Building an Arduino oscilloscope with OLED display is an affordable way for electronics hobbyists and students to visualize electrical waveforms without spending hundreds of dollars on commercial equipment. This comprehensive guide demonstrates how to create a DIY Arduino based oscilloscope using an Arduino Nano oscilloscope platform with a 1.3" OLED screen that accurately displays sine, square, and triangular waveforms. An oscilloscope is an electronic test device that can monitor the steady change of any electrical voltage using two-dimensional graphs, where the change of one or more electric voltages is plotted over time on the vertical Y-axis. In general, every electronic hobbyist or someone interested in dealing with electronics will require an oscilloscope at some point. However, it is prohibitively expensive for students, hobbyists, and that's why in this article we will discuss how to make a mini oscilloscope at home using Arduino. We have also previously built many oscilloscope projects, like a DIY oscilloscope using Raspberry Pi and a Serial monitor-based Arduino Oscilloscope. You can check them out if you are interested. Whether you are seeking Arduino oscilloscope projects for educational purposes or simply want a compact signal analyzer to troubleshoot circuits, the oscilloscope using Arduino provides all the functionality you will need for less than $20. This tutorial includes Arduino oscilloscope programming code, circuit assembly, calibration, and waveform testing to make your oscilloscope a fully functional signal measurement device.
In this detailed tutorial, we'll construct a simple, low-cost Arduino-based oscilloscope featuring a 1.3-inch OLED display capable of accurately visualizing waveforms. This project is inspired by Peter Balch Oscilloscope in a Matchbox project. We have changed a few codes and hardware to suit our requirements.
Table of Contents
What is an Arduino Oscilloscope?
An oscilloscope is an electronic test instrument that visualizes electrical voltage changes over time using two-dimensional graphs displayed on a screen. The oscilloscope built on an Arduino solves the cost problem because it uses the ATmega328P microcontroller's 10-bit analog-to-digital converter (ADC) to sample voltage signals at sampling rates of up to 10,000 samples per second. This Arduino Nano oscilloscope project has many features popular among the electronic hobbyists and electronics students doing electronics hobbyist projects.
Why Build an Arduino Oscilloscope OLED?
This Arduino Oscilloscope OLED project has a lot to provide for those of you who consider yourself electronic hobbyists.
» Affordable: You can build the oscilloscopes with Arduino for under $20, compared to the several hundred dollars to several thousand dollars for an equivalent commercial oscilloscope.
» Portable: It has a 1.3-inch OLED and is small enough to take into the field and use for lab testing.
» Learning Opportunity: It is the best learning experience to become familiar with signal analysis and the Arduino oscilloscope programming.
» Expandable: You can change the code and hardware to fit any project that you are involved in with an Arduino oscilloscope.
» Real Waveforms: OLED displays sine, square, and triangle waveforms.
Arduino Oscilloscope vs Commercial Oscilloscope: Detailed Comparison
| Feature | Arduino Oscilloscope | Entry-Level Commercial | Professional Oscilloscope |
| Cost | $18-24 | $300-500 | $1,000-3,000+ |
| Bandwidth | Up to 5 kHz | 20-50 MHz | 100-200 MHz+ |
| Sampling Rate | 10 kS/s (10,000 samples/sec) | 250 MS/s - 1 GS/s | 1-5 GS/s |
| ADC Resolution | 10-bit (1024 levels) | 8-bit (256 levels) | 8-bit to 12-bit |
| Voltage Resolution | ~5mV (0-5V range) | Variable with range | Variable with range |
| Portability | Pocket-sized, battery powered | Desktop unit (5-10 lbs) | Bench-top equipment (10-20 lbs) |
| Display | 1.3" OLED (128×64 pixels) | 7" color LCD | 10-12" high-resolution touchscreen |
| Best For | Learning, audio circuits, hobbyist projects, sensors | Small repairs, education, basic diagnostics | Professional diagnostics, R&D, production testing |
| Input Channels | 1 (expandable to 2 with code mods) | 2 channels standard | 2-4 channels (up to 8 for mixed signal) |
| Voltage Range | 0-5V direct (0-50V with divider) | ±40V per division | ±300V per division or higher |
| Triggering Modes | Basic edge triggering | Edge, pulse, slope | Advanced (pattern, timeout, serial protocol) |
| Time Base Range | 1ms - 500ms per division | 1ns - 50s per division | 1ps - 1000s per division |
| Measurement Functions | Manual voltage/time measurement | Auto measurements (frequency, period, Vpp, Vrms) | Advanced analysis (FFT, statistics, math functions) |
| Storage/Recording | Can add SD card with code | Internal memory, USB export | Large internal storage, network connectivity |
| Customization | Fully programmable, open-source firmware | Limited firmware updates | Proprietary software, licensed options |
| Learning Curve | Low to moderate | Moderate | Moderate to high |
| Repair/Maintenance | Easy DIY repair, cheap replacement parts | Requires service center | Expensive professional calibration required |
Materials Required to Build an Arduino-Based Oscilloscope
The following components are required to make this portable, mini Oscilloscope using Arduino Nano.
Qty | Value | Device | Package | Parts | Description |
2 | Tactile Switch | Buttons | TH | S1, S2 | Tactile switch / Buttons |
1 | Arduino Nano | Microcontroller | ARDUINO_NANO | ARDUINO_NANO1 | Arduino Nano Board |
4 | 0.1uF / 16V | Capacitor | TH | C1, C2, C3, C4 | 0.1uF/16V/Ceramic Disc |
1 | 100K | Resistor | TH | R2 | 100K/1/4W/TH |
1 | 10K | Resistor | TH | R7 | 10K/1/4W/TH |
1 | 1K | Resistor | TH | R3 | 1K/1/4W/TH |
2 | 1M | Resistor | TH | R6, R8 | 1M/1/4W/TH |
2 | 270K | Resistor | TH | R4, R5 | 270K/1/4W/TH |
3 | 4.7K | Resistor | TH | R1, R9, R10 | 4.7K/1/4W/TH |
1 | LM358 | Op-AMP | DIL08 | IC1 | LM358 |
2 | PIN1-2 | Pin Header | TH | Display / Input | 4Pin / M/F |
Circuit Diagram for Arduino Oscilloscope
The circuit schematic for this oscilloscope using Arduino is straightforward and uses minimal components. The schematics to build an Arduino-based Oscilloscope are very simple and only require a few parts. You can check out the complete circuit diagram below.
The main part of the schematic uses a single op-amp IC, which is the LM358, which includes two op-amps inside one single chip. As the input signal will be AC and we do not have split rail construction, there are two op-amps (from a single Op-Amp 8-pin package) used to make the signal ac-coupled. Both the op-amp is fed with a reference voltage that is used to offset the signal, and using analog inputs, it is plotted on the scope graph. The offset can be changed using the potentiometer (which has 100K resistance). Both the op-amps are set with the same negative feedback with an x5 gain setting.
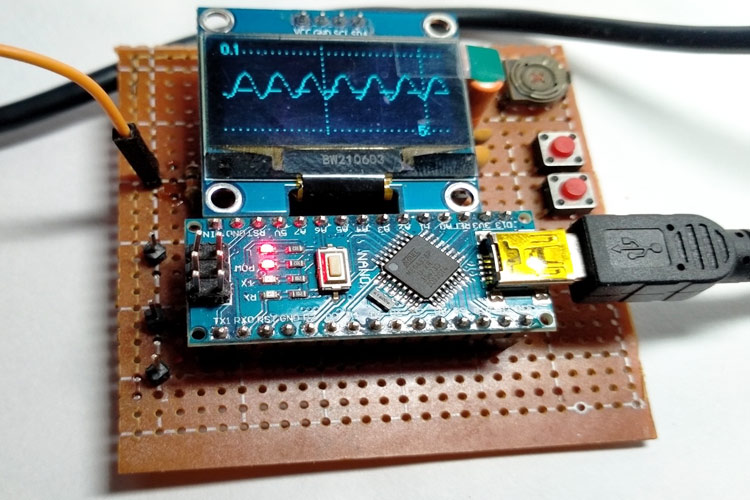
Other than this, the OLED is connected over the A4 and A5 is the I2C SCL and SDA pin with a 4.7K pull-up resistor. It could work with a simple USB connector. The buttons are used to set the parameters of the Oscilloscope. We have built the complete circuit on top of a perf board, and when I completed my setup, it looked something like this.

Arduino Oscilloscope Programming Guide
The Arduino oscilloscope programming involves configuring the ADC for fast sampling, implementing trigger functions, and rendering waveforms on the OLED display. The coding part is complex. To understand how the coding works, please check the code snippets below-
First of all, the library for the Oscope is used from Peter Balch's SimpleSH1106.h library. It is a very fast library for the OLED that uses the SH1106 chipset.
The libraries are defined in the lines below.
#include <Wire.h>
#include <limits.h>
#include "SimpleSH1106.h"
#include <math.h>The defines and typedefs are defined in the lines below -
ifndef getBit
#define getBit(sfr, bit) (_SFR_BYTE(sfr) & _BV(bit))
#endif
enum Tmode {DC5V, AC500mV, AC100mV, AC20mV,
mLogic,
mVoltmeter,
maxMode1
};
const Tmode maxMode = maxMode1 - 1;Further, the required constants and the variables are declared below -
/-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Global Constants
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
bool bHasLogic = true;
bool bHasFreq = true;
bool bHasVoltmeter = true;
bool bHasTestSignal = true;
bool bHasSigGen = false;
const long BAUDRATE = 115200; // Baud rate of UART in bps
const int COMMANDDELAY = 10; // ms to wait for the filling of Serial buffer
const int COMBUFFERSIZE = 4; // Size of buffer for incoming numbers
const int testSignalPin = 3;
const char ack = '@'; // acknowledge for comms command
const byte SampPerA = 5 + 6; // 6 nops
#define LoopNops __asm__("nop\n nop\n nop\n nop\n nop\n nop\n")
const int SampPerB = 20;
const int BtnHorz = 4; // pushbutton
const int BtnVert = 7; // pushbutton
const int FreeRunTimeout = 0x10; // 0.5 sec for free run
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Global Variables
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
Tmode curMode = DC5V;
uint8_t curVref = 1;
uint8_t curPeriod = 200;
uint8_t curPrescaler = 7;
char commandBuffer[COMBUFFERSIZE + 1];
bool TrigFalling = true;
uint8_t curSweep = 0;
byte yGraticulePage0, yGraticuleByte0, yGraticulePage1, yGraticuleByte1, yGraticulePage2, yGraticuleByte2;
byte* pxGratLabel;
byte* pyGratLabel;
byte xGratLabelLen, yGratLabelLen;
byte yGraticule0, yGraticule1, yGraticule2, xGraticule1, xGraticule2;
TmenuSel sel = sTime; // for main menu
byte adj[4] = {0, 0, 0, 0}; // for main menu
bool SendingSerial = false;
int curPwmMode = 0;
const int ADCBUFFERSIZE = 128;
uint8_t ADCBuffer[ADCBUFFERSIZE];
int ButtonsTimer1 = 0;
long Vin = 0; // used to display VoltmeterThe Images on the menu are declared here -
/-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
// images for the main menu
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
const byte imgMainMenuTop[] PROGMEM = {
128, // width
2, // pages
1, 224, 147, 32, 130, 0, 3, 248, 252, 6, 130, 2, 3, 6, 252, 248, 130, 0, 2, 96, 240, 130, 144, 2, 176, 32, 130, 0, 2, 224, 240, 130,
16, 3, 48, 32, 0, 130, 246, 130, 0, 130, 254, 130, 0, 130, 254, 130, 0, 2, 224, 240, 130, 16, 2, 240, 224, 130, 0, 2, 96, 240, 130,
144, 2, 176, 32, 130, 0, 2, 224, 240, 130, 16, 5, 48, 32, 0, 224, 240, 130, 16, 2, 240, 224, 130, 0, 130, 240, 130, 16, 2, 240, 224,
130, 0, 2, 224, 240, 130, 80, 2, 112, 96, 130, 0, 149, 32, 2, 224, 255, 149, 0, 3, 1, 3, 6, 130, 4, 3, 6, 3, 1, 130, 0, 2, 2, 6, 130,
4, 2, 7, 3, 130, 0, 2, 3, 7, 130, 4, 3, 6, 2, 0, 130, 7, 130, 0, 130, 7, 130, 0, 130, 7, 130, 0, 2, 3, 7, 130, 4, 2, 7, 3, 130, 0, 2, 2, 6,
130, 4, 2, 7, 3, 130, 0, 2, 3, 7, 130, 4, 5, 6, 2, 0, 3, 7, 130, 4, 2, 7, 3, 130, 0, 130, 63, 130, 4, 2, 7, 3, 130, 0, 2, 3, 7, 130, 4, 2,
6, 2, 151, 0, 1, 255
};
const byte imgMainMenuMid[] PROGMEM = {
128, // width
1, // pages
1, 255, 254, 0, 1, 255
};
const byte imgMainMenuBot[] PROGMEM = {
128, // width
1, // pages
1, 255, 254, 128, 1, 255
};
const byte imgBoxTop[] PROGMEM = {
128, // width
1, // pages
1, 248, 254, 8, 1, 248
};
const byte imgCaret1[] PROGMEM = {
4, // width
1, // pages
4, 255, 126, 60, 24
};
const byte imgCaret2[] PROGMEM = {
7, // width
1, // pages
7, 32, 48, 56, 60, 56, 48, 32
};
const byte imgTrian[] PROGMEM = {
14, // width
2, // pages
28, 3,12,48,192,0,0,0,0,0,0,192,48,12,3,128,128,128,128,131,140,176,176,140,131,128,128,128,128};
const byte imgSine[] PROGMEM = {
14, // width
2, // pages
28, 1,2,28,224,0,0,0,0,0,0,224,28,2,1,128,128,128,129,142,144,160,160,144,142,129,128,128,128};
const byte imgSquare[] PROGMEM = {
14, // width
2, // pages
28, 0,0,0,255,1,1,1,1,1,1,255,0,0,0,160,160,160,191,128,128,128,128,128,128,191,160,160,160};The drawings and lines are declared here -
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
// FillBar
// fills the bits of a screen column from bit y1 to bit y2
// makes a bar that must be part of 'page'
// returns the bar
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
byte FillBar(byte y1, byte y2, byte page) {
static byte lob[] = {0x00, 0x01, 0x03, 0x07, 0x0F, 0x1F, 0x3F, 0x7F, 0xFF};
byte bar;
if (page == y1 / 8) {
if (page == y2 / 8)
bar = lob[(y2 & 7) + 1];
else
bar = 0xFF;
return bar - lob[y1 & 7];
}
else if (page == y2 / 8)
return lob[(y2 & 7) + 1];
else if ((page > y1 / 8) & (page < y2 / 8))
return 0xFF;
else
return 0;
}
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
// draw box
// draws a box around the screen with s written at top-left
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
void drawBox(char* s) {
// clearSH1106();
DrawImageSH1106(0, 0, imgBoxTop);
for (int i = 1; i < 7; i++)
DrawImageSH1106(0, i, imgMainMenuMid);
DrawImageSH1106(0, 7, imgMainMenuBot);
DrawCharSH1106(' ', 6, 0, SmallFont);
DrawStringSH1106(s, 7, 0, SmallFont);
}
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
// drawScreen
// draws a graph like an oscilloscope
// takes about 40mS
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
void drawScreen(void) {
byte i, j, k, y, yPrev, bar, page, lastDrawn;
byte* pxbz;
byte* pybz;
byte pxlenz, pylenz;
switch (curMode) {
case mVoltmeter:
drawBox("Voltmeter");
i = 20;
if (Vin == LONG_MAX)
DrawStringSH1106("++++", i, 3, LargeDigitsFont);
else if (Vin == -LONG_MAX)
DrawStringSH1106("----", i, 3, LargeDigitsFont);
else {
i += DrawIntDP2(Vin / 10, i, 3, LargeDigitsFont);
DrawStringSH1106("Volts", i, 4, SmallFont);
}
return;
case AC100mV:
for ( i = 0; i < ADCBUFFERSIZE; i++ )
ADCBuffer[i] = ADCBuffer[i] / 4;
break;
default:
for ( i = 0; i < ADCBUFFERSIZE; i++ )
ADCBuffer[i] = 63 - ADCBuffer[i] / 4;
}
if ((curPeriod == 0) && (curMode <= AC20mV)) {
yPrev = ADCBuffer[0];
y = ADCBuffer[1];
for ( i = 1; i < ADCBUFFERSIZE - 1; i++ ) {
ADCBuffer[i] = (yPrev + y + ADCBuffer[i + 1]) / 3;
yPrev = y;
y = ADCBuffer[i + 1];
}
}
pxbz = pxGratLabel;
pxlenz = xGratLabelLen;
pybz = pyGratLabel;
pylenz = yGratLabelLen;
for (page = 0; page <= 7; page++) {
yPrev = ADCBuffer[0];
lastDrawn = 255;
setupPage(page);
setupCol(0);
Wire.beginTransmission(addr);
Wire.write(0x40); // the following bytes are data
for (i = 0; i < ADCBUFFERSIZE; i++) {
if (i % 26 == 0) {
Wire.endTransmission();
Wire.beginTransmission(addr);
Wire.write(0x40); // the following bytes are data
}
y = ADCBuffer[i];
if (yPrev > y + 1) {
if (yPrev == lastDrawn)
yPrev--;
bar = FillBar(y + 1, yPrev, page);
lastDrawn = yPrev + 1;
} else {
bar = FillBar(yPrev, yPrev, page);
lastDrawn = yPrev;
}
// }
if ((page == 0) && (bar == 0x01) && (i & 1))
bar = 0;
if ((page == 7) && (bar == 0x80) && (i & 1))
bar = 0;
if (page == yGraticulePage0) {
if (i & 8)
bar = bar | yGraticuleByte0;
}
else if (page == yGraticulePage1) {
if (i < pylenz)
{
bar |= *pybz;
pybz++;
}
else if (i % 4 == 0)
bar |= yGraticuleByte1;
}
else if (page == yGraticulePage2) {
if (i % 4 == 0)
bar |= yGraticuleByte2;
}
if ((i == xGraticule1) | (i == xGraticule2))
bar = bar | 0x22;
if ((page == 7) && (i > xGraticule2 - pxlenz - 2) && (i < xGraticule2 - 1)) {
bar |= *pxbz;
pxbz++;
}
Wire.write(bar);
yPrev = y;
}
Wire.endTransmission();
}
}The ADC is declared here -
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
// initADC()
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
void initADC(void) {
if (curMode > AC20mV)
return;
ACSR = 0x10;
ADCSRA = 0x97;
ADCSRB = 0x0 ; //ADC Control and Status Register B
// 0 Bit 6 – ACME: Analog Comparator Multiplexer Enable
// 000 Bits 2:0 – ADTSn: ADC Auto Trigger Source [n = 2:0] Free Running mode
ADMUX = 0x20 + (curVref << 6) + curMode; // ADC Multiplexer Selection Register
// rr Bits 7:6 – REFSn: Reference Selection = Vcc
// 1 Bit 5 – ADLAR: ADC Left Adjust Result
// aaaa Bits 3:0 – MUXn: Analog Channel Selection
DIDR0 = 0x3F; // Digital Input Disable Register 0
// ADC0D=1, ADC1D=1, ADC2D=1, ADC3D=1, ADC4D=1, ADC5D=1, ADC6D=0, ADC7D=0
}The sweep of the signals on the screen is declared below -
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
// setSweep
// set period and ADC prescaler
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
void setSweep(byte Sweep) {
int x;
long t;
if (Sweep == 255) {
if (curSweep == 0)
curSweep = 6;
else
curSweep--;
} else
curSweep = Sweep;
switch (curSweep) {
case 0: curPeriod = 0; curPrescaler = 2; t = 100; pxGratLabel = &ax0_1[0]; xGratLabelLen = sizeof(ax0_1); break;
case 1: curPeriod = 4; curPrescaler = 2; t = 400; pxGratLabel = &ax0_4[0]; xGratLabelLen = sizeof(ax0_4); break;
case 2: curPeriod = 11; curPrescaler = 3; t = 1000; pxGratLabel = &ax1[0]; xGratLabelLen = sizeof(ax1); break;
case 3: curPeriod = 24; curPrescaler = 3; t = 2000; pxGratLabel = &ax2[0]; xGratLabelLen = sizeof(ax2); break;
case 4: curPeriod = 62; curPrescaler = 4; t = 5000; pxGratLabel = &ax5[0]; xGratLabelLen = sizeof(ax5); break;
case 5: curPeriod = 125; curPrescaler = 4; t = 10000; pxGratLabel = &ax10[0]; xGratLabelLen = sizeof(ax10); break;
case 6: curPeriod = 255; curPrescaler = 5; t = 20000; pxGratLabel = &ax20[0]; xGratLabelLen = sizeof(ax20); break;
}
if (curSweep == 0)
x = t;
else
x = 16 * t / (curPeriod * SampPerA + SampPerB);
xGraticule1 = x / 2;
xGraticule2 = x;
SendAck();
}
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Sweep
// sweeps siggen freq continuously
// takes n mS for whole sweep
// SDC regs are saved and restored
// stops when receives a serial char
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
void Sweep(int n) {
byte oldACSR = ACSR;
byte oldADCSRA = ADCSRA;
byte oldADCSRB = ADCSRB;
byte oldADMUX = ADMUX;
byte oldDIDR0 = DIDR0;
byte oldDIDR1 = DIDR1;
int fmin,fmax;
fmin = calcFreq(freqSGLo);
fmax = calcFreq(freqSGHi);
int i=0;
do {
long f = exp((log(fmax) - log(fmin))*i/(n-1) + log(fmin)) +0.5;
SG_freqSet(f, waveType);
delay(1);
i++;
if (i >= n) i = 0;
} while (!Serial.available());
SG_freqSet(calcFreq(freqSGLo), waveType);
ACSR = oldACSR;
ADCSRA = oldADCSRA;
ADCSRB = oldADCSRB;
ADMUX = oldADMUX;
DIDR0 = oldDIDR0;
DIDR1 = oldDIDR1;
}The buttons increment and mode set are done in the below -
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
// incMode
// increment Mode
// wrap around from max
// skip over modes that are not allowed
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
int incMode(int mode) {
mode++;
//if ((mode == mLogic) && (!bHasLogic)) mode++;
// if ((mode == mFreqLogic) && ((!bHasFreq) || (!bHasLogic))) mode++;
// if ((mode == mFreqAC) && (!bHasFreq)) mode++;
if ((mode == mVoltmeter) && (!bHasVoltmeter)) mode++;
if (mode > maxMode)
return DC5V;
else
return mode;
}
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
// setMode
// set mode and Vref
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
void setMode(int mode) {
int i;
if (mode == 255) {
curMode = incMode(curMode);
} else
curMode = mode;
switch (curMode) {
case DC5V:
curVref = 1;
i = (long)4000 * 64 / readVcc();
if (i <= 63) {
yGraticule1 = 63 - i;
yGraticule2 = 63 - i / 2;
yGraticule0 = 255;
pyGratLabel = &ax4V[0];
yGratLabelLen = sizeof(ax4V);
} else {
yGraticule2 = 63 - i;
yGraticule1 = 63 - i / 2;
yGraticule0 = 255;
pyGratLabel = &ax2V[0];
yGratLabelLen = sizeof(ax2V);
}
break;
case AC500mV:
curVref = 3;
i = (byte)(0.5 / 1.1 * 256 / 4);
yGraticule1 = 32 - i;
yGraticule2 = 32 + i;
yGraticule0 = 32;
pyGratLabel = &ax0_5[0];
yGratLabelLen = sizeof(ax0_5);
break;
case AC100mV:
curVref = 3;
i = (byte)(0.1 / 1.1 * (R1 + R2) / R2 * 256 / 4);
yGraticule1 = 32 - i;
yGraticule2 = 32 + i;
yGraticule0 = 32;
pyGratLabel = &ax0_1[0];
yGratLabelLen = sizeof(ax0_1);
break;
case AC20mV:
curVref = 3;
i = (byte)(0.02 / 1.1 * (R1 + R2) / R2 * (R1 + R2) / R2 * 256 / 4);
yGraticule1 = 32 - i;
yGraticule2 = 32 + i;
yGraticule0 = 32;
pyGratLabel = &ax20[0];
yGratLabelLen = sizeof(ax20);
break;
default:
curVref = 1;
yGraticule1 = 255;
yGraticule2 = 255;
yGraticule0 = 255;
pyGratLabel = &ax20[0];
yGratLabelLen = sizeof(ax20);
break;
}
The Drawing of the main menu is done using the code snippets below -
void drawMainMenu(void) {
int ofs, x, yVcc, pg;
switch (sel) {
case sMode: ofs = -1; break;
case sTrigger: ofs = -2; break;
case sTestSig: ofs = -5; break;
case sSigGen: ofs = bHasTestSignal ? -7 : -5; break;
default: ofs = 0;
}
// DrawImageSH1106(0,ofs,imgMainMenu);
DrawImageSH1106(0, ofs + 0, imgMainMenuTop);
for (x = 2; x < 14; x++)
DrawImageSH1106(0, ofs + x, imgMainMenuMid);
DrawImageSH1106(0, ofs + 10 + bHasTestSignal * 2 + bHasSigGen * 2, imgMainMenuBot);
DrawImageSH1106(6, 3 + sel * 2 + ofs, imgCaret1);
BoldSH1106 = true;
pg = 3 + ofs;
DrawStringSH1106("Time:", 12, pg, SmallFont); pg += 2;
DrawStringSH1106((adj[1] <= AC20mV ? "Gain:" : "Mode:"), 12, pg, SmallFont); pg += 2;
DrawStringSH1106("Trigger:", 12, pg, SmallFont); pg += 2;
if (bHasTestSignal) {
DrawStringSH1106("Test sig:", 12, pg, SmallFont); pg += 2;
if (bHasSigGen) {
DrawStringSH1106("Signal Generator", 12, pg, SmallFont); pg += 2;
}
DrawStringSH1106("Vcc:", 12, pg, SmallFont); yVcc = pg; pg += 2;
} else {
if (bHasSigGen) {
DrawStringSH1106("Vcc:", 12, pg, SmallFont); yVcc = pg; pg += 2;
DrawStringSH1106("Signal Generator", 12, pg, SmallFont); pg += 2;
} else {
DrawStringSH1106("Vcc:", 12, pg, SmallFont); yVcc = pg; pg += 2;
}
}
BoldSH1106 = false;
x = 62;
pg = 3 + ofs;
switch (adj[0]) {
case 0: DrawStringSH1106("1mS", x, pg, SmallFont); break;
case 1: DrawStringSH1106("2mS", x, pg, SmallFont); break;
case 2: DrawStringSH1106("5mS", x, pg, SmallFont); break;
case 3: DrawStringSH1106("10mS", x, pg, SmallFont); break;
case 4: DrawStringSH1106("20mS", x, pg, SmallFont); break;
case 5: DrawStringSH1106("50mS", x, pg, SmallFont); break;
case 6: DrawStringSH1106("100mS", x, pg, SmallFont); break;
}
pg += 2;
switch (adj[1]) {
case DC5V: DrawStringSH1106("5V DC", x, pg, SmallFont); break;
case AC500mV: DrawStringSH1106("0.5V AC", x, pg, SmallFont); break;
case AC100mV: DrawStringSH1106("0.1V AC", x, pg, SmallFont); break;
case AC20mV: DrawStringSH1106("20mV AC", x, pg, SmallFont); break;
//case mLogic: DrawStringSH1106("Logic", x, pg, SmallFont); break;
//case mFreqLogic: DrawStringSH1106("Freq Logic", x, pg, SmallFont); break;
//case mFreqAC: DrawStringSH1106("Freq AC", x, pg, SmallFont); break;
case mVoltmeter: DrawStringSH1106("Voltmeter", x, pg, SmallFont); break;
}
pg += 2;
switch (adj[2]) {
case 1: DrawStringSH1106("Fall", x, pg, SmallFont); break;
default: DrawStringSH1106("Rise", x, pg, SmallFont);
}
pg += 2;
if (bHasTestSignal) {
switch (adj[3]) {
case 1: DrawStringSH1106("31250Hz 32uS", x, pg, SmallFont); break;
case 2: DrawStringSH1106("3906Hz 256uS", x, pg, SmallFont); break;
case 3: DrawStringSH1106("977Hz 1024uS", x, pg, SmallFont); break;
case 4: DrawStringSH1106("488Hz 2048uS", x, pg, SmallFont); break;
case 5: DrawStringSH1106("244Hz 4096uS", x, pg, SmallFont); break;
case 6: DrawStringSH1106("122Hz 8192uS", x, pg, SmallFont); break;
case 7: DrawStringSH1106("31Hz 32768uS", x, pg, SmallFont); break;
default: DrawStringSH1106("Off", x, pg, SmallFont);
}
pg += 2;
}
if (bHasSigGen)
pg += 2;
if (yVcc <= 7) {
x += DrawIntDP2(readVcc() / 10, x, yVcc, SmallFont);
DrawCharSH1106('V', x, yVcc, SmallFont);
}
}The button handlers used in the below -
void CheckButtons(void) {
const byte timeout = 70; // 1 sec to show menu
static int prevHorz = HIGH;
static int prevVert = HIGH;
int i;
if (digitalRead(BtnHorz) == LOW) {
if (prevHorz == HIGH) {
switch (curMode) {
//case mFreqLogic:
// case mFreqAC:
case mVoltmeter:
ExecMenu();
return;
}
ButtonsTimer1 = 0;
myDelay(15);
setSweep(255);
prevHorz = LOW;
} else {
if (ButtonsTimer1 > timeout) {
ExecMenu();
return;
}
}
} else {
prevHorz = HIGH;
}
if (digitalRead(BtnVert) == LOW) {
if (prevVert == HIGH) {
ButtonsTimer1 = 0;
myDelay(15);
setMode(255);
prevVert = LOW;
} else {
if (ButtonsTimer1 > timeout) {
ExecMenu();
return;
}
}
} else {
prevVert = HIGH;
}
}The frequency measurement is done using a complex timer logic in the below -
//=========================================================================
// Timer1 overflows every 65536 counts
//=========================================================================
ISR (TIMER1_OVF_vect)
{
FC_overflowCount++;
}
//=========================================================================
// Timer1 Capture interrupt
// invoked by comparator
// read the current timer1 capture value
// used in freq meter
//=========================================================================
ISR (TIMER1_CAPT_vect) {
// grab counter value before it changes any more
unsigned int timer1CounterValue = ICR1; // see datasheet, page 117 (accessing 16-bit registers)
unsigned long overflowCopy = FC_overflowCount;
unsigned long t;
static unsigned long prevT;
// if just missed an overflow
if ((TIFR1 & bit(TOV1)) && timer1CounterValue < 0x7FFF)
overflowCopy++;
t = (overflowCopy << 16) + timer1CounterValue;
if ((!FC_firstAC) && (t-prevT > 100) && (t-prevT > FC_MaxPeriodAC))
FC_MaxPeriodAC = t-prevT;
prevT = t;
FC_firstAC = false;
}
//=========================================================================
// Timer0 Interrupt Service is invoked by hardware Timer0 every 1ms = 1000 Hz
// used by frequancy counter
// called every 1mS
//=========================================================================
ISR(TIMER0_COMPA_vect) {
if (FC_Timeout >= FC_LogicPeriod) { // end of gate time, measurement ready
TCCR1B &= ~7; // Gate Off / Counter T1 stopped
bitClear(TIMSK0, OCIE0A); // disable Timer0 Interrupt
FC_OneSec = true; // set global flag for end count period
// calculate now frequeny value
FC_freq = 0x10000 * FC_overflowCount; // mult #overflows by 65636
FC_freq += TCNT1; // add counter1 value
}
FC_Timeout++; // count number of interrupt events
if (TIFR1 & 1) { // if Timer/Counter 1 overflow flag
FC_overflowCount++; // count number of Counter1 overflows
bitSet(TIFR1, TOV1); // clear Timer/Counter 1 overflow flag
}
}
//=========================================================================
// FC_InitLogic
// count number of rising edges at D5 over mS period
//=========================================================================
void FC_InitLogic() {
noInterrupts ();
TIMSK0 = 0x00;
delayMicroseconds(50); // wait if any ints are pending
FC_OneSec = false; // reset period measure flag
FC_Timeout = 0; // reset interrupt counter
TCCR1A = 0x00; // timer output off
TCCR1B = 0x07; // External clock source on T1 pin. Clock on rising edge.
TCNT1 = 0x00; // counter = 0
TCCR0A = 0x02; // compare output off; max count = OCRA
TCCR0B = 0x03; // input clk is 16M/64
TCNT0 = 0x16; // counter = 0 - why is this not 0? cos of set-up time?
TIMSK0 = 0x00;
OCR0A = 248; // max count value = CTC divider by 250 = 1mS
GTCCR = 0x02; // reset prescaler
FC_overflowCount = 0;
bitSet(TIMSK0, OCIE0A); // enable Timer0 Interrupt
interrupts ();
}
//=========================================================================
// FC_InitAC
// ACfreqAdcPin = 0..5 - use that ADC mux and measure period with Timer1
//=========================================================================
void FC_InitAC() {
noInterrupts ();
FC_disable();
TCCR1A = 0; // reset Timer 1
TCCR1B = bit(CS10) | bit(ICES1); // no prescaler, Input Capture Edge Select
TIFR1 = bit(ICF1) | bit(TOV1); // clear flags so we don't get a bogus interrupt
TCNT1 = 0; // Timer1 to zero
FC_overflowCount = 0; // for Timer1 overflows
TIMSK1 = bit(TOIE1) | bit(ICIE1); // interrupt on Timer 1 overflow and input capture
ADCSRA = 0;
DIDR1 = 1; // digital input of D6 is off
ADMUX = ACfreqAdcPin;
ACSR = bit(ACI) | bit(ACIC) | (B10 << ACIS0); // "clear" interrupt flag; timer capture from comparator; falling edge
ADCSRB = bit(ACME); // Comparator connected to ADC mux
FC_firstAC = true;
FC_Timeout = 0;
FC_MaxPeriodAC = 0;
interrupts ();
}
//=========================================================================
// FC_disable
// turn off freq counter interrupts
//=========================================================================
void FC_disable() {
TCCR0A = 0x03; // no compare output; Fast PWM up to 0xFF
TCCR0B = 0x03; // no Output Compare; prescaler = 16MHz/64; overflow approx every 1mS
TIMSK0 = 0x00; // Interrupt Mask Register = none
GTCCR = 0x00; // Control Register = none
OCR0A = 0x00; // Output Compare Register A = none
OCR0B = 0x00; // Output Compare Register B = none
TCCR1A = 0xC0;
TCCR1B = 0x05;
TCCR1C = 0x00;
TIMSK1 = 0x00;
}
//=========================================================================
// FC_OneSecPassed
// has 1 second passed?
//=========================================================================
bool FC_OneSecPassed() {
static byte prevTimer1 = 0;
byte i;
static unsigned long t = 0;
if (bitRead(TIFR0, TOV0)) // overflow every 1mS
FC_Timeout++;
bitSet(TIFR0, TOV0);
return FC_Timeout > 1000;
}
//=========================================================================
// FC_CheckLogic
// frequency measurer
// call repeatedly
// returns true when has timed out
// result in FC_freq
//=========================================================================
bool FC_CheckLogic() {
return FC_OneSec;
}
//=========================================================================
// FC_CheckAC
// frequency measurer
// call repeatedly
// returns true when has timed out
// result in FC_freq
//=========================================================================
bool FC_CheckAC() {
unsigned long FC_elapsedTime;
if (FC_OneSecPassed()) {
if (FC_MaxPeriodAC > 0)
FC_freq = 100 * F_CPU*1.004 / FC_MaxPeriodAC; // mult by 100 so can display 2 d.p.
else
FC_freq = 0;
FC_InitAC();
return true;
}
return false;
}
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
// myDelay
// delays for approx mS milliSeconds
// doesn't use any timers
// doesn't affect interrupts
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
void myDelay(int mS) {
for (int j = 0; j < mS; j++)
delayMicroseconds(1000);
}
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
// MeasureVoltmeter
// measures Voltmeter at Vin in mV
// assumes resistors have been connected to pin:
// Ra from pin to 5V
// Rb from pin to 0V
// Rc from pin to Vin
//----------------------------------------------------------------------------In the setup, the UART, ADC, and OLED are started, the memory buffer is set, and I2C begins.
void setup (void) {
// Open serial port with a baud rate of BAUDRATE b/s
Serial.begin(baud rate);
// Clear buffers
memset( (void *)commandBuffer, 0, sizeof(commandBuffer) );
// Activate interrupts
sei();
initADC();
Serial.println("ArdOsc " __DATE__); // compilation date
Serial.println("OK");
setMode(0); // y-gain 5V
setSweep(5);
setPwmFrequency(testSignalPin, 3); // test signal 976Hz 1024uS
pinMode(BtnHorz, INPUT_PULLUP);
pinMode(BtnVert, INPUT_PULLUP);
pinMode(LED_BUILTIN, OUTPUT);
Wire.begin(); // join i2c bus as master
TWBR = 1; // freq=888kHz period=1.125uS
initSH1106();
}In the void loop, the loop depends on the switch state at which mode it is residing, and the button is pressed to select the mode.
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Main routines
// loop
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
void loop (void) {
static int ButtonsTimer2 = 0;
switch (curMode) {
case mVoltmeter:
if (CheckVoltmeter())
drawScreen();
break;
default:
if (!SendingSerial) {
SendADC();
switch (sweepType) {
case sw20Frames: case sw100Frames: case sw500Frames:
SG_StepSweep();
}
}
}
CheckButtons();
}Technical Summary and GitHub Repository
The Technical Summary provides an in-depth overview of the project’s design, working principles, and implementation details. Explore the GitHub Repository for complete source code, circuit files, and documentation to replicate or modify the project.
How the Arduino Oscilloscope Works
All the components are soldered on the board and powered using the USB cable, and different waves are tested against the input. Understanding the working principle behind this oscilloscope using Arduino helps in troubleshooting and customization. The system operates through coordinated sampling, triggering, and display refresh cycles.
Signal Acquisition Process
The input signal is connected to the voltage divider network, making sure that the signal is within the voltage range of 0-5V which is safe for the Arduino Nano's 10-bit ADC to sample it without any problem. One sample represents one moment in time and the total of the samples constitutes the waveform viewed on the screen.
Triggering Mechanism
Triggering keeps repetitive waveforms stable on the display. The Arduino oscilloscope uses edge triggering, which detects when the signal crosses a threshold voltage. This allows us to align the display with the input signal and to create a stable waveform instead of a rolling display.
Display Refresh Cycle
The OLED display refreshes approximately 100 times a second to allow smooth visualisation of the waveform. During each refresh cycle, the previous frame is deleted, the grid is drawn, the new sample data is plotted, and the information bar is updated. This Arduino OLED implementation of the oscilloscope attempts to balance display refresh rate with sample speed to maintain a balance, rendering coherence to the user.
Timing Considerations
The maximum sampling rate will vary based on the following considerations:
- ADC Conversion Time: The default Arduino ADC uses ~100 microseconds in time to convert a single sample
- Prescaler Settings: The prescaler has been modified in this code that allow sampling speed closer to ~13 microseconds
- I2C Communication: Refreshing the display of the OLED consumes a significant amount of time consumed by the refresh cycle
- Processing Overhead: Trigger detection and data processing take additional system time as well, but often not large.
All the components are soldered on the board and powered using the USB cable, and different waves are tested against the input. The following are the images of a Sine wave, a Square wave, and a Triangular wave.
Real-World Uses for Arduino Oscilloscope Projects
This Arduino Oscilloscope has many practical applications in electronics work:
∗ Circuit Debugging: You can visualize signal issues in either digital or analog circuits.
∗ Audio Analysis: You can look at audio waveforms produced by amplifiers, synths, and effects circuits.
∗ PWM Verification: You can verify the duty cycle and frequency of pulse-width modulation signals.
∗ Sensor Testing: You can observe output signals of different types of sensors.
∗ Teaching: Allows you to teach concepts of electronics through visual representation of signals.
∗ Evaluating Filter Response: You can evaluate low-pass, high-pass, and band-pass filter responses.
∗ Oscillator Circuits: You can check for frequency stability and quality of a waveform.
∗ Testing Signal Generators: You can check output signals from function generators, along with distortion levels.
Frequently Asked Questions on Arduino Oscilloscope Projects
⇥ Q1: What is the maximum frequency an Arduino oscilloscope can measure?
An Arduino Nano oscilloscope can reliably measure signals up to 10-20 kHz. The maximum frequency is a function of the ADC conversion time and the sampling time. With very efficient code and set the ADC prescaler to fast the configuration, you can achieve a sample rate of about 76 kHz which allows decent viewing of signals about 10 kHz with depth considered due to the factors of Nyquist theorem obeyed for for fidelity representation of the signal intended for representation.
⇥ Q2: Can I measure AC mains voltage with an Arduino oscilloscope?
No. You should never connect AC mains voltage directly to the inputs of the Arduino oscilloscope. The Arduino Nano can only withstand 0-5V DC. If you would want to measure AC mains then you would need to use an isolated transformer online, isolating relays to a voltage divider with high voltage rated droppers. In summary you may only use this basic DIY oscilloscope design for a low voltage DC and AC signals. If you desire mains voltage then look toward a commercial oscilloscope with safety rating and features.
⇥ Q3: How does an Arduino-based oscilloscope accuracy compare to commercial models?
Arduino oscilloscopes are approximately 5-10% accurate on their voltage measurement, which is good enough for simple visualization of signals/fault finding. Commercial oscilloscopes will give you between 1-3% accurate, for a range of probes that would have been calibrated, with the manufacturer specifications of the ADC being superior. The Arduino Nano oscilloscope would be a great educational tool or a low-cost option for hobbyist projects. If you are seeking accurate readings, technical or precision, then buy commercial equipment.
⇥ Q4: Which OLED display for Arduino oscilloscope projects?
The 1.3-inch OLED with SSD1306 driver and I2C interface provides the best balance of size, resolution and refresh rate for Arduino oscilloscope OLED implementations.This display will have 128x64 pixel resolution, fast update if using I2C protocol, and low power consumption compared with other displays that may have similar pixel resolutions and sizes. Alternatively, there is the 0.96-inch OLEDs, but with a smaller viewable area. Avoid SPI displays, just because they are usually faster, but they require more Arduino pins.
⇥ Q5: What programming language knowledge is needed for Arduino oscilloscope programming?
The basic knowledge of programming Arduino will have you eventually making this oscilloscope with the help of the Arduino. Additionally, you will have to know how to read an analog input (analogRead), include libraries, and utilize basic loops. The code provided gives you an insight into what each section does with the help of comments. Advanced topics such as modifying the ADC prescaler and interrupt handling can also be utilized for performance enhancement but are not mandatory. Even inexperienced users can upload the code to their microcontroller using Arduino IDE by just going through the patient step-by-step instructions given.
⇥ Q6: Can Arduino Uno be used for oscilloscope projects instead of Arduino Nano?
Certainly! The Arduino Uno can very well serve as a basis for oscilloscope-related projects because it has the same ATmega328P chip as the Arduino Nano. However, the disparity between the two lies in the area where the Arduino Nano is better placed. That is, in the case of portable scope design, the footprint of the Arduino Nano is much smaller than that of the Arduino Uno, so the latter has to consider the double-checking of the pin assignments, especially for I2C, and maybe uploading the same code without any modifications.
⇥ Q7: What measures can I take to ensure voltage spikes do not damage my Arduino oscilloscope?
Voltage spikes pose a severe danger to your oscillation detection based on the Arduino, and so it is better to take precautionary measures. The very first step is to use 5.1V Zener diodes on the analog inputs for voltage clamping. Next, series-connect a 1kΩ resistor with the inputs for current limiting. You may also include TVS diodes for transient protection, check the voltage divider ratios beforehand if you are connecting unknown signals, and ensure that you do not apply more than 5V on any Arduino pin. It is also advisable to place a fuse on the power supply line which is a 'short-circuit' protective measure.
Conclusion
The comprehensive guide available hereunder illustrates the process of making a working oscilloscope using Arduino Nano and an OLED display for less than $20. This project merges practical electronics skills, programming knowledge of Arduino oscilloscopes, and signal processing concepts into one accessible and handy tool. This oscilloscope based on DIY Arduino, can be of different uses one who is a student learning basic electronics, a hobbyist who is making Arduino oscilloscope projects, or an engineer who is in need of a quick troubleshooting tool.
The adoption of the Arduino oscilloscope OLED makes it public that low-cost microcontroller platforms are the ones that let people access what used to be expensive test equipment. By simply using generic components, straightforward circuit designs, and thoroughly documented Arduino oscilloscope programming, anyone can create this tool.
The complete working of this project can be found in the video, linked at the bottom of this page. Further, this project can also be modified and improved to a BNC connector-based mini oscilloscope with battery-powered operations. If you have more ideas, drop them in the comment section and for any questions, you can use our forum.
Innovative Projects Using Oscilloscope
Discover unique and hands-on projects that utilise oscilloscopes for advanced circuit testing, signal analysis, and waveform visualisation. These projects help you understand real-time electronic behaviour and enhance your skills in measurement and diagnostics.
And the advanced oscilloscopes cost a few thousand dollars, which puts them beyond the reach of basic users. But what if we could create one that is cheaper, compact, and easy to make? That is the question that led to this DIY ESP32 oscilloscope project.
Arduino-Based Real-Time Oscilloscope
Today I will be demonstrating how to use the Arduino and a software, which will be developed with my favourite programming language, Python, to build a low-cost, 4-channel Arduino oscilloscope capable of performing the tasks for which some of the cheap oscilloscopes are deployed, like the display of waveforms and determination of voltage levels for signals.
Raspberry Pi-Based Oscilloscope
So Today, I will be sharing how to build a Raspberry Pi-based makeshift version of one of the most important tools in Electrical/Electronics engineering: The Oscilloscope.
Complete Project Code
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Copyright 2018 Peter Balch
// subject to the GNU General Public License
// displays samples on SH1106 screen as an oscilloscope
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
#include <Wire.h>
#include <limits.h>
#include "SimpleSH1106.h"
#include <math.h>
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Defines and Typedefs
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
// get register bit - faster: doesn't turn it into 0/1
#ifndef getBit
#define getBit(sfr, bit) (_SFR_BYTE(sfr) & _BV(bit))
#endif
enum Tmode {DC5V, AC500mV, AC100mV, AC20mV,
mLogic,
mVoltmeter,
maxMode1
};
const Tmode maxMode = maxMode1 - 1;
enum TmenuSel {sTime, sMode, sTrigger, sTestSig, sSigGen};
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Global Constants
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
bool bHasLogic = true;
bool bHasFreq = true;
bool bHasVoltmeter = true;
bool bHasTestSignal = true;
bool bHasSigGen = false;
const long BAUDRATE = 115200; // Baud rate of UART in bps
const int COMMANDDELAY = 10; // ms to wait for the filling of Serial buffer
const int COMBUFFERSIZE = 4; // Size of buffer for incoming numbers
const int testSignalPin = 3;
const char ack = '@'; // acknowledge for comms command
const byte SampPerA = 5 + 6; // 6 nops
#define LoopNops __asm__("nop\n nop\n nop\n nop\n nop\n nop\n")
const int SampPerB = 20;
const int BtnHorz = 4; // pushbutton
const int BtnVert = 7; // pushbutton
const int FreeRunTimeout = 0x10; // 0.5 sec for free run
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Global Variables
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
Tmode curMode = DC5V;
uint8_t curVref = 1;
uint8_t curPeriod = 200;
uint8_t curPrescaler = 7;
char commandBuffer[COMBUFFERSIZE + 1];
bool TrigFalling = true;
uint8_t curSweep = 0;
byte yGraticulePage0, yGraticuleByte0, yGraticulePage1, yGraticuleByte1, yGraticulePage2, yGraticuleByte2;
byte* pxGratLabel;
byte* pyGratLabel;
byte xGratLabelLen, yGratLabelLen;
byte yGraticule0, yGraticule1, yGraticule2, xGraticule1, xGraticule2;
TmenuSel sel = sTime; // for main menu
byte adj[4] = {0, 0, 0, 0}; // for main menu
bool SendingSerial = false;
int curPwmMode = 0;
const int ADCBUFFERSIZE = 128;
uint8_t ADCBuffer[ADCBUFFERSIZE];
int ButtonsTimer1 = 0;
long Vin = 0; // used to display Voltmeter
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
// globals used in SigGen
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
const byte numberOfDigits = 6; // number of digits in the frequency
byte freqSGLo[numberOfDigits] = {0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0}; // 1000Hz SelSG = 0..numberOfDigits-1
byte freqSGHi[numberOfDigits] = {0, 0, 0, 0, 2, 0}; // 20kHz SelSG = numberOfDigits..2*numberOfDigits-1
byte SelSG = numberOfDigits-1;
const byte SelSGSweep = 2*numberOfDigits;
const byte SelSGSine = 2*numberOfDigits+1;
const int wSine = 0b0000000000000000;
const int wTriangle = 0b0000000000000010;
const int wSquare = 0b0000000000101000;
enum TsweepType {swOff,sw20Frames,sw100Frames,sw500Frames,sw1Sec,sw5Sec,sw20Sec};
int waveType = wSine;
TsweepType sweepType = swOff;
const int SG_fsyncPin = 2;
const int SG_CLK = 13;
const int SG_DATA = 12;
int SG_iSweep,SG_nSweep;
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
// globals used in frequency counter
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
volatile boolean FC_OneSec;
volatile boolean FC_firstAC;
volatile unsigned long FC_overflowCount;
volatile unsigned long FC_MaxPeriodAC;
unsigned long FC_Timeout = 0;
unsigned long FC_freq;
const int ACfreqAdcPin = 3;
const int FC_LogicPeriod = 1006; // mS slightly longer than 1 Sec for calibration
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
// labels for graticule
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
const int R1 = 100;
const int R2 = 27;
const byte ax2V[] = {98, 81, 73, 70, 0, 3, 28, 96, 28, 3};
const byte ax4V[] = {24, 22, 127, 16, 0, 3, 28, 96, 28, 3};
const byte ax0_1[] = {62, 65, 65, 62, 0, 64, 0, 2, 127 };
const byte ax0_2[] = {62, 65, 65, 62, 0, 64, 0, 98, 81, 73, 70 };
const byte ax0_4[] = {62, 65, 65, 62, 0, 64, 0, 24, 22, 127, 16 };
const byte ax0_5[] = {62, 65, 65, 62, 0, 64, 0, 47, 69, 69, 57};
const byte ax1[] = {2, 127 };
const byte ax2[] = {98, 81, 73, 70 };
const byte ax4[] = {24, 22, 127, 16 };
const byte ax5[] = {47, 69, 69, 57};
const byte ax10[] = {2, 127, 0, 62, 65, 65, 62 };
const byte ax20[] = {98, 81, 73, 70, 0, 62, 65, 65, 62 };
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
// images for main menu
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
const byte imgMainMenuTop[] PROGMEM = {
128, // width
2, // pages
1, 224, 147, 32, 130, 0, 3, 248, 252, 6, 130, 2, 3, 6, 252, 248, 130, 0, 2, 96, 240, 130, 144, 2, 176, 32, 130, 0, 2, 224, 240, 130,
16, 3, 48, 32, 0, 130, 246, 130, 0, 130, 254, 130, 0, 130, 254, 130, 0, 2, 224, 240, 130, 16, 2, 240, 224, 130, 0, 2, 96, 240, 130,
144, 2, 176, 32, 130, 0, 2, 224, 240, 130, 16, 5, 48, 32, 0, 224, 240, 130, 16, 2, 240, 224, 130, 0, 130, 240, 130, 16, 2, 240, 224,
130, 0, 2, 224, 240, 130, 80, 2, 112, 96, 130, 0, 149, 32, 2, 224, 255, 149, 0, 3, 1, 3, 6, 130, 4, 3, 6, 3, 1, 130, 0, 2, 2, 6, 130,
4, 2, 7, 3, 130, 0, 2, 3, 7, 130, 4, 3, 6, 2, 0, 130, 7, 130, 0, 130, 7, 130, 0, 130, 7, 130, 0, 2, 3, 7, 130, 4, 2, 7, 3, 130, 0, 2, 2, 6,
130, 4, 2, 7, 3, 130, 0, 2, 3, 7, 130, 4, 5, 6, 2, 0, 3, 7, 130, 4, 2, 7, 3, 130, 0, 130, 63, 130, 4, 2, 7, 3, 130, 0, 2, 3, 7, 130, 4, 2,
6, 2, 151, 0, 1, 255
};
const byte imgMainMenuMid[] PROGMEM = {
128, // width
1, // pages
1, 255, 254, 0, 1, 255
};
const byte imgMainMenuBot[] PROGMEM = {
128, // width
1, // pages
1, 255, 254, 128, 1, 255
};
const byte imgBoxTop[] PROGMEM = {
128, // width
1, // pages
1, 248, 254, 8, 1, 248
};
const byte imgCaret1[] PROGMEM = {
4, // width
1, // pages
4, 255, 126, 60, 24
};
const byte imgCaret2[] PROGMEM = {
7, // width
1, // pages
7, 32, 48, 56, 60, 56, 48, 32
};
const byte imgTrian[] PROGMEM = {
14, // width
2, // pages
28, 3,12,48,192,0,0,0,0,0,0,192,48,12,3,128,128,128,128,131,140,176,176,140,131,128,128,128,128};
const byte imgSine[] PROGMEM = {
14, // width
2, // pages
28, 1,2,28,224,0,0,0,0,0,0,224,28,2,1,128,128,128,129,142,144,160,160,144,142,129,128,128,128};
const byte imgSquare[] PROGMEM = {
14, // width
2, // pages
28, 0,0,0,255,1,1,1,1,1,1,255,0,0,0,160,160,160,191,128,128,128,128,128,128,191,160,160,160};
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
// FillBar
// fills the bits of a screen column from bit y1 to bit y2
// makes a bar that must be part of 'page'
// returns the bar
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
byte FillBar(byte y1, byte y2, byte page) {
static byte lob[] = {0x00, 0x01, 0x03, 0x07, 0x0F, 0x1F, 0x3F, 0x7F, 0xFF};
byte bar;
if (page == y1 / 8) {
if (page == y2 / 8)
bar = lob[(y2 & 7) + 1];
else
bar = 0xFF;
return bar - lob[y1 & 7];
}
else if (page == y2 / 8)
return lob[(y2 & 7) + 1];
else if ((page > y1 / 8) & (page < y2 / 8))
return 0xFF;
else
return 0;
}
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
// drawBox
// draws a box around the screen with s written aat top-left
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
void drawBox(char* s) {
// clearSH1106();
DrawImageSH1106(0, 0, imgBoxTop);
for (int i = 1; i < 7; i++)
DrawImageSH1106(0, i, imgMainMenuMid);
DrawImageSH1106(0, 7, imgMainMenuBot);
DrawCharSH1106(' ', 6, 0, SmallFont);
DrawStringSH1106(s, 7, 0, SmallFont);
}
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
// drawScreen
// draws a graph like an oscilloscope
// takes about 40mS
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
void drawScreen(void) {
byte i, j, k, y, yPrev, bar, page, lastDrawn;
byte* pxbz;
byte* pybz;
byte pxlenz, pylenz;
switch (curMode) {
case mVoltmeter:
drawBox("Voltmeter");
i = 20;
if (Vin == LONG_MAX)
DrawStringSH1106("++++", i, 3, LargeDigitsFont);
else if (Vin == -LONG_MAX)
DrawStringSH1106("----", i, 3, LargeDigitsFont);
else {
i += DrawIntDP2(Vin / 10, i, 3, LargeDigitsFont);
DrawStringSH1106("Volts", i, 4, SmallFont);
}
return;
case AC100mV:
for ( i = 0; i < ADCBUFFERSIZE; i++ )
ADCBuffer[i] = ADCBuffer[i] / 4;
break;
default:
for ( i = 0; i < ADCBUFFERSIZE; i++ )
ADCBuffer[i] = 63 - ADCBuffer[i] / 4;
}
if ((curPeriod == 0) && (curMode <= AC20mV)) {
yPrev = ADCBuffer[0];
y = ADCBuffer[1];
for ( i = 1; i < ADCBUFFERSIZE - 1; i++ ) {
ADCBuffer[i] = (yPrev + y + ADCBuffer[i + 1]) / 3;
yPrev = y;
y = ADCBuffer[i + 1];
}
}
pxbz = pxGratLabel;
pxlenz = xGratLabelLen;
pybz = pyGratLabel;
pylenz = yGratLabelLen;
for (page = 0; page <= 7; page++) {
yPrev = ADCBuffer[0];
lastDrawn = 255;
setupPage(page);
setupCol(0);
Wire.beginTransmission(addr);
Wire.write(0x40); // the following bytes are data
for (i = 0; i < ADCBUFFERSIZE; i++) {
if (i % 26 == 0) {
Wire.endTransmission();
Wire.beginTransmission(addr);
Wire.write(0x40); // the following bytes are data
}
y = ADCBuffer[i];
if (yPrev > y + 1) {
if (yPrev == lastDrawn)
yPrev--;
bar = FillBar(y + 1, yPrev, page);
lastDrawn = yPrev + 1;
} else {
bar = FillBar(yPrev, yPrev, page);
lastDrawn = yPrev;
}
// }
if ((page == 0) && (bar == 0x01) && (i & 1))
bar = 0;
if ((page == 7) && (bar == 0x80) && (i & 1))
bar = 0;
if (page == yGraticulePage0) {
if (i & 8)
bar = bar | yGraticuleByte0;
}
else if (page == yGraticulePage1) {
if (i < pylenz)
{
bar |= *pybz;
pybz++;
}
else if (i % 4 == 0)
bar |= yGraticuleByte1;
}
else if (page == yGraticulePage2) {
if (i % 4 == 0)
bar |= yGraticuleByte2;
}
if ((i == xGraticule1) | (i == xGraticule2))
bar = bar | 0x22;
if ((page == 7) && (i > xGraticule2 - pxlenz - 2) && (i < xGraticule2 - 1)) {
bar |= *pxbz;
pxbz++;
}
Wire.write(bar);
yPrev = y;
}
Wire.endTransmission();
}
}
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
// initADC()
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
void initADC(void) {
if (curMode > AC20mV)
return;
ACSR = 0x10;
ADCSRA = 0x97;
ADCSRB = 0x0 ; //ADC Control and Status Register B
// 0 Bit 6 – ACME: Analog Comparator Multiplexer Enable
// 000 Bits 2:0 – ADTSn: ADC Auto Trigger Source [n = 2:0] Free Running mode
ADMUX = 0x20 + (curVref << 6) + curMode; // ADC Multiplexer Selection Register
// rr Bits 7:6 – REFSn: Reference Selection = Vcc
// 1 Bit 5 – ADLAR: ADC Left Adjust Result
// aaaa Bits 3:0 – MUXn: Analog Channel Selection
DIDR0 = 0x3F; // Digital Input Disable Register 0
// ADC0D=1, ADC1D=1, ADC2D=1, ADC3D=1, ADC4D=1, ADC5D=1, ADC6D=0, ADC7D=0
}
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
// printStatus
// print various register values
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
// setPwmFrequency
// timer mode=1 mode=2 mode=3 mode=4 mode=5 mode=6 mode=7
// pin=5 0 f=62500/1 f=62500/8 f=62500/64 f=62500/256 f=62500/1024
// pin=6 0 f=62500/1 f=62500/8 f=62500/64 f=62500/256 f=62500/1024
// pin=9 1 f=31250/1 f=31250/8 f=31250/64 f=31250/256 f=31250/1024
// pin=10 1 f=31250/1 f=31250/8 f=31250/64 f=31250/256 f=31250/1024
// pin=3 2 f=31250/1 f=31250/8 f=31250/32 f=31250/64 f=31250/128 f=31250/256 f=31250/1024
// pin=11 2 f=31250/1 f=31250/8 f=31250/32 f=31250/64 f=31250/128 f=31250/256 f=31250/1024
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
void setPwmFrequency(int pin, byte mode) {
SendAck();
curPwmMode = mode;
if (mode == 0) {
analogWrite(pin, 0);
} else {
analogWrite(pin, 128);
if (pin == 5 || pin == 6 || pin == 9 || pin == 10) {
if (pin == 5 || pin == 6) {
TCCR0B = TCCR0B & 0b11111000 | mode;
} else {
TCCR1B = TCCR1B & 0b11111000 | mode;
}
} else if (pin == 3 || pin == 11) {
TCCR2B = TCCR2B & 0b11111000 | mode;
}
}
}
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
// StartTimer1
// TIFR1 becomes non-zero after
// overflow*1024/16000000 sec
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
void StartTimer1(word overflow) {
TCCR1A = 0xC0; // Set OC1A on Compare Match
TCCR1B = 0x05; // prescaler = 1024
TCCR1C = 0x00; // no pwm output
OCR1AH = highByte(overflow);
OCR1AL = lowByte(overflow);
OCR1BH = 0;
OCR1BL = 0;
TIMSK1 = 0x00; // no interrupts
TCNT1H = 0; // must be written first
TCNT1L = 0; // clear the counter
TIFR1 = 0xFF; // clear all flags
}
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
// SendAck
// if sending serial then send @
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
void SendAck(void) {
if (SendingSerial)
Serial.print(ack);
}
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
// readVcc
// result in mV
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
long readVcc(void) {
long result;
ACSR = 0x10;
ADCSRA = 0x97;
ADCSRB = 0x0;
// Read 1.1V reference against AVcc
ADMUX = _BV(REFS0) | _BV(MUX3) | _BV(MUX2) | _BV(MUX1);
myDelay(2);
ADCSRA |= _BV(ADSC); // Convert
while (bit_is_set(ADCSRA, ADSC));
result = ADCL;
result |= ADCH << 8;
result = 1125300L / result; // Back-calculate AVcc in mV
initADC(); // to set up for next sweep
return result;
}
void GetADCSamples(void) {
uint8_t d;
uint8_t* p;
const int hysteresis = 2;
bool Trig;
Trig = TrigFalling ^ (curMode != AC100mV);
initADC();
ADCSRA = 0x80 + (curPrescaler & 7); // ADC Control and Status Register A
// 1 Bit 7 – ADEN: ADC Enable
// 0 Bit 6 – ADSC: ADC Start Conversion
// 0 Bit 5 – ADATE: ADC Auto Trigger Enable
// 0 Bit 4 – ADIF: ADC Interrupt Flag
// 0 Bit 3 – ADIE: ADC Interrupt Enable
// nnn Bits 2:0 – ADPSn: ADC Prescaler Select [n = 2:0]
StartTimer1(0); // no timeout
for (d = 0; d < 10; d++ ) { // make sure ADC is running
bitSet(ADCSRA, ADSC); // start ADC conversion
while (!getBit(ADCSRA, ADIF)) ; // wait for ADC
bitSet(ADCSRA, ADIF); // clear the flag
}
if (curPeriod == 0) { // 1Msps
while (Trig ? (ADCH >= 0x80 - hysteresis) : (ADCH < 0x80 + hysteresis)) {
d = TCNT1L; // to force read of TCNT1H
if (TCNT1H > FreeRunTimeout) goto freeRunFast;
bitSet(ADCSRA, ADSC);
}
while (Trig ? (ADCH < 0x80 + hysteresis) : (ADCH >= 0x80 - hysteresis)) {
d = TCNT1L; // to force read of TCNT1H
if (TCNT1H > FreeRunTimeout) goto freeRunFast;
bitSet(ADCSRA, ADSC);
}
freeRunFast:
for (p = ADCBuffer; p < ADCBuffer + ADCBUFFERSIZE; p++ ) {
*p = ADCH;
__asm__("nop"); // pad it to 16 instructions
__asm__("nop"); // pad it to 16 instructions
bitSet(ADCSRA, ADSC);
}
} else { // slower than 1Msps
do { // wait for comparator low
bitSet(ADCSRA, ADSC); // start ADC conversion
for (d = 0; d < curPeriod; d++ )
LoopNops;
d = TCNT1L; // to force read of TCNT1H
if (TCNT1H > FreeRunTimeout) goto freeRunSlow;
} while (Trig ? (ADCH >= 0x80 - hysteresis) : (ADCH < 0x80 + hysteresis));
do { // wait for comparator high
bitSet(ADCSRA, ADSC); // start ADC conversion
for (d = 0; d < curPeriod; d++ )
LoopNops;
d = TCNT1L; // to force read of TCNT1H
if (TCNT1H > FreeRunTimeout) goto freeRunSlow;
} while (Trig ? (ADCH < 0x80 + hysteresis) : (ADCH >= 0x80 - hysteresis));
freeRunSlow:
bitSet(ADCSRA, ADSC); // start ADC conversion
for ( p = ADCBuffer; p < ADCBuffer + ADCBUFFERSIZE; p++ ) {
for (d = 0; d < curPeriod; d++ )
LoopNops;
*p = ADCH;
bitSet(ADCSRA, ADSC); // start ADC conversion
}
}
}
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
// SendADC
// uses curPrescaler,curPeriod,curMode,curVref
//
// read and Tx a buffer-full of samples
// prescaler
// 7 128
// 6 64
// 5 32
// 4 16
// 3 8
// 2 4
// 1 2
// 0 2
// period: sample period
// 0: 16 clocks
// n: n*SampPerA+SampPerB clocks
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
void SendADC() {
memset( (void *)ADCBuffer, 0, sizeof(ADCBuffer) );
noInterrupts();
// if (curMode == mLogic)
// GetLogicSamples();
// else
GetADCSamples();
interrupts();
digitalWrite(LED_BUILTIN, HIGH);
if (SendingSerial) {
Serial.write((uint8_t)0xAA);
Serial.write((uint8_t)0xBB);
Serial.write((uint8_t)0xCC);
Serial.write((uint8_t *)ADCBuffer, ADCBUFFERSIZE);
}
drawScreen();
digitalWrite(LED_BUILTIN, LOW);
int t = TCNT1L; // to force read of TCNT1H
ButtonsTimer1 += TCNT1H;
}
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
// setSweep
// set period and ADC prescaler
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
void setSweep(byte Sweep) {
int x;
long t;
if (Sweep == 255) {
if (curSweep == 0)
curSweep = 6;
else
curSweep--;
} else
curSweep = Sweep;
switch (curSweep) {
case 0: curPeriod = 0; curPrescaler = 2; t = 100; pxGratLabel = &ax0_1[0]; xGratLabelLen = sizeof(ax0_1); break;
case 1: curPeriod = 4; curPrescaler = 2; t = 400; pxGratLabel = &ax0_4[0]; xGratLabelLen = sizeof(ax0_4); break;
case 2: curPeriod = 11; curPrescaler = 3; t = 1000; pxGratLabel = &ax1[0]; xGratLabelLen = sizeof(ax1); break;
case 3: curPeriod = 24; curPrescaler = 3; t = 2000; pxGratLabel = &ax2[0]; xGratLabelLen = sizeof(ax2); break;
case 4: curPeriod = 62; curPrescaler = 4; t = 5000; pxGratLabel = &ax5[0]; xGratLabelLen = sizeof(ax5); break;
case 5: curPeriod = 125; curPrescaler = 4; t = 10000; pxGratLabel = &ax10[0]; xGratLabelLen = sizeof(ax10); break;
case 6: curPeriod = 255; curPrescaler = 5; t = 20000; pxGratLabel = &ax20[0]; xGratLabelLen = sizeof(ax20); break;
}
if (curSweep == 0)
x = t;
else
x = 16 * t / (curPeriod * SampPerA + SampPerB);
xGraticule1 = x / 2;
xGraticule2 = x;
SendAck();
}
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
// incMode
// increment Mode
// wrap around from max
// skip over modes that are not allowed
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
int incMode(int mode) {
mode++;
//if ((mode == mLogic) && (!bHasLogic)) mode++;
// if ((mode == mFreqLogic) && ((!bHasFreq) || (!bHasLogic))) mode++;
// if ((mode == mFreqAC) && (!bHasFreq)) mode++;
if ((mode == mVoltmeter) && (!bHasVoltmeter)) mode++;
if (mode > maxMode)
return DC5V;
else
return mode;
}
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
// setMode
// set mode and Vref
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
void setMode(int mode) {
int i;
if (mode == 255) {
curMode = incMode(curMode);
} else
curMode = mode;
switch (curMode) {
case DC5V:
curVref = 1;
i = (long)4000 * 64 / readVcc();
if (i <= 63) {
yGraticule1 = 63 - i;
yGraticule2 = 63 - i / 2;
yGraticule0 = 255;
pyGratLabel = &ax4V[0];
yGratLabelLen = sizeof(ax4V);
} else {
yGraticule2 = 63 - i;
yGraticule1 = 63 - i / 2;
yGraticule0 = 255;
pyGratLabel = &ax2V[0];
yGratLabelLen = sizeof(ax2V);
}
break;
case AC500mV:
curVref = 3;
i = (byte)(0.5 / 1.1 * 256 / 4);
yGraticule1 = 32 - i;
yGraticule2 = 32 + i;
yGraticule0 = 32;
pyGratLabel = &ax0_5[0];
yGratLabelLen = sizeof(ax0_5);
break;
case AC100mV:
curVref = 3;
i = (byte)(0.1 / 1.1 * (R1 + R2) / R2 * 256 / 4);
yGraticule1 = 32 - i;
yGraticule2 = 32 + i;
yGraticule0 = 32;
pyGratLabel = &ax0_1[0];
yGratLabelLen = sizeof(ax0_1);
break;
case AC20mV:
curVref = 3;
i = (byte)(0.02 / 1.1 * (R1 + R2) / R2 * (R1 + R2) / R2 * 256 / 4);
yGraticule1 = 32 - i;
yGraticule2 = 32 + i;
yGraticule0 = 32;
pyGratLabel = &ax20[0];
yGratLabelLen = sizeof(ax20);
break;
default:
curVref = 1;
yGraticule1 = 255;
yGraticule2 = 255;
yGraticule0 = 255;
pyGratLabel = &ax20[0];
yGratLabelLen = sizeof(ax20);
break;
}
switch (curMode) {
case mVoltmeter:
Vin = 0;
drawScreen();
break;
default: FC_disable();
}
yGraticulePage0 = yGraticule0 / 8;
yGraticuleByte0 = 1 << (yGraticule0 % 8);
yGraticulePage1 = yGraticule1 / 8;
yGraticuleByte1 = 1 << (yGraticule1 % 8);
yGraticulePage2 = yGraticule2 / 8;
yGraticuleByte2 = 1 << (yGraticule2 % 8);
SendAck();
}
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
// drawMainMenu
// draw the main menu for values of sel and adj
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
void drawMainMenu(void) {
int ofs, x, yVcc, pg;
switch (sel) {
case sMode: ofs = -1; break;
case sTrigger: ofs = -2; break;
case sTestSig: ofs = -5; break;
case sSigGen: ofs = bHasTestSignal ? -7 : -5; break;
default: ofs = 0;
}
// DrawImageSH1106(0,ofs,imgMainMenu);
DrawImageSH1106(0, ofs + 0, imgMainMenuTop);
for (x = 2; x < 14; x++)
DrawImageSH1106(0, ofs + x, imgMainMenuMid);
DrawImageSH1106(0, ofs + 10 + bHasTestSignal * 2 + bHasSigGen * 2, imgMainMenuBot);
DrawImageSH1106(6, 3 + sel * 2 + ofs, imgCaret1);
BoldSH1106 = true;
pg = 3 + ofs;
DrawStringSH1106("Time:", 12, pg, SmallFont); pg += 2;
DrawStringSH1106((adj[1] <= AC20mV ? "Gain:" : "Mode:"), 12, pg, SmallFont); pg += 2;
DrawStringSH1106("Trigger:", 12, pg, SmallFont); pg += 2;
if (bHasTestSignal) {
DrawStringSH1106("Test sig:", 12, pg, SmallFont); pg += 2;
if (bHasSigGen) {
DrawStringSH1106("Signal Generator", 12, pg, SmallFont); pg += 2;
}
DrawStringSH1106("Vcc:", 12, pg, SmallFont); yVcc = pg; pg += 2;
} else {
if (bHasSigGen) {
DrawStringSH1106("Vcc:", 12, pg, SmallFont); yVcc = pg; pg += 2;
DrawStringSH1106("Signal Generator", 12, pg, SmallFont); pg += 2;
} else {
DrawStringSH1106("Vcc:", 12, pg, SmallFont); yVcc = pg; pg += 2;
}
}
BoldSH1106 = false;
x = 62;
pg = 3 + ofs;
switch (adj[0]) {
case 0: DrawStringSH1106("1mS", x, pg, SmallFont); break;
case 1: DrawStringSH1106("2mS", x, pg, SmallFont); break;
case 2: DrawStringSH1106("5mS", x, pg, SmallFont); break;
case 3: DrawStringSH1106("10mS", x, pg, SmallFont); break;
case 4: DrawStringSH1106("20mS", x, pg, SmallFont); break;
case 5: DrawStringSH1106("50mS", x, pg, SmallFont); break;
case 6: DrawStringSH1106("100mS", x, pg, SmallFont); break;
}
pg += 2;
switch (adj[1]) {
case DC5V: DrawStringSH1106("5V DC", x, pg, SmallFont); break;
case AC500mV: DrawStringSH1106("0.5V AC", x, pg, SmallFont); break;
case AC100mV: DrawStringSH1106("0.1V AC", x, pg, SmallFont); break;
case AC20mV: DrawStringSH1106("20mV AC", x, pg, SmallFont); break;
//case mLogic: DrawStringSH1106("Logic", x, pg, SmallFont); break;
//case mFreqLogic: DrawStringSH1106("Freq Logic", x, pg, SmallFont); break;
//case mFreqAC: DrawStringSH1106("Freq AC", x, pg, SmallFont); break;
case mVoltmeter: DrawStringSH1106("Voltmeter", x, pg, SmallFont); break;
}
pg += 2;
switch (adj[2]) {
case 1: DrawStringSH1106("Fall", x, pg, SmallFont); break;
default: DrawStringSH1106("Rise", x, pg, SmallFont);
}
pg += 2;
if (bHasTestSignal) {
switch (adj[3]) {
case 1: DrawStringSH1106("31250Hz 32uS", x, pg, SmallFont); break;
case 2: DrawStringSH1106("3906Hz 256uS", x, pg, SmallFont); break;
case 3: DrawStringSH1106("977Hz 1024uS", x, pg, SmallFont); break;
case 4: DrawStringSH1106("488Hz 2048uS", x, pg, SmallFont); break;
case 5: DrawStringSH1106("244Hz 4096uS", x, pg, SmallFont); break;
case 6: DrawStringSH1106("122Hz 8192uS", x, pg, SmallFont); break;
case 7: DrawStringSH1106("31Hz 32768uS", x, pg, SmallFont); break;
default: DrawStringSH1106("Off", x, pg, SmallFont);
}
pg += 2;
}
if (bHasSigGen)
pg += 2;
if (yVcc <= 7) {
x += DrawIntDP2(readVcc() / 10, x, yVcc, SmallFont);
DrawCharSH1106('V', x, yVcc, SmallFont);
}
}
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
// incAdj
// increment the value of adj
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
void incAdj(void) {
if (sel == sSigGen)
return;
if (sel == sMode) {
adj[1] = incMode(adj[1]);
} else {
adj[sel]++;
if (adj[0] > 6) adj[0] = 0;
if (adj[2] > 1) adj[2] = 0;
if (adj[3] > 7) adj[3] = 0;
}
drawMainMenu;
}
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
// incSel
// increment the value of sel
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
void incSel(void) {
if (bHasTestSignal) {
if (bHasSigGen) {
if (sel == sSigGen)
sel = sTime - 1;
} else {
if (sel == sTestSig)
sel = sTime - 1;
}
} else {
if (bHasSigGen) {
if (sel == sSigGen)
sel = sTime - 1;
if (sel == sTrigger)
sel = sSigGen - 1;
} else {
if (sel == sTrigger)
sel = sTime - 1;
}
}
sel = sel + 1;
drawMainMenu;
}
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
// DrawIntDP2
// draws the int 1234 with format 12.34
// at x,page
// returns width drawn
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
int DrawIntDP2(int i, byte x, byte page, word Font) {
int start;
start = x;
if (i < 0) {
i = -i;
x += DrawCharSH1106('-', x, page, Font);
}
x += DrawIntSH1106(i / 100, x, page, Font);
x += DrawCharSH1106('.', x, page, Font);
x += DrawIntSH1106((i / 10) % 10, x, page, Font);
x += DrawIntSH1106(i % 10, x, page, Font);
return x - start;
}
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
// drawSigGenMenu
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
void drawSigGenMenu(void) {
byte x,y,i;
drawBox("Signal Generator");
if (sweepType == swOff) {
x = 20;
y = 3;
for (i = numberOfDigits - 1; i < numberOfDigits; i--) {
if (i == SelSG)
DrawImageSH1106(x+2, y+2, imgCaret2);
x += DrawIntSH1106(freqSGLo[i], x, y, LargeDigitsFont);
}
} else {
x = 60;
y = 2;
DrawStringSH1106("Max Freq:", 12, y, SmallFont);
for (i = numberOfDigits - 1; i < numberOfDigits; i--) {
if (i == SelSG-numberOfDigits)
DrawImageSH1106(x-2, y+1, imgCaret2);
x += DrawIntSH1106(freqSGHi[i], x, y, SmallFont);
}
DrawStringSH1106(" Hz", x, y, SmallFont);
x = 60;
y = 4;
DrawStringSH1106("Min Freq:", 12, y, SmallFont);
for (i = numberOfDigits - 1; i < numberOfDigits; i--) {
if (i == SelSG)
DrawImageSH1106(x-2, y+1, imgCaret2);
x += DrawIntSH1106(freqSGLo[i], x, y, SmallFont);
}
DrawStringSH1106(" Hz", x, y, SmallFont);
}
x = 12;
y = 6;
if (SelSG == SelSGSine)
DrawImageSH1106(x-6, y, imgCaret1);
// switch (waveType) {
// case wSine: DrawStringSH1106("Sine", x, y, SmallFont); break;
// case wTriangle: DrawStringSH1106("Triangle", x, y, SmallFont); break;
// case wSquare: DrawStringSH1106("Square", x, y, SmallFont); break;
// }
for (x=12;x<40;x+=14)
switch (waveType) {
case wSine: DrawImageSH1106(x, y, imgSine); break;
case wTriangle: DrawImageSH1106(x, y, imgTrian); break;
case wSquare: DrawImageSH1106(x, y, imgSquare); break;
}
x = 54;
y = 6;
switch (sweepType) {
case swOff: DrawStringSH1106("Constant", x, y, SmallFont); break;
case sw1Sec: DrawStringSH1106("Sweep 1 Sec", x, y, SmallFont); break;
case sw5Sec: DrawStringSH1106("Sweep 5 Sec", x, y, SmallFont); break;
case sw20Sec: DrawStringSH1106("Sweep 20 Sec", x, y, SmallFont); break;
case sw20Frames: DrawStringSH1106("Swp 20 frames", x, y, SmallFont); break;
case sw100Frames: DrawStringSH1106("Swp 100 frames", x, y, SmallFont); break;
case sw500Frames: DrawStringSH1106("Swp 500 frames", x, y, SmallFont); break;
}
if (SelSG == SelSGSweep)
DrawImageSH1106(x-6, y, imgCaret1);
}
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
//returns 10^y
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
unsigned long Power(int y) {
unsigned long t = 1;
for (byte i = 0; i < y; i++)
t = t * 10;
return t;
}
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
//calculate the frequency from the array.
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
unsigned long calcFreq(byte* freqSG) {
unsigned long i = 0;
for (byte x = 0; x < numberOfDigits; x++)
i = i + freqSG[x] * Power(x);
return i;
}
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
// SG_WriteRegister
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
void SG_WriteRegister(word dat) {
digitalWrite(SG_CLK, LOW);
digitalWrite(SG_CLK, HIGH);
digitalWrite(SG_fsyncPin, LOW);
for (byte i = 0; i < 16; i++) {
if (dat & 0x8000)
digitalWrite(SG_DATA, HIGH);
else
digitalWrite(SG_DATA, LOW);
dat = dat << 1;
digitalWrite(SG_CLK, HIGH);
digitalWrite(SG_CLK, LOW);
}
digitalWrite(SG_CLK, HIGH);
digitalWrite(SG_fsyncPin, HIGH);
}
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
// SG_Reset
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
void SG_Reset() {
delay(100);
SG_WriteRegister(0x100);
delay(100);
}
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
// SG_freqReset
// reset the SG regs then set the frequency and wave type
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
void SG_freqReset(long frequency, int wave) {
long fl = frequency * (0x10000000 / 25000000.0);
SG_WriteRegister(0x2100);
SG_WriteRegister((int)(fl & 0x3FFF) | 0x4000);
SG_WriteRegister((int)((fl & 0xFFFC000) >> 14) | 0x4000);
SG_WriteRegister(0xC000);
SG_WriteRegister(wave);
waveType = wave;
}
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
// SG_freqSet
// set the SG frequency regs
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
void SG_freqSet(long frequency, int wave) {
long fl = frequency * (0x10000000 / 25000000.0);
SG_WriteRegister(0x2000 | wave);
SG_WriteRegister((int)(fl & 0x3FFF) | 0x4000);
SG_WriteRegister((int)((fl & 0xFFFC000) >> 14) | 0x4000);
}
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
// SG_StepSweep
// increment the FG frequency
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
void SG_StepSweep(void) {
if (SG_iSweep > SG_nSweep) SG_iSweep = 0;
long f = exp((log(calcFreq(freqSGHi)) - log(calcFreq(freqSGLo)))*SG_iSweep/SG_nSweep + log(calcFreq(freqSGLo))) +0.5;
SG_freqSet(f, waveType);
SG_iSweep++;
}
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Sweep
// sweeps siggen freq continuously
// takes n mS for whole sweep
// SDC regs are saved and restored
// stops when receives a serial char
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
void Sweep(int n) {
byte oldACSR = ACSR;
byte oldADCSRA = ADCSRA;
byte oldADCSRB = ADCSRB;
byte oldADMUX = ADMUX;
byte oldDIDR0 = DIDR0;
byte oldDIDR1 = DIDR1;
int fmin,fmax;
fmin = calcFreq(freqSGLo);
fmax = calcFreq(freqSGHi);
int i=0;
do {
long f = exp((log(fmax) - log(fmin))*i/(n-1) + log(fmin)) +0.5;
SG_freqSet(f, waveType);
delay(1);
i++;
if (i >= n) i = 0;
} while (!Serial.available());
SG_freqSet(calcFreq(freqSGLo), waveType);
ACSR = oldACSR;
ADCSRA = oldADCSRA;
ADCSRB = oldADCSRB;
ADMUX = oldADMUX;
DIDR0 = oldDIDR0;
DIDR1 = oldDIDR1;
}
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
// incSelSG
// increment digit for SigGen Menu
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
void incSelSG(void) {
if (SelSG == SelSGSine) {
switch (waveType) {
case wSine: waveType = wTriangle; break;
case wTriangle: waveType = wSquare; break;
case wSquare: waveType = wSine; break;
}
} else
if (SelSG == SelSGSweep) {
if (sweepType == sw20Sec)
sweepType = swOff;
else
sweepType = sweepType+1;
} else
if (SelSG < numberOfDigits) {
if (freqSGLo[SelSG] >= 9)
freqSGLo[SelSG] = 0;
else
freqSGLo[SelSG]++;
} else
if (sweepType != swOff) {
if (freqSGHi[SelSG-numberOfDigits] >= 9)
freqSGHi[SelSG-numberOfDigits] = 0;
else
freqSGHi[SelSG-numberOfDigits]++;
}
drawSigGenMenu();
}
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
// incAdjSG
// increment caret position for SigGen Menu
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
void incAdjSG(void) {
if (SelSG == 0)
SelSG = SelSGSine;
else
SelSG--;
if ((SelSG >= numberOfDigits) && (SelSG < 2*numberOfDigits) && (sweepType == swOff))
SelSG = numberOfDigits-1;
drawSigGenMenu();
}
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
// ExecSigGenMenu
// SigGen menu
// user presses sel or Adj buttons
// return if no button for 2 sec
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
void ExecSigGenMenu(void) {
static int prevHorz = 0;
static int prevVert = 0;
int i;
const byte timeout = 0xC0; // 3 sec to exit
FC_disable();
drawSigGenMenu();
while ((digitalRead(BtnHorz) == LOW) || (digitalRead(BtnVert) == LOW))
; // wait until buttons off
StartTimer1(0);
SG_iSweep = 0;
do {
i = digitalRead(BtnVert);
if (i != prevVert) {
prevVert = i;
if (i == LOW) {
incSelSG();
drawSigGenMenu();
SG_freqReset(calcFreq(freqSGLo), waveType);
}
myDelay(100);
StartTimer1(0);
}
i = digitalRead(BtnHorz);
if (i != prevHorz) {
prevHorz = i;
if (i == LOW) {
incAdjSG();
drawSigGenMenu();
}
myDelay(100);
StartTimer1(0);
}
if (sweepType != swOff) {
switch (sweepType) {
case sw1Sec: SG_nSweep = (long) 1000*65/100; break;
case sw5Sec: SG_nSweep = (long) 5000*65/100; break;
case sw20Sec: SG_nSweep = (long)20000*65/100; break;
case sw20Frames: SG_nSweep = 20; break;
case sw100Frames: SG_nSweep = 100; break;
case sw500Frames: SG_nSweep = 500; break;
}
SG_StepSweep();
}
i = TCNT1L; // to force read of TCNT1H
} while ((TCNT1H < timeout) || (sweepType >= sw1Sec));
}
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
// ExecMenu
// show main menu
// user presses sel or Adj buttons
// return if no button for 2 sec
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
void ExecMenu(void) {
static int prevHorz = 0;
static int prevVert = 0;
int i;
const byte timeout = 0x80; // 2 sec to exit
adj[0] = curSweep;
adj[1] = curMode;
adj[2] = TrigFalling;
adj[3] = curPwmMode;
FC_disable();
drawMainMenu();
while ((digitalRead(BtnHorz) == LOW) || (digitalRead(BtnVert) == LOW))
; // wait until buttons off
StartTimer1(0);
do {
i = digitalRead(BtnVert);
if (i != prevVert) {
prevVert = i;
if (i == LOW) {
incSel();
drawMainMenu();
}
myDelay(100);
StartTimer1(0);
}
i = digitalRead(BtnHorz);
if (i != prevHorz) {
prevHorz = i;
if (i == LOW) {
if (sel == sSigGen)
break;
incAdj();
if (sel == sTestSig)
setPwmFrequency(testSignalPin, adj[3]);
drawMainMenu();
}
myDelay(100);
StartTimer1(0);
}
i = TCNT1L; // to force read of TCNT1H
} while (TCNT1H < timeout);
if (sel == sSigGen) {
sel = sTime;
ExecSigGenMenu();
}
setSweep(adj[0]);
setMode(adj[1]);
TrigFalling = adj[2] != 0;
clearSH1106();
}
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
// CheckButtons
// if BtnVert button pressed, change gain
// if BtnHorz button pressed, change sweep
// if button held for 2 sec, show menu
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
void CheckButtons(void) {
const byte timeout = 70; // 1 sec to show menu
static int prevHorz = HIGH;
static int prevVert = HIGH;
int i;
if (digitalRead(BtnHorz) == LOW) {
if (prevHorz == HIGH) {
switch (curMode) {
//case mFreqLogic:
// case mFreqAC:
case mVoltmeter:
ExecMenu();
return;
}
ButtonsTimer1 = 0;
myDelay(15);
setSweep(255);
prevHorz = LOW;
} else {
if (ButtonsTimer1 > timeout) {
ExecMenu();
return;
}
}
} else {
prevHorz = HIGH;
}
if (digitalRead(BtnVert) == LOW) {
if (prevVert == HIGH) {
ButtonsTimer1 = 0;
myDelay(15);
setMode(255);
prevVert = LOW;
} else {
if (ButtonsTimer1 > timeout) {
ExecMenu();
return;
}
}
} else {
prevVert = HIGH;
}
}
//=========================================================================
// Timer1 overflows every 65536 counts
// used in freq meter
//=========================================================================
ISR (TIMER1_OVF_vect)
{
FC_overflowCount++;
}
//=========================================================================
// Timer1 Capture interrupt
// invoked by comparator
// read the current timer1 capture value
// used in freq meter
//=========================================================================
ISR (TIMER1_CAPT_vect) {
// grab counter value before it changes any more
unsigned int timer1CounterValue = ICR1; // see datasheet, page 117 (accessing 16-bit registers)
unsigned long overflowCopy = FC_overflowCount;
unsigned long t;
static unsigned long prevT;
// if just missed an overflow
if ((TIFR1 & bit(TOV1)) && timer1CounterValue < 0x7FFF)
overflowCopy++;
t = (overflowCopy << 16) + timer1CounterValue;
if ((!FC_firstAC) && (t-prevT > 100) && (t-prevT > FC_MaxPeriodAC))
FC_MaxPeriodAC = t-prevT;
prevT = t;
FC_firstAC = false;
}
//=========================================================================
// Timer0 Interrupt Service is invoked by hardware Timer0 every 1ms = 1000 Hz
// used by frequancy counter
// called every 1mS
//=========================================================================
ISR(TIMER0_COMPA_vect) {
if (FC_Timeout >= FC_LogicPeriod) { // end of gate time, measurement ready
TCCR1B &= ~7; // Gate Off / Counter T1 stopped
bitClear(TIMSK0, OCIE0A); // disable Timer0 Interrupt
FC_OneSec = true; // set global flag for end count period
// calculate now frequeny value
FC_freq = 0x10000 * FC_overflowCount; // mult #overflows by 65636
FC_freq += TCNT1; // add counter1 value
}
FC_Timeout++; // count number of interrupt events
if (TIFR1 & 1) { // if Timer/Counter 1 overflow flag
FC_overflowCount++; // count number of Counter1 overflows
bitSet(TIFR1, TOV1); // clear Timer/Counter 1 overflow flag
}
}
//=========================================================================
// FC_InitLogic
// count number of rising edges at D5 over mS period
//=========================================================================
void FC_InitLogic() {
noInterrupts ();
TIMSK0 = 0x00;
delayMicroseconds(50); // wait if any ints are pending
FC_OneSec = false; // reset period measure flag
FC_Timeout = 0; // reset interrupt counter
TCCR1A = 0x00; // timer output off
TCCR1B = 0x07; // External clock source on T1 pin. Clock on rising edge.
TCNT1 = 0x00; // counter = 0
TCCR0A = 0x02; // compare output off; max count = OCRA
TCCR0B = 0x03; // input clk is 16M/64
TCNT0 = 0x16; // counter = 0 - why is this not 0? cos of set-up time?
TIMSK0 = 0x00;
OCR0A = 248; // max count value = CTC divider by 250 = 1mS
GTCCR = 0x02; // reset prescaler
FC_overflowCount = 0;
bitSet(TIMSK0, OCIE0A); // enable Timer0 Interrupt
interrupts ();
}
//=========================================================================
// FC_InitAC
// ACfreqAdcPin = 0..5 - use that ADC mux and measure period with Timer1
//=========================================================================
void FC_InitAC() {
noInterrupts ();
FC_disable();
TCCR1A = 0; // reset Timer 1
TCCR1B = bit(CS10) | bit(ICES1); // no prescaler, Input Capture Edge Select
TIFR1 = bit(ICF1) | bit(TOV1); // clear flags so we don't get a bogus interrupt
TCNT1 = 0; // Timer1 to zero
FC_overflowCount = 0; // for Timer1 overflows
TIMSK1 = bit(TOIE1) | bit(ICIE1); // interrupt on Timer 1 overflow and input capture
ADCSRA = 0;
DIDR1 = 1; // digital input of D6 is off
ADMUX = ACfreqAdcPin;
ACSR = bit(ACI) | bit(ACIC) | (B10 << ACIS0); // "clear" interrupt flag; timer capture from comparator; falling edge
ADCSRB = bit(ACME); // Comparator connected to ADC mux
FC_firstAC = true;
FC_Timeout = 0;
FC_MaxPeriodAC = 0;
interrupts ();
}
//=========================================================================
// FC_disable
// turn off freq counter interrupts
//=========================================================================
void FC_disable() {
TCCR0A = 0x03; // no compare output; Fast PWM up to 0xFF
TCCR0B = 0x03; // no Output Compare; prescaler = 16MHz/64; overflow approx every 1mS
TIMSK0 = 0x00; // Interrupt Mask Register = none
GTCCR = 0x00; // Control Register = none
OCR0A = 0x00; // Output Compare Register A = none
OCR0B = 0x00; // Output Compare Register B = none
TCCR1A = 0xC0;
TCCR1B = 0x05;
TCCR1C = 0x00;
TIMSK1 = 0x00;
}
//=========================================================================
// FC_OneSecPassed
// has 1 second passed?
//=========================================================================
bool FC_OneSecPassed() {
static byte prevTimer1 = 0;
byte i;
static unsigned long t = 0;
if (bitRead(TIFR0, TOV0)) // overflow every 1mS
FC_Timeout++;
bitSet(TIFR0, TOV0);
return FC_Timeout > 1000;
}
//=========================================================================
// FC_CheckLogic
// frequency measurer
// call repeatedly
// returns true when has timed out
// result in FC_freq
//=========================================================================
bool FC_CheckLogic() {
return FC_OneSec;
}
//=========================================================================
// FC_CheckAC
// frequency measurer
// call repeatedly
// returns true when has timed out
// result in FC_freq
//=========================================================================
bool FC_CheckAC() {
unsigned long FC_elapsedTime;
if (FC_OneSecPassed()) {
if (FC_MaxPeriodAC > 0)
FC_freq = 100 * F_CPU*1.004 / FC_MaxPeriodAC; // mult by 100 so can display 2 d.p.
else
FC_freq = 0;
FC_InitAC();
return true;
}
return false;
}
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
// myDelay
// delays for approx mS milliSeconds
// doesn't use any timers
// doesn't affect interrupts
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
void myDelay(int mS) {
for (int j = 0; j < mS; j++)
delayMicroseconds(1000);
}
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
// MeasureVoltmeter
// measures Voltmeter at Vin in mV
// assumes resistors have been connected to pin:
// Ra from pin to 5V
// Rb from pin to 0V
// Rc from pin to Vin
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
long MeasureVoltmeter(int pin) {
const long Ra = 120; // from pin to 5V
const long Rb = 150; // from pin to 0V
const long Rc = 470; // from pin to Vin
const int calibrateZero = +20; // Calibrate so 0V = "0V"
const int calibrateVolts = 1024; // Calibrate so 10V = "10V"
long Aa, Vb;
byte oldACSR = ACSR;
byte oldADCSRA = ADCSRA;
byte oldADCSRB = ADCSRB;
byte oldADMUX = ADMUX;
byte oldDIDR0 = DIDR0;
byte oldDIDR1 = DIDR1;
Vb = readVcc();
Aa = analogRead(pin); // set up the ADC
myDelay(1); // high input impedance so allow to settle
Aa = analogRead(pin); // read ADC
ACSR = oldACSR;
ADCSRA = oldADCSRA;
ADCSRB = oldADCSRB;
ADMUX = oldADMUX;
DIDR0 = oldDIDR0;
DIDR1 = oldDIDR1;
if (Aa > 1023 - 10)
return LONG_MAX;
if (Aa < 10)
return -LONG_MAX;
return (Aa * Vb - Rc * ((Vb * 1024 - Aa * Vb) / Ra - Aa * Vb / Rb)) / calibrateVolts + calibrateZero;
}
//=========================================================================
// CheckVoltmeter
// Voltmeter measurer
//=========================================================================
bool CheckVoltmeter() {
const byte n = 50;
static byte i = 0;
static long sum = 0;
long v;
myDelay(5);
v = MeasureVoltmeter(6);
i++;
if ((v | sum) & 0x40000000) {
sum = v;
Vin = v;
} else {
sum += v;
Vin = sum / i;
}
if (i >= n) {
sum = 0;
i = 0;
return true;
}
return false;
}
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
// InitSigGen
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
void InitSigGen(void) {
pinMode(SG_DATA, OUTPUT);
pinMode(SG_CLK, OUTPUT);
pinMode(SG_fsyncPin, OUTPUT);
digitalWrite(SG_fsyncPin, HIGH);
digitalWrite(SG_CLK, HIGH);
SG_Reset();
SG_freqReset(calcFreq(freqSGLo), waveType);
}
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Main routines
// The setup function
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
void setup (void) {
// Open serial port with a baud rate of BAUDRATE b/s
Serial.begin(BAUDRATE);
// Clear buffers
memset( (void *)commandBuffer, 0, sizeof(commandBuffer) );
// Activate interrupts
sei();
initADC();
Serial.println("ArdOsc " __DATE__); // compilation date
Serial.println("OK");
setMode(0); // y-gain 5V
setSweep(5);
setPwmFrequency(testSignalPin, 3); // test signal 976Hz 1024uS
pinMode(BtnHorz, INPUT_PULLUP);
pinMode(BtnVert, INPUT_PULLUP);
pinMode(LED_BUILTIN, OUTPUT);
Wire.begin(); // join i2c bus as master
TWBR = 1; // freq=888kHz period=1.125uS
initSH1106();
}
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Main routines
// loop
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
void loop (void) {
static int ButtonsTimer2 = 0;
switch (curMode) {
case mVoltmeter:
if (CheckVoltmeter())
drawScreen();
break;
default:
if (!SendingSerial) {
SendADC();
switch (sweepType) {
case sw20Frames: case sw100Frames: case sw500Frames:
SG_StepSweep();
}
}
}
CheckButtons();
}
Comments
CAN I USE UNO INSTEAD
I like to translate this project to Dutch Language and publice it in our Ham Radio Magazine
Its a very nice, small, Arduino project
Please can someone of Circuit Design give me a reply on this request via my private email
Thanks
Cor Struyk
sorry, Circuit Digest ofcourse
Hello, awesome project, thank-you for putting it together!
Could a Nano Every be used without changing anything?
I am trying to build this oscilloscope, but when I try to compile the code in Arduino IDE, I get an error SimpleSH1106 no such file or directory. Please help.


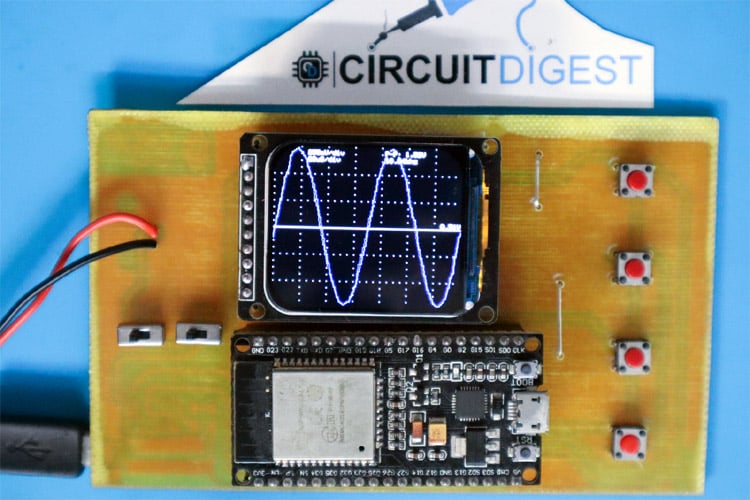






WHAT IS THE MAXIMUM FREQUENCY IT CAN MEASURE AND THE MAXIMUM INPUT VOLTAGE IT CAN ACCEPT AC AND DC