems.
5. Advanced Lithium-Ion Innovations
Traditional lithium-ion technology continues to evolve with significant improvements in 2025:
- Ultra-fast charging: New cell designs achieving 5-80% charge in 5 minutes
- Extended range capabilities: Battery packs delivering over 1,500 km range
- Improved cycle life: Over 10,000 charge cycles for stationary applications
- Enhanced safety features: Advanced thermal management and abuse tolerance
6. AI-Optimized Battery Management
Artificial Intelligence integration is revolutionizing battery design and management in 2025:
- Predictive analytics: AI algorithms predict battery health and optimize charging patterns
- Material discovery: Machine learning accelerates development of new battery chemistries
- Performance optimization: Real-time adjustment of battery parameters for maximum efficiency
- Manufacturing quality: AI-controlled production processes ensuring consistent quality
Future Battery Technologies Beyond 2025
The next generation of battery technologies promises even more revolutionary changes in energy storage. Here are the most promising developments currently in research and early development phases:
Quantum Batteries
Utilizing quantum mechanical effects to achieve instantaneous charging and enhanced energy storage capacity through quantum entanglement and coherence effects.
Nuclear Diamond Batteries
Long-lasting power sources using radioactive carbon-14 encased in synthetic diamonds, potentially providing thousands of years of power for specialized applications.
Sand Batteries
Thermal energy storage systems using sand as a medium, capable of storing renewable energy for months with minimal losses.
Flow Batteries for Grid Storage
Large-scale energy storage systems using liquid electrolytes in external tanks, offering virtually unlimited capacity scaling for renewable energy storage.
Organic Flow Batteries
Environmentally friendly alternatives using organic molecules instead of metals, promising lower costs and reduced environmental impact.
These technologies represent the cutting edge of battery research and may define energy storage solutions for the next decade and beyond.






Sir,
Please let us know technology spot welding for cells as well as connecting bars &where can we locate for spot weling.
Regards
Seema Joshi