
4G network architecture completely changes the single mobile connectivity, the speed of 4G networks and the technological design. 4G mobile technology provides peak download speeds of 1 Gbps and upload speeds of 500 Mbps, which is a landmark improvement and the basis of development for today's 4G mobile telecom networks in all regions of the world. This guide goes through how the 4G mobile communications technology has changed the wireless communication space, the technical specifications of the 4G network technology, and performance network data from major telecom companies around the world.
Upgrading the 4 G network architecture is a significant step forward in the capabilities of telecommunication for 4 G. As it relates to 4G, the 3GPP LTE-Advanced technical specifications require that 4G operates at frequencies between 2-8 GHz with a theoretical 4G network speed that can reach up to 1 GB [benchmark] download and 500 MB [benchmark] upload, respectively.
Today’s 4G mobile network utilises advanced 4G communication technology, including OFDMA (Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiple Access) and MIMO (Multiple-Input Multiple-Output) antenna systems, to allow for some 2-4x improvement in spectral efficiency over the existing 3 G network.
With impressive network capabilities, 4G enhancement promises to bring the wireless experience to an entirely new level with impressive user applications, such as sophisticated graphical user interfaces, high-end gaming, high-definition video and high-performance imaging. Consumer expectations for mobile handsets and similar products are becoming more and more sophisticated.
Table of Contents
Evolution of 4G Communication Technologies: From 1G to 4G Timeline
The predecessor technologies to it are 1G, 2G and 3G technologies; 5G technology is also set up in the sequence, with the expectation to hit the market by 2020. Here is the timeline for various communication technologies.
Generation | Launch Period | Key Technology | Max Speed | Primary Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1G | Early 1980s | AMPS (Advanced Mobile Phone System) | 2.4 kbps | Voice calls only |
2G | Late 1980s | GSM, CDMA digital protocols | 64 kbps | Voice + SMS |
3G | Early 2000s | UMTS, W-CDMA, HSPA | 2-42 Mbps | Mobile internet, video calls |
4G | Late 2000s | LTE, LTE-Advanced (3GPP Release 8+) | 100 Mbps - 1 Gbps | HD streaming, IoT, mobile broadband |
5G | 2019-2025 | 5G NR (New Radio), mmWave | 1-20 Gbps | Ultra-low latency, massive IoT |
Along with these major ivolvements in wireless communication technologies, there have been some intermediate inventions like 2.5G GPRS (General Packet Radio Service), which stands for "second and a half generation," is a cellular wireless technology developed in between its predecessor, 2G, and its successor, 3G and also 2.75 – EDGE (Enhanced Data rates for GSM Evolution)
Understanding 4G Network Architecture and Key Technologies
4G network architecture is significantly more complex than previous generations, in part due to an all-IP (Internet Protocol) design. 3G networks in contrast, were based on both circuit and packet switching, while 4G network technology operates solely with packet switching, with the advantage of reducing the latency within network traffic (typically latency ranges between 20-40ms), along with increased efficiency of data transmissions.
Main Components of 4G Mobile Technology:
• eNodeB (Evolved Node B): Base stations providing radio communications.
• MME (Mobility Management Entity): Used for mobility and authentication procedures.
• S-GW/P-GW: Serving and Packet Data Network Gateways.
• HSS (Home Subscriber Server): User database functionality.
4G Network Speed and Performance Statistics Worldwide
Real-life 4G network speed performance differs widely between geographies and operators. Based on Opensignal's recent mobile network experience report (2024), below is how 4G mobile network penetration and performance globally compare.
COUNTRY | PENETRAION | FREQUENCY |
SOUTH KOREA | 62% | 800MHz, 1800MHz |
JAPAN | 21.3% |
|
AUSTARLIA | 21.1% |
|
UNITED STATES | 19% |
|
SWEDEN | 14% |
|
CANADA | 8% |
|
UNITED KINGDON | 5% | 800MHz, 1800MHz, 2600MHz |
GERMANY | 3% |
|
RUSSIA | 2% | 2600MHz |
PHILIPPINES | 1% |
|
Key Benefits of 4G Network Technology
- Faster network speeds up to 20-50 Mbps (up to 100x faster than 3G)
- Newest 4G network architecture: Always on - any time, anywhere. Reduced complexity for management costs because of all-IP architecture for 4G technologies.
- New communication technologies. Support for HD voice, video calling and large bandwidth applications, 2-3x more capacity level for 4 G.
- More efficient use of spectrum capacity. OFDMA technology will increase total capacity on repeaters to 3-6 X/PER MHz.
- Allows you to roam (reach out from another country) around the world without complication. 4 G is the standard 4G mobile globally.
4G vs 3G Technology: Comprehensive Comparison
Specification | 3G Technology | 4G Technology | Improvement Factor |
|---|---|---|---|
Network Speed (Real-world) | 1-3 Mbps average | 20-50 Mbps average | 10-20x faster |
Peak Download Speed | 42 Mbps (HSPA+) | 1 Gbps (LTE-Advanced Pro) | 24x increase |
Peak Upload Speed | 5.76 Mbps | 500 Mbps | 87x increase |
Latency | 100-500ms | 20-40ms | 5-12x reduction |
Network Architecture | Circuit + Packet switching | All-IP packet switching | Simplified, efficient |
Frequency Bands | 800MHz-2.1GHz | 700MHz-3.8GHz (expanding) | More spectrum available |
Modulation | QPSK, 16-QAM | 64-QAM, 256-QAM, MIMO | 4-6x spectral efficiency |
Standards Body | 3GPP Releases 5-7 | 3GPP Releases 8-15 | Continuous evolution |
Future of Wireless Communication Technologies
ITU (International Telecommunication Union) has established the overall roadmap for the development of 5G mobile and defined the term it will apply to it as “IMT-2020”. The ITU-R Radio Communication Assembly, which meets in October 2015, is expected to formally adopt the term “IMT-2020”.
Frequently Asked Questions
⇥ What is 4G technology, and how does it work?
4G technology is the fourth generation of wireless communication that uses modern network architecture that is all-IP based. Grounded in the use of several technologies, such as OFDMA, MIMO, and the LTE-Advanced protocols standardised by 3GPP, 4G delivered possible peak download speeds up to 1 Gbps and average upload speeds up to 500 Mbps (3GPP).
⇥ Is LTE 4G or 3.9G technology?
LTE would be considered 3.9G technology because it has not met all the ITU-R IMT-Advanced requirements for 4 G technology. LTE-Advanced (3GPP Release 10+) can be considered true 4 G. LTE-Advanced can deliver peak speeds up to 1 Gbps download speeds and up to 500 Mbps upload speeds, and can support carrier aggregation and advanced forms of MIMO.
⇥ What is the real speed difference between 3G and 4G?,
3 G networks typically deliver average speeds of 1-3 Mbps peak (using HSPA+) of 42 Mbps, whereas 4G networks deliver average speeds of 20-50 Mbps and have a peak theoretical speed of 1 Gbps. 4G is 10-20x better in the real world and has 24x more capacity in peak speed.
⇥ What makes 4G network architecture different from 3 G?
4G is designed with a completely new all-IP packet switching architecture with eNodeB base stations, MME for mobility, and S-GW/P-GW gateways. Using a pure packet-switching design eliminates the hybrid circuit/packet switching in 3G, which results in lower latency of 20-40ms instead of 100-500ms and 3-5x more efficient use of spectrum.
⇥ What makes 4G network architecture different from 3 G?
4G is designed with a completely new all-IP packet switching architecture with eNodeB base stations, MME for mobility, and S-GW/P-GW gateways. Using a pure packet-switching design eliminates the hybrid circuit/packet switching in 3G, which results in lower latency of 20-40ms instead of 100-500ms and 3-5x more efficient use of spectrum.
⇥ Can I make voice calls using 4G networks without degrading to 3 G?
Yes, some 4G carriers offer voice-over LTE (VoLTE) technology, which offers HD voice and more rapid call connection times. Many of the 4G phones launched between 2010 and 2013 use CSFB (Circuit Switched Fallback) technology to hook into 3 G and 2G networks for voice calls instead of VoLTE.
⇥ Why do mobile 4G download speeds appear to change so significantly from one place to another?
There are several factors in mobile 4G download speeds, depending on network congestion, distance to the cell towers, frequency bands (700MHz vs 2600MHz), carrier aggregation, and MIMO configuration. Urban areas typically average download speeds of 30-70 Mbps, while rural 4G generally averages 5-20 Mbps, depending on congestion.
Enhance Your Understanding with These Practical 4G & GPS Projects
Enhance your grasp of 4G technology and GPS communication by diving into these hands-on Arduino projects. Whether you're curious about integrating A7672S modules, building real-time trackers, or sending data to the cloud via GSM, these tutorials give you the perfect launchpad to apply concepts in the real world.
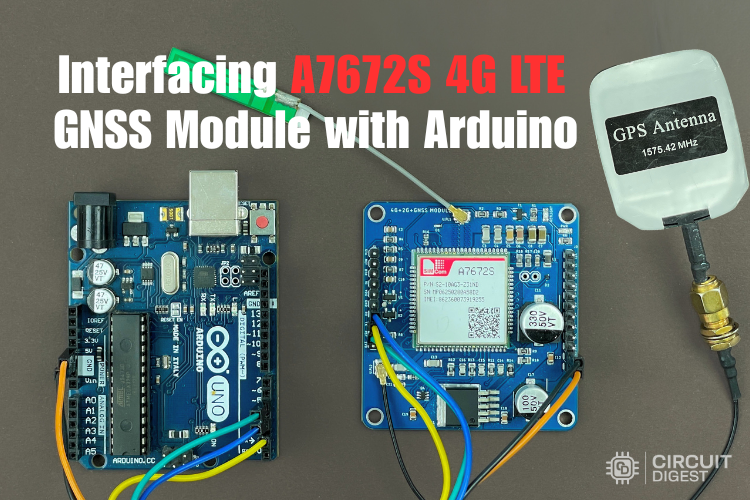
Interfacing the A7672S 4G LTE GNSS Module with Arduino
Learn how to use the A7672S 4G LTE GNSS module with Arduino for GPS tracking and IoT communication. This guide covers pinout, interfacing, AT commands, and HTTPS data upload. Ideal for mobile projects like smart vehicles, remote monitors, and asset tracking, the A7672S offers reliable cellular connectivity and precise location data without Wi-Fi dependency
Arduino Location Tracker using SIM800L GSM Module and NEO-6M GPS Module
This comprehensive project shows you how to create a fully functional GPS tracking system using Arduino UNO R3, SIM800L GSM module, and NEO-6M GPS module, a perfect low-cost DIY combination for vehicle monitoring, asset protection, or personal safety applications.
How to Send Data to Web Server using Arduino and SIM900A GPRS/GSM Module
Here we send data to the Sparkfun server using Arduino and GPRS. This is an IoT based project in which we will user GPRS, present on the GSM Module SIM900A board, to send some data to the web service on the internet.






Wow the came a long way from 5 Mbps upload rate in the 3G to 500 Mbps! It is very huge different. I do know about the 3G and 4G tech, but I didn't got into details before reading this post. Thanks for making this guide Tushar.