
Drones, also known as Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs), have become popular in recent years due to their wide range of applications. They are used in photography, agriculture, security, delivery services, and even in military operations. But how do drones work? This article will cover the fundamental concepts of drones, their components, how they fly, and their various uses.
What is a Drone?
A drone is a flying device that does not require a human pilot on board. It is controlled remotely by an operator or autonomously by onboard computers and sensors. Drones come in various sizes and designs, from small hobbyist drones to large military-grade UAVs.
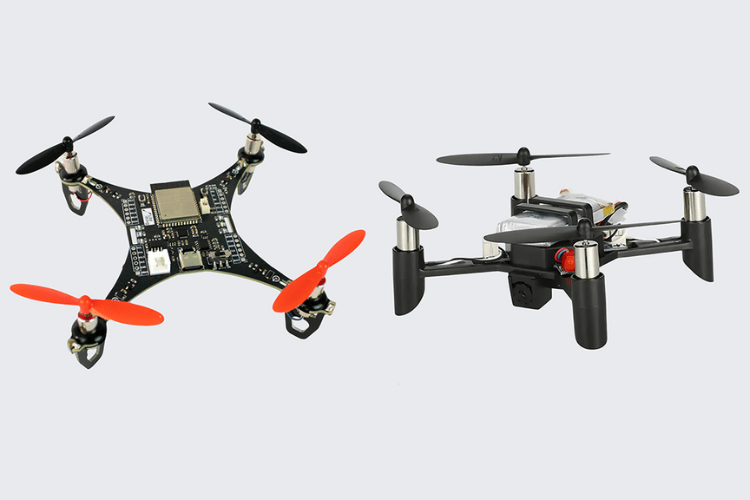
Basic Components of a Drone
Drones consist of several essential parts that work together to enable flight and control. Below are the key components:
1.Frame
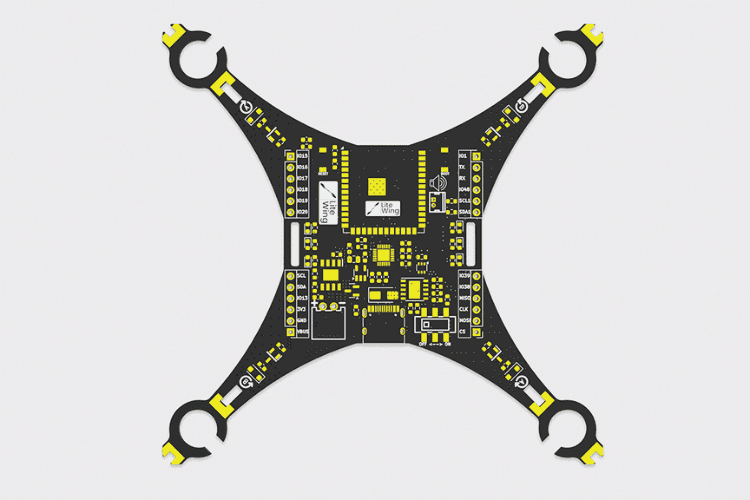
The frame is the main structure of the drone. It holds all the components together and provides support for the motors and propellers. Drone frames are typically made of lightweight materials such as carbon fiber or plastic to improve flight efficiency. Here with the LiteWing, we have used the PCB itself as the frame to reduce the need for additional frame materials.
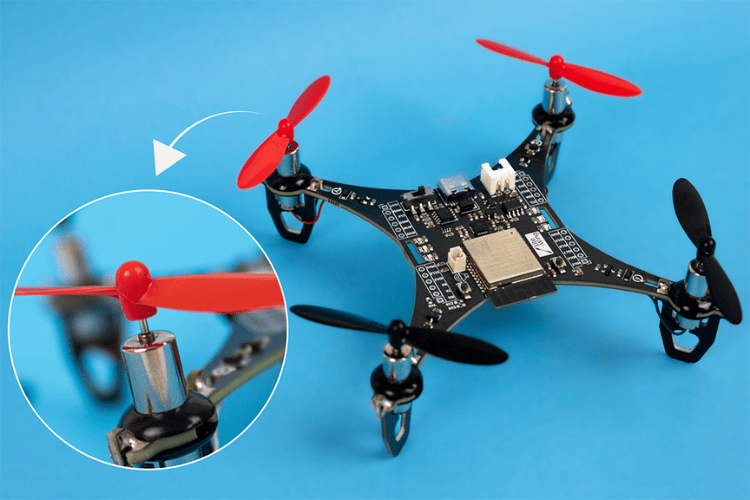
2.Propellers
Propellers generate lift and thrust to keep the drone airborne. The number of propellers varies depending on the type of drone. The most common type uses 4 propellers and is thus called a quadcopter. Just like any other quadcopter, the LiteWing also has 4 propellers, of which two of them are clockwise and the other two are counterclockwise propellers.
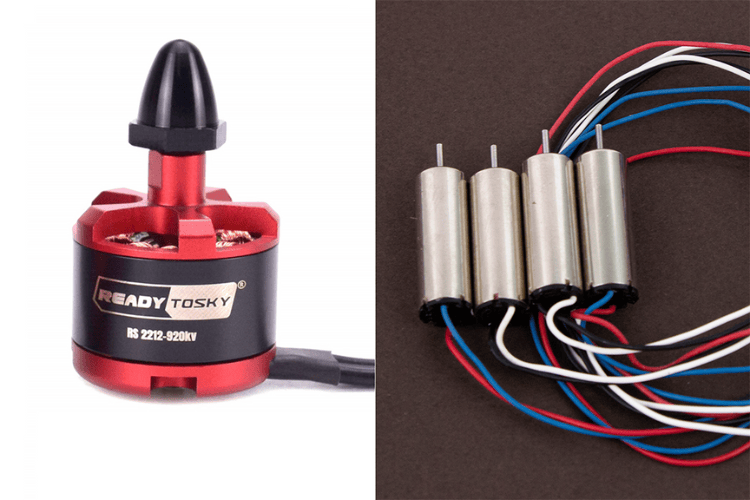
3.Motors
Each propeller is attached to a motor. The motors can be either brushed or brushless. Brushless motors are commonly used in drones because they are efficient and durable. However, since we need lightweight, small form factor motors, we have used the 720 coreless brushed motors with the LiteWing. Not only that, with the use of brushed motors, we can replace the ESC with simple motor drivers. Just like the propellers, the brushed motors are also of two types, clockwise and counterclockwise. Despite the type of motor used, these motors spin at high speeds to generate the necessary thrust.
4.Flight Controller
The flight controller is the brain of the drone. It processes data from sensors, such as gyroscopes and accelerometers, to stabilise the drone and keep it flying smoothly. The flight controller also communicates with the remote control or an autonomous navigation system. In LiteWing the frame, flight controller and the motor drivers are all in the same PCB, reducing the number of components to the minimum.
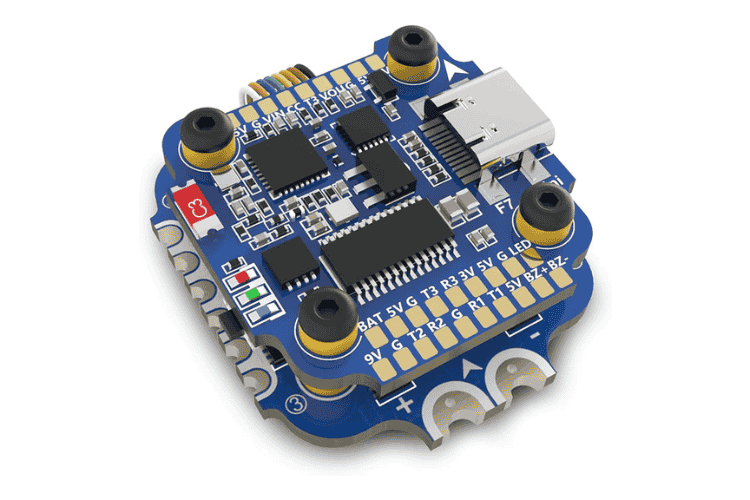
5.Battery and Power System
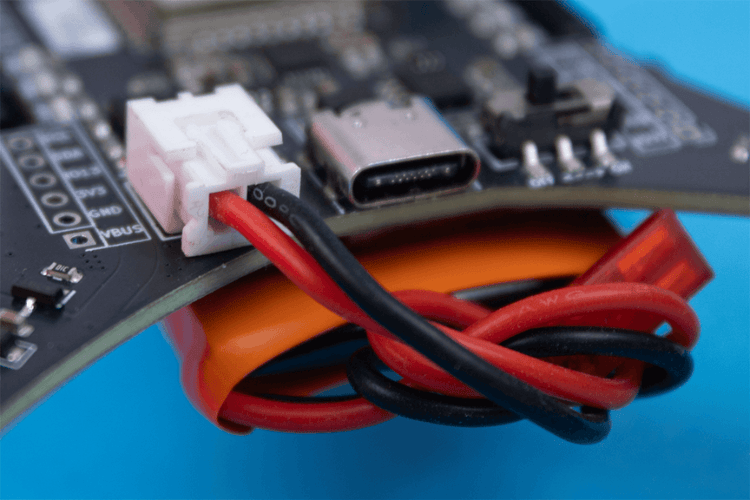
Drones are powered by lithium-polymer (LiPo) batteries, which provide the necessary energy to run the motors and electronics. The flight time of a drone depends on the battery capacity and efficiency of the system. Most commercial systems tend to use external battery chargers instead of integrated ones. This is because they are built to be used by swapping batteries whenever the one used is depleted. In LiteWing we have integrated battery charging circuitry allowing us to recharge the drone battery with any available USB power source.
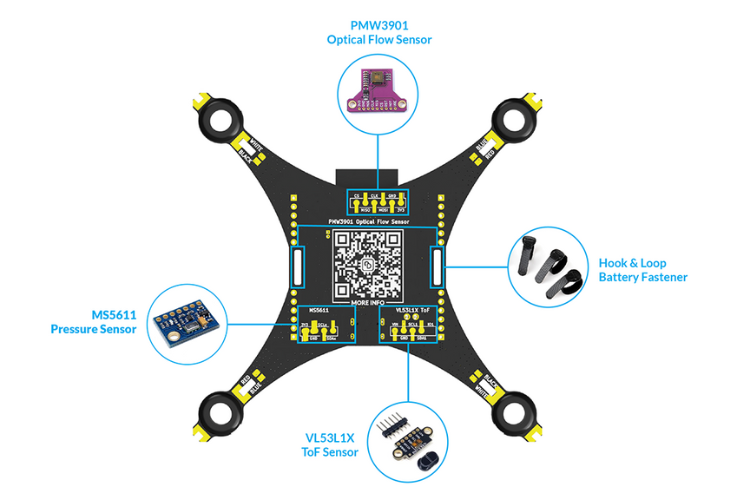
6.Sensors
Drones use various sensors to navigate and maintain stability. Common sensors include:
Gyroscope and Accelerometer: Help maintain balance and orientation.
GPS: Enables navigation and location tracking.
Barometer: Measures altitude and helps with stability.
Obstacle Avoidance Sensors: Detect obstacles to prevent collisions.
Time Of Flight(ToF) Sensors: For height holding and obstacle detection.
Optical Flow Sensors: For indoor position holding.
The LiteWing features an integrated IMU which integrates the Gyroscope and Accelerometer in a single package. LiteWing also supports ToF
7.Remote Controller
The remote controller allows the pilot to control the drone wirelessly. It usually operates on 2.4 GHz or 5.8 GHz frequencies and communicates with the drone via radio signals. Some may also support smartphone controls, just like the LiteWing, which can be controlled remotely using a smartphone or a computer.
How Drones Fly
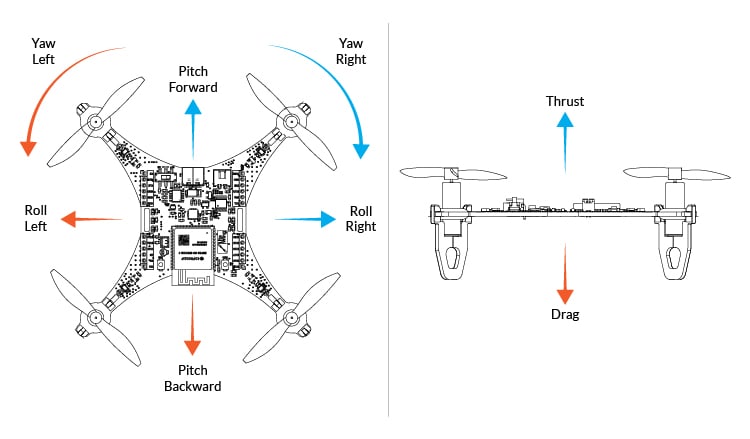
Drones fly by controlling the speed of their propellers, creating different amounts of lift and thrust. Here’s how it works:
Hovering: All propellers spin at the same speed, generating equal lift to keep the drone in place.
Ascending: Increasing the speed of all propellers generates more lift, causing the drone to rise.
Descending: Reducing propeller speed decreases lift, making the drone descend.
Moving Forward/Backward: Increasing the speed of the rear propellers and decreasing the speed of the front propellers tilts the drone forward, causing movement.
Turning (Yaw): Increasing the speed of one set of diagonal propellers while decreasing the speed of the other set allows the drone to rotate.
Different Types of Drones
Drones are classified based on their design and purpose. The main categories include:
Multi-Rotor Drones
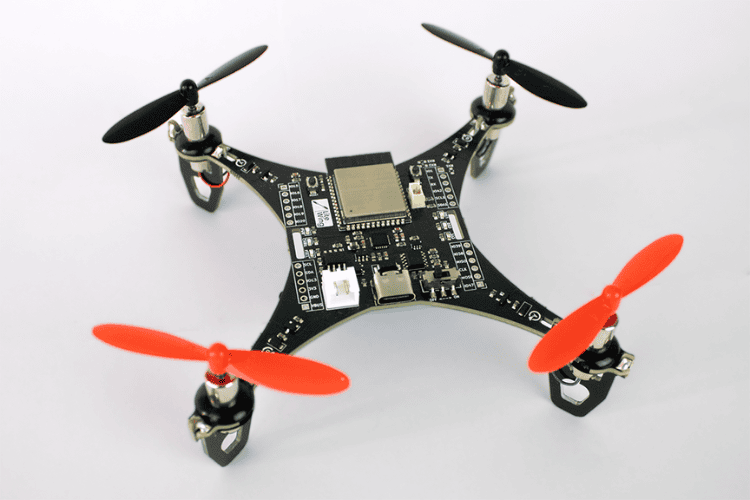

These are the most common consumer drones. They are easy to control and used for photography, videography, and hobby flying.
Fixed-Wing Drones
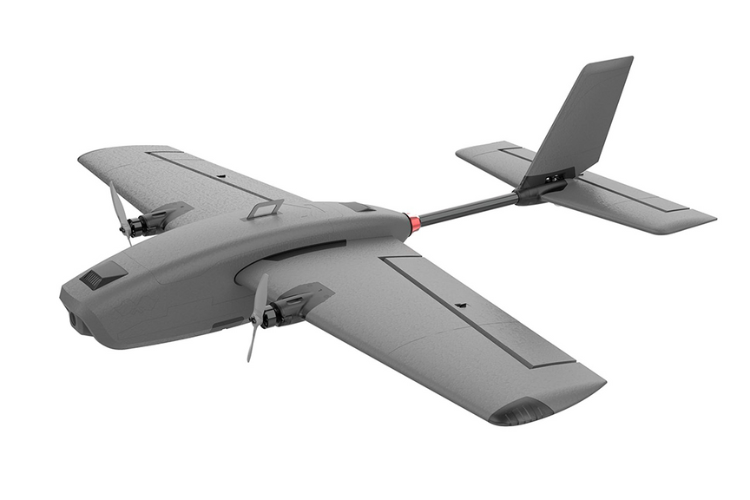

These drones resemble small aeroplanes and are more efficient for long-distance flights. They are commonly used in surveying, mapping, and military applications.
Hybrid Drones
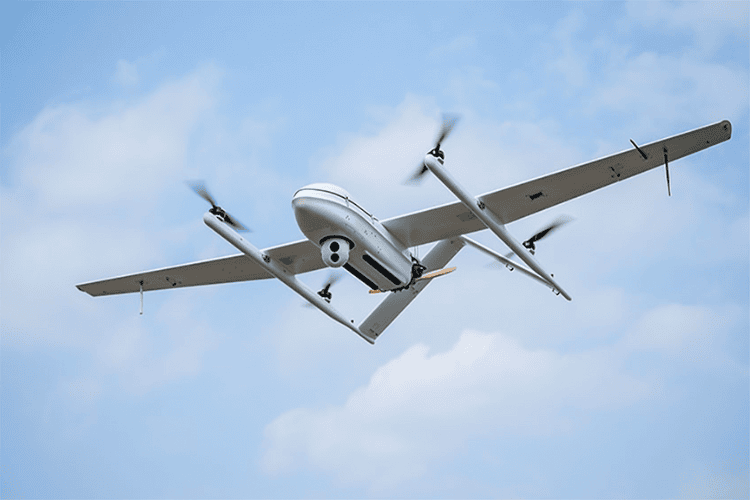

A combination of multi-rotor and fixed-wing designs, hybrid drones offer both vertical takeoff and long-distance flight capabilities.
Applications of Drones
Drones have various practical uses across different industries. Some of the most common applications include:
Aerial Photography and Videography
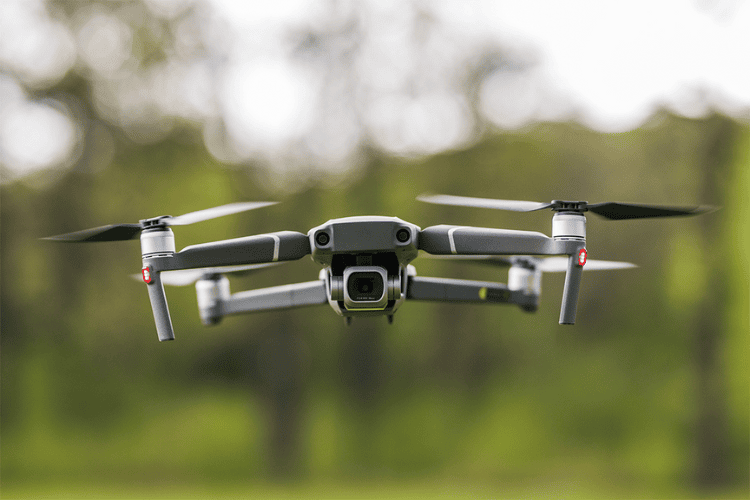

Drones equipped with high-resolution cameras capture stunning aerial shots used in filmmaking, journalism, and real estate.
Agriculture
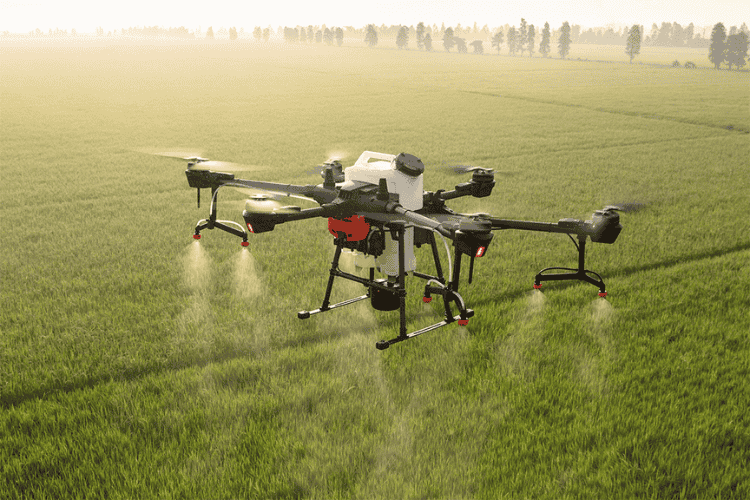

Farmers use drones for crop monitoring, spraying pesticides, and analyzing soil health to improve yields.
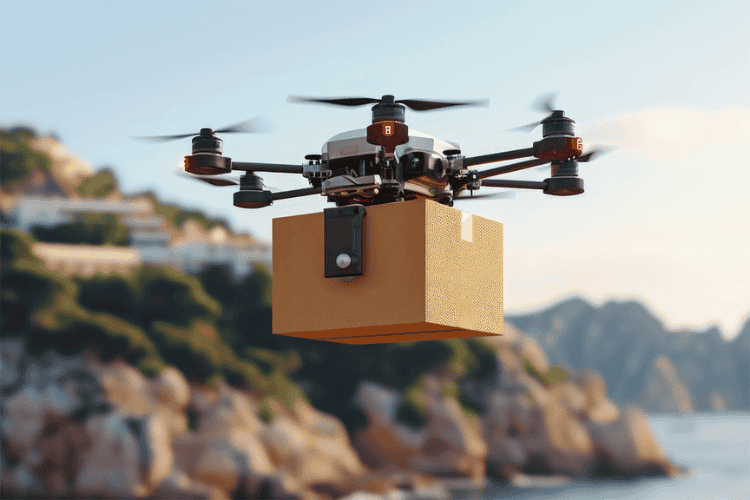

Companies like Amazon and UPS are testing drone delivery services to transport packages quickly and efficiently.
Search and Rescue
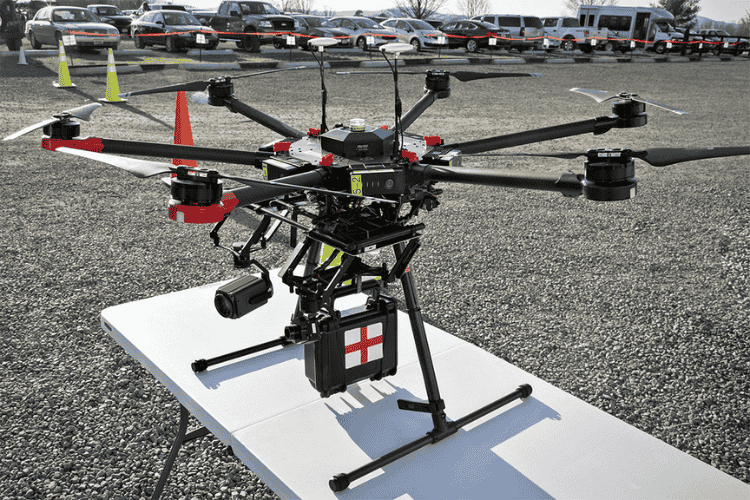

Drones help locate missing persons, deliver supplies in disaster areas, and assist emergency responders.
Military and Defense
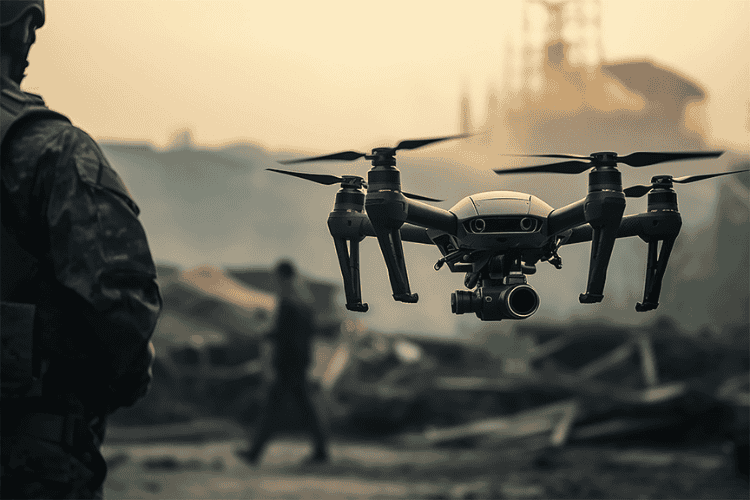

Drones are used in surveillance, reconnaissance, and combat missions, reducing risks for human soldiers.
Mapping and Surveying
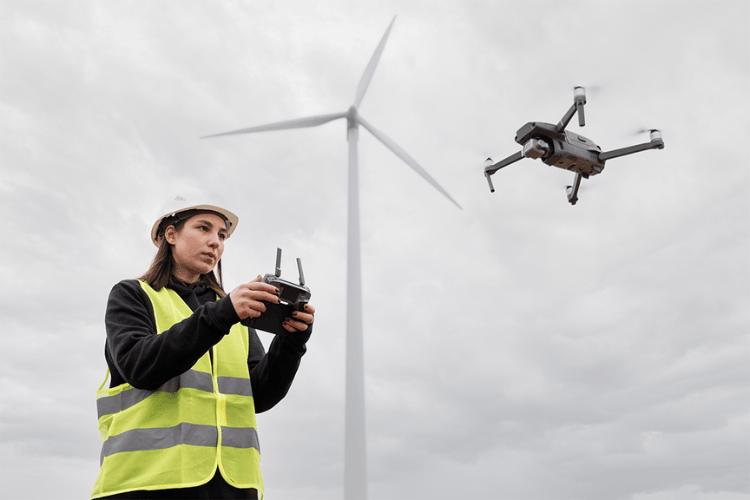

Surveyors use drones for 3D mapping, land assessment, and infrastructure inspections.
Recreational Use

Many people fly drones as a hobby, participating in drone racing or casual flying.
Challenges and Limitations of Drones
While drones offer many benefits, they also face some challenges:
Battery Life: Most consumer drones have limited flight times (typically 20-30 minutes).
Weather Conditions: High winds and rain can affect drone performance.Regulations: Many countries have strict drone flying rules to ensure safety and privacy.
Cost: Advanced drones with high-quality sensors and cameras can be expensive.Payload Capacity: The payload capacity of a drone highly depends on the size of the drone as well as the maximum thrust it can produce. So for large payloads, you will have to use huge drones.





