| Pulse Peak Power (Pt) | ||
| Maximum Power Gain (G) | dBi | |
| Antenna Aperture (Ae) | ||
| Radar Cross Section Area | Sq. Mts | |
| Detectable Signal (Pmin) |
The radar range calculator is designed to determine the theoretical maximum detection distance of a radar system, beyond which the target/object can no longer be detected and analysed, based on the fundamental relationships between transmitted power, antenna parameters, and target properties. Understanding radar range calculations is essential for radar engineers working with surveillance systems, air traffic control, and target tracking applications.
The core of this tool is the radar range equation calculator function, which models how signal power diminishes over a two-way path. The standard form of the radar range equation is:
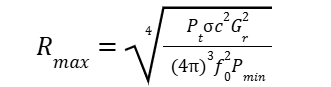
where R_max is the maximum range, Pt is the transmitter's peak power, Gr is the gain of the radar antenna, C is the speed of light, σ represents the radar cross-section, f0 is the radar signal frequency, and Pmin is the minimum detectable signal power at the receiver.
Example of Radar Range Equation Calculator
Find the detection range for a small aircraft (σ = 10 m²) using radar with Pt = 1 MW, Gr = 40 dB, f = 10 GHz, Pmin = -90 dBm.
Convert:
Pt = 1,000,000 W
Gr = 10,000
f = 10^10 Hz
Pmin = 10-12 W
R_max = ∜[(106 × 10 × 9×1016 × 108) / (248 × 1020 × 10-12)]
R_max ≈ 95 km
Frequently Asked Questions on Radar Range Calculator
⇥ What is radar cross-section (RCS)?
RCS (σ) is a measure of how detectable an object is by radar. It represents the effective area that intercepts and reradiates radar energy back to the receiver. Larger objects generally have larger RCS.
⇥ Why is the equation a fourth root?
Radar involves a two-way path: the signal travels to the target (R²) and back (R²), resulting in R⁴ in the denominator. Taking the fourth root solves for range.
⇥ What affects radar range most?
Power and antenna gain have the strongest effect (fourth root), while frequency has an inverse effect. Doubling the transmit power only increases range by 19%.
⇥ How does the weather affect radar range?
Weather causes:
- Attenuation (rain, fog) reduces the effective range
- Clutter returns that can mask targets
- Atmospheric ducting that can extend or reduce range
- Typical rain attenuation: 0.003 dB/km at 3 GHz, 0.1 dB/km at 10 GHz
Related Calculators for RF and Wireless System Design
Designing or analyzing wireless systems? These calculators help you estimate signal strength, component values, and critical transmission parameters, ensuring your RF and radar applications are both efficient and reliable.
The microstrip line calculator is designed to determine the characteristic impedance and effective dielectric constant of microstrip transmission lines in a PCB, based on physical dimensions and substrate properties.
RF Power Conversion Calculator
The RF power conversion calculator is designed to simplify the process of converting between various RF power units commonly used in radio frequency applications and telecommunications systems.
You can also use this calculator to find out the Power Gain and Voltage Gain from the Decibel value. Just enter the Decibel value and leave Power Gain & Voltage Gain blank, and then hit the Calculate button.




