Drones, also known as unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs), have evolved into essential tools across multiple industries. Their diverse designs and flight mechanisms cater to a wide range of applications, from personal hobbies to military operations. Understanding the different types of drones helps in identifying their specific roles and advantages. Based on the design, we can categories the drones into the following categories.
1.Multi-Rotor Drones
Multi-rotor drones are the most commonly used UAVs. These drones rely on multiple propellers for lift and stability. The most popular among them is the quadcopter, which has four rotors arranged in an "X" or "+" configuration. Tricopters, hexacopters, and octocopters are variations with three, six, and eight rotors, respectively. Additional rotors provide enhanced stability, greater payload capacity, and redundancy in case of motor failure.
![Multicopter Drones]](/sites/default/files/inlineimages/u5/Multicopter-Drones.png)
Due to their ease of control and vertical take-off capability, multi-rotor drones are widely used for aerial photography, surveillance, and inspection tasks. They are often equipped with high-resolution cameras, GPS stabilisation, and autonomous flight modes. Despite their advantages, their flight endurance is limited by battery life, typically ranging from 15 to 45 minutes per charge. Their efficiency is lower compared to fixed-wing drones, as more energy is required to maintain lift.
2.Fixed-Wing Drones
Fixed-wing drones are designed like traditional aeroplanes, using aerodynamic wings to generate lift instead of relying on rotors. This allows them to cover large distances with minimal energy consumption. Unlike multi-rotor drones, they cannot hover in place but can remain airborne for hours, making them ideal for surveying, mapping, and long-range reconnaissance.
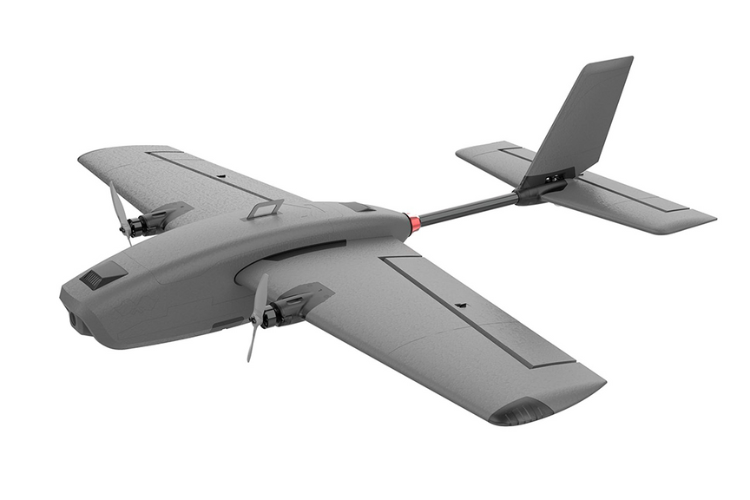

These drones often feature internal combustion engines or electric motors that provide continuous thrust. Because of their high efficiency, they are used in agriculture for crop monitoring, in military applications for intelligence gathering, and in environmental studies for tracking wildlife or assessing land changes. However, their inability to hover means they require a runway or a launching mechanism for takeoff and landing. Some models incorporate vertical take-off and landing (VTOL) capabilities to overcome this limitation.
3.Hybrid VTOL Drones
Hybrid VTOL drones combine the best features of multi-rotor and fixed-wing designs. They can take off and land vertically like quadcopters but switch to fixed-wing mode for efficient forward flight. This versatility allows them to operate in environments where traditional fixed-wing drones would struggle, such as remote locations without runways.
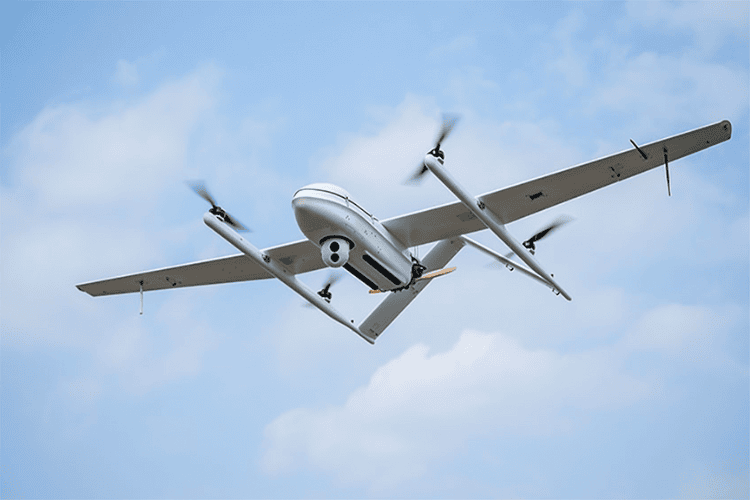

These drones are commonly used in industrial inspections, large-scale mapping, and cargo transport. Many hybrid VTOL models incorporate advanced navigation systems and automation, making them suitable for tasks requiring long endurance and high precision. They offer greater efficiency compared to pure multi-rotor designs while retaining the ability to hover, which is crucial for certain applications like aerial surveys and infrastructure monitoring.
Classification Of Drones Based on Usage
Drones are designed for a variety of tasks, ranging from recreational flying to industrial inspections and military operations. Their features, capabilities, and specifications vary depending on the intended application. Classifying drones based on their usage helps in understanding their specialised roles and how they contribute to different industries. Here are some of the popular Drone categories based on the application area.
Consumer Drones
Consumer drones are primarily designed for recreational use, photography, and social media content creation. They are typically compact, lightweight, and equipped with user-friendly flight controls. Many models feature built-in cameras with gimbal stabilisation, GPS-assisted navigation, and obstacle avoidance systems. Their affordability and accessibility have contributed to their popularity among hobbyists and content creators.
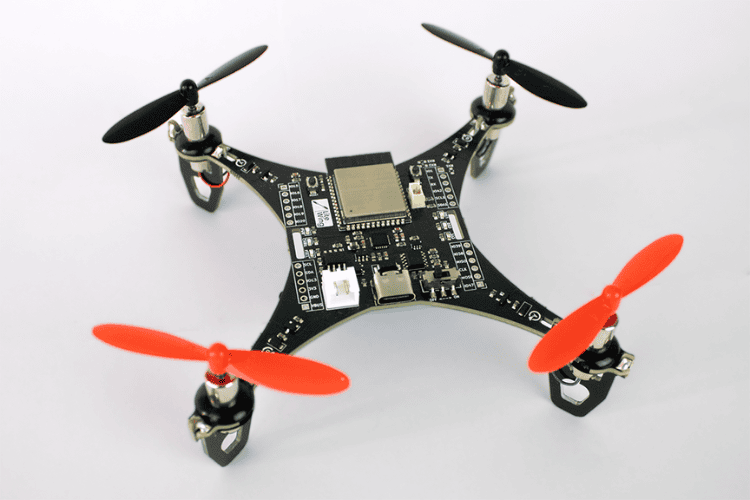

These drones are often used in travel vlogging, live streaming, and event documentation. They generally have a limited flight range and endurance compared to professional models, with battery life averaging between 20 to 30 minutes. Their primary limitation is their small payload capacity, which restricts their use in commercial applications requiring specialised sensors or heavy equipment.
Commercial Drones
Commercial drones are built for professional applications such as agriculture, infrastructure inspection, and logistics. Unlike consumer drones, these UAVs are designed with advanced sensors, longer flight times, and higher payload capacities. They are commonly used for tasks such as crop monitoring, power line inspections, and package deliveries.
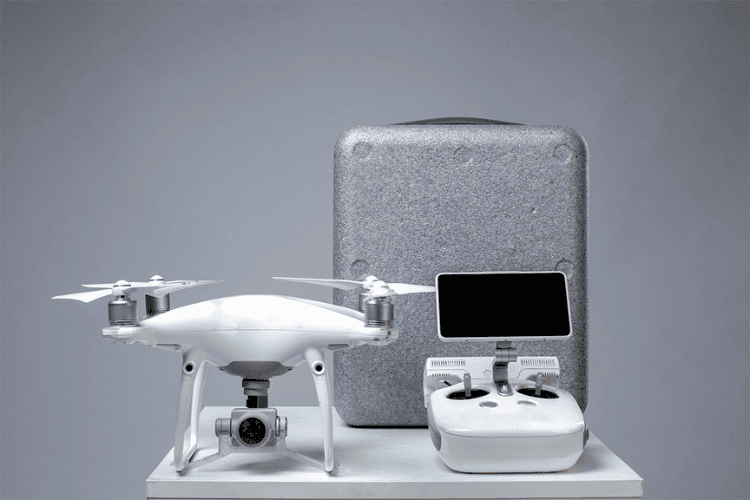

In agriculture, commercial drones equipped with multispectral cameras provide valuable data on crop health, irrigation levels, and pest infestations. Similarly, industrial sectors use them for inspecting oil pipelines, wind turbines, and bridges, reducing the need for human workers in hazardous environments. Some models are equipped with LiDAR sensors, thermal cameras, and AI-powered analytics, enabling precise data collection and real-time decision-making.
Military Drones
Military UAVs serve critical roles in reconnaissance, surveillance, and combat missions. These drones vary in size, ranging from small, hand-launched models to large, long-endurance aircraft capable of carrying weapons. Surveillance drones gather intelligence by capturing high-resolution images and real-time video feeds, assisting military forces in strategic planning.
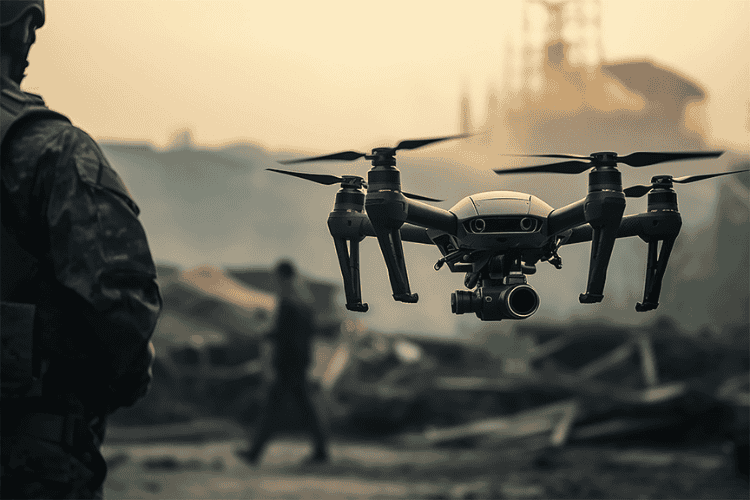

Combat drones, also known as unmanned combat aerial vehicles (UCAVs), are equipped with missiles and guided munitions for precision strikes. These UAVs operate autonomously or under remote control, reducing the risks faced by human pilots in combat zones. Some military drones, such as high-altitude long-endurance (HALE) models, can stay airborne for more than 24 hours, monitoring large areas and relaying critical data to command centres. Their use has transformed modern warfare by enabling targeted operations with minimal collateral damage.
Industrial and Delivery Drones
Industries rely on specialised drones for inspections, mapping, and material transportation. In the energy sector, drones equipped with thermal cameras are used for power grid monitoring, detecting faults in electrical transmission lines before they cause outages. Similarly, oil and gas companies use UAVs to inspect offshore rigs and pipelines, improving safety and operational efficiency.
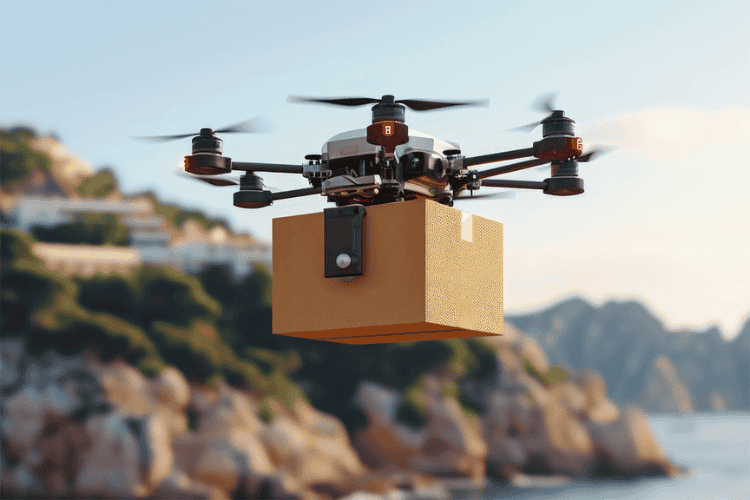

Delivery drones are an emerging technology aimed at revolutionising logistics. Companies such as Amazon and UPS have tested UAV-based delivery systems for transporting small packages. Medical supply deliveries in remote areas have also benefited from drone technology, enabling rapid transport of essential medicines and vaccines. These drones require precise navigation systems and regulatory approvals to operate efficiently in urban environments.
FPV Racing Drones
First-person view (FPV) racing drones are built for speed and agility. Pilots control these UAVs using FPV goggles that provide a real-time video feed from the onboard camera, creating an immersive flight experience. These drones feature powerful motors, lightweight frames, and customisable components for high-speed manoeuvring.
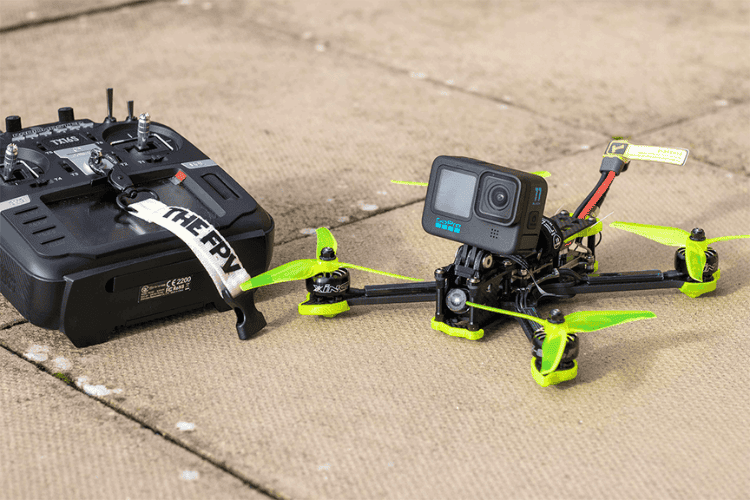

FPV racing has become a competitive sport, with organised events showcasing skilled pilots navigating obstacle courses at high speeds. Beyond racing, FPV drones are also used for freestyle aerial cinematography, capturing dynamic shots that would be impossible with conventional camera drones. The combination of manual control and real-time video transmission makes FPV drones popular among enthusiasts seeking high-performance flight capabilities.
Agriculture Drones
Agriculture drones play a vital role in modern farming practices. These UAVs are used for crop monitoring, precision spraying, and yield estimation. Mapping drones equipped with multispectral cameras help farmers analyse soil conditions and optimise irrigation, reducing resource wastage.
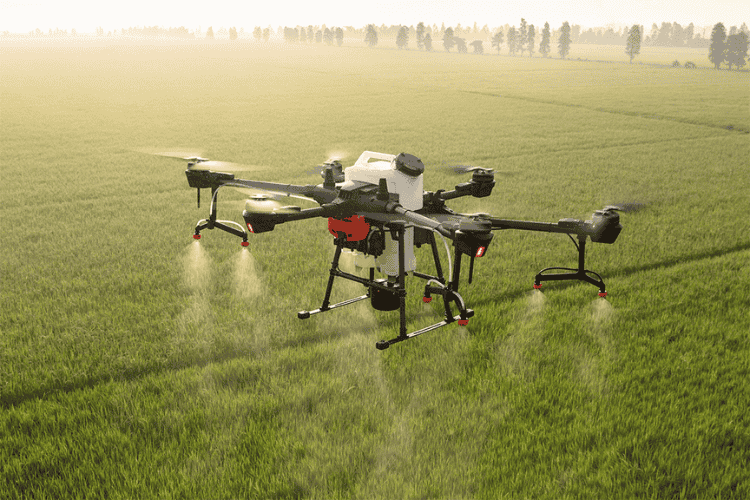

Spraying drones automate the application of fertilisers and pesticides, covering large areas efficiently while minimising human exposure to chemicals. Some advanced models integrate AI-driven analytics to detect plant diseases early, enabling proactive intervention. The use of drones in agriculture has significantly improved productivity and sustainability, reducing operational costs while increasing crop yields.
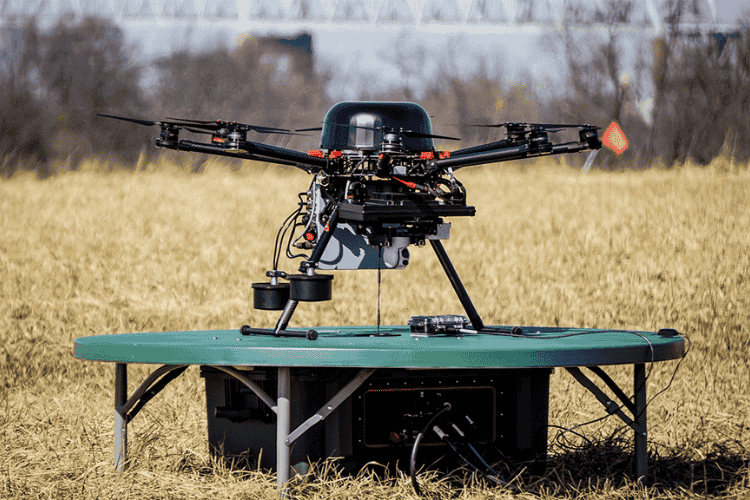
Tethered Drones
Tethered drones are designed for extended flight durations. Unlike battery-powered UAVs, these drones are connected to a ground power source via a cable, allowing them to stay airborne for hours or even days. They are primarily used for live event surveillance, disaster response, and military communications.
These drones provide stable aerial coverage in situations requiring persistent monitoring, such as large public gatherings or search and rescue operations. Their continuous power supply eliminates battery limitations, making them ideal for missions requiring long-term aerial observation. Some models incorporate autonomous tracking systems, enabling them to follow predefined flight paths while relaying real-time data to operators on the ground.






