Embedded systems have a wide range of application in all the electronic devices around us, an evident example is the mini laptop that we carry around with us all the time, yes I am referring to our mobile phones.
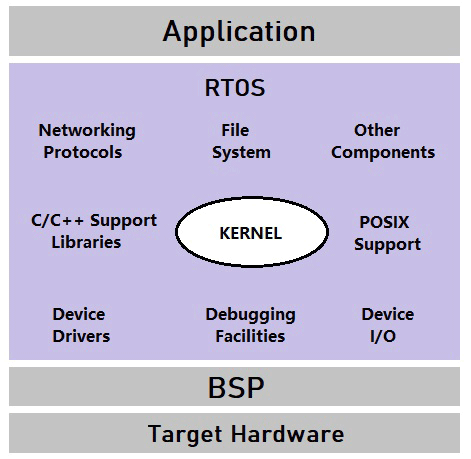
Whenever embedded system comes into picture it is always a combination of hardware like Microcontrollers or Microprocessors and software like a firmware or Operating system. An Operating System forms the base of all the electronics devices and manages both the hardware and the software within any electronic device. The term operating system is not only limited to Unix and Windows for computers but can also extend to microcontrollers. One such operating system that can run on Microcontrollers is called as Real time operating system. Here we will learn about RTOS and applications of real time operating system.
What is RTOS?
Real time operating system popularly known as RTOS provides controller with the ability to respond to input and complete tasks within a specific period of time based on priority. On the first look, an RTOS might sound like just any other embedded program or firmware, but it is built on the architecture of an Operating system. Hence, like any operating system RTOS can allow multiple programs to execute at the same time supporting multiplexing. As we know the core of a processor or controller can only execute a single instruction at a time, but the RTOS has something called the scheduler which decides which instruction to execute first and thus executes the instructions of multiple programs one after the other. Technically an RTOS only creates an illusion of multi-taking by executing paralleled instructions one at a time.
This makes RTOS suitable for various applications in real world. In RTOS for any input whenever a logic has been evaluated which gives the corresponding output. This logic is measured on the basis of not only the logical creativeness but also on the time duration in which the specific task has been performed. If a system fails in performing task in that specific duration of time it is known as system failure.
Why RTOS??
- Availability of drivers: There are many drivers available within RTOS, which allows us to use them directly for various applications.
- Scheduled files: RTOS takes care of scheduling so instead of focusing on scheduling any system we can simply focus on developing application. For example, task scheduling files are used to define certain actions whenever a set of conditions are met. RTOS uses certain advanced algorithms for scheduling typically running, ready and blocked states which while running RTOS keeps more focus on developing application rather than scheduling.
- Flexibility of adding features: Within RTOS even if you are willing to add new features , you can simply add it without disturbing the existing features
Difference between Real time Operating System & Operating System
There are various differences between real time operating system and operating systems like Windows, Linux etc. Let’s have a look at them one by one with the help of table format:
| S.No | Operating System | Real time System |
| 1 | Time sharing is the basis of execution of processes in operating system | Processes are executed on the basis of the order of their priority |
| 2 | Operating system acts as an interface between the hardware and software of a system | Real time system is designed to have its execution for the real world problems |
| 3 | Managing memory is not a critical issue when it comes to execution of operating system | Memory management is difficult as based on the real time issue memory is allocated , which itself is critical |
| 4 | Applications: Office , Data centers , System for home etc | Applications: Controlling aircraft or nuclear reactor , scientific research equipments |
| 5 | Examples : Microsoft Windows , Linux ,OS | Examples: Vx Works ,QNX , Windows CE |
Types of RTOS
We can categorize real time operating system majorly into three parts namely
- Hard real time operating system
- Soft real time operating system
- Firm real time operating system
1. Hard real time operating system
Let’s start understanding this type of operating system using an example, the live example of it is flight control system. Within flight control system whatever tasks is given by the pilot in the form of an input it should be performed on time. In a hard real time Operating system, system failures can be tolerated. The features of hard RTOS are:
- To perform tasks on time
- Failure to meet deadline is fatal
- Guaranteed worse case response time
- Can lead to system failure
2. Soft real time operating system
Easiest example of using soft RTOS is online database, as within soft RTOS the parameter we are more worried about is speed. Hence, the features of soft RTOS are:
- Tasks should be performed as fast as possible
- Late completion of tasks is undesirable but not fatal
- There is a possibility of performance degradation
- Cannot lead to system failure
3. Firm real-time operating system
Robot arm which is used to pick objects can be considered as among one of the example of firm RTOS. Here, within this firm RTOS even if the process is delayed it’s tolerated.
Benefits of using free RTOS
The following are the advantages of using RTOS in your applications.
- No firewall issues
- Low bandwidth for enhanced performance
- Improved security and privacy
- Low cost, due to reduction in hardware and software components used for development
Some major issues related to RTOS
Now, despite of having many advantages for RTOS in real world application, it has various disadvantages also. Some of the issues related to it are discussed here.
- Interrupts are normally used in programs to halt the executing program to divert the flow to some other important part of the code. Here, within RTOS since quick response time is required; it is recommended that interrupts should be disabled for a minimum possible time.
- Since, the kernel should also respond for various events it is required to have lesser size of kernel so that it should fit properly within ROM
- Sophisticated features of RTOS should be removed as there is no concept of as such virtual memory within it.
How to use RTOS
Now that you know what is RTOS and where you can use it, to get started with RTOS you normally have to use the Tornado or the FreeRTOS development environment. Let us take a brief look into both these development environment.
Tornado – VxWorks
Tornado is an integrated environment to develop real time related embedded RTOS applications on the target system. Tornado consists of three basic elements which are listed below.
1) VxWorks
2) Application building tools (compiler and associated programs)
3) Integrated development environment, which can manage, debug and monitor VxWorks application
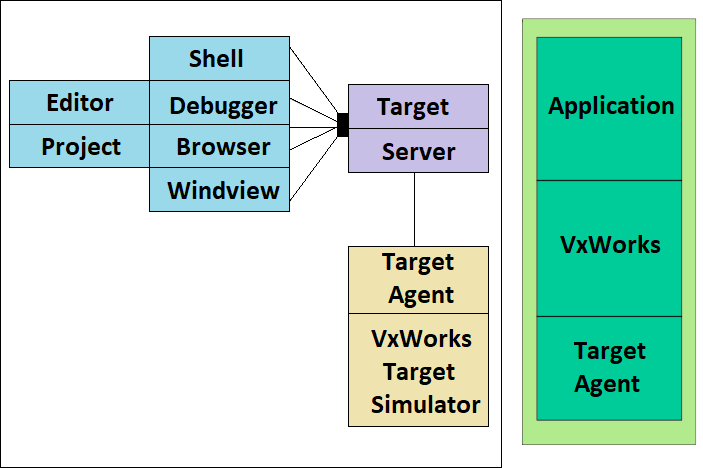
VxWorks is a networked real time operating system. To begin with VxWorks we should have one development kit (target) along with one workstation. Here, development kit is nothing but the target host or component which communicates with the target server on the workstation. The target here connects tornado tools such as the shell and the debugger. Therefore, using VxWorks we will configure and built the systems while Tornado provides us a graphical user interface and command line tools for configuration and build.
Very important point which comes into picture here is that while installing tornado within your system the installation directory should use the pathnames as:
installDir/target. For example if you wish to store your tornado in C:\tornado on a windows host the full pathname should be identified in that case as installDir/target/h/vxworks.h.
Here, we will not discuss in detail regarding the features of Vx works (we will leave that for next tutorial) but we will discuss how the development can be done using C++ within Vxworks using WindRiver GNU. WindRiver GNU helps us in providing a graphical analysis regarding the interrupt involved during execution as well as the memory usage report.
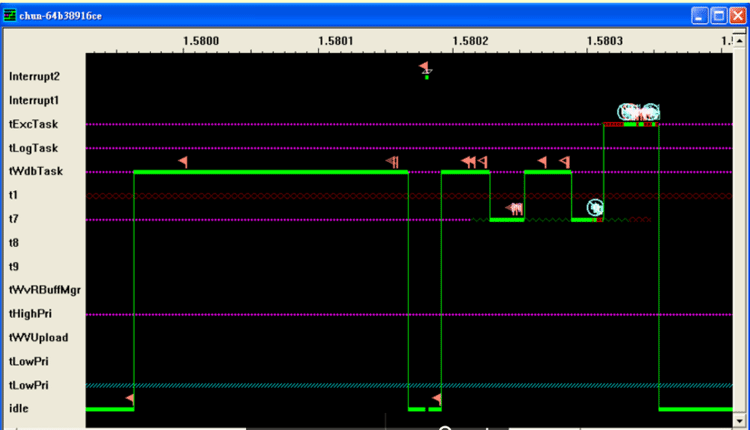
For example, the above stated view of WindRiver explains the associated processor number along with the priority of tasks (tLowPri & tHighPri). Idle state i.e green color line stated the time period for which processor is not in its working state, which is observed to be after every few seconds. t1 , t7, t8 & t9 are nothing but the various processors used. Here, we are selecting only t7 processor.
Hence, this Windriver is capable of invoking both VxWorks and application module subroutines. You can launch the Windriver application either form the tornado launch tool bar (-> i button) later click on menu and then click on shell. Lastly, from the command prompt type “>windsh target server”.
Now to program using C++ , it’s important to include INCLUDE_CPLUS_DEMANGLER component , this demangler component allows target shell symbols to return human readable forms of C++ symbol names. Before , downloading C++ module to Vxworks target , follow process known as munching . Here, munching refers to additional host processing step.
Compile C++ application source program and get for example hello.cpp file . Later run it to munch on the .o and compile the generated ctdt.c file. Further, link the application with ctdt.o to generate downloadable module , hello.out within VxWorks. The output after executing this VxWorks will be a make file which will be using on some target .
Free RTOS
Generally, whenever we begin with RTOS we generally prefer Vx Works RTOS. But , here let’s have a discussion in brief regarding the Free RTOS , which can also be used to by beginners to go through concept of real time operating system . Free RTOS is developed by Richard Barry and FreeRTOS team ,also it is owned by Real time engineers ltd but it is free to use and can be simply downloaded by clicking on the link below
Latest version of free RTOS being used at the time of this article is version 10, stated as FreeRTOS V10.
The biggest advantage of free RTOS which makes it superior in terms of the other RTOS is its platform independent behavior in terms of hardware i.e the c code which we will be using to execute an operating system can run on various platforms having different architecture. Therefore irrespective of whether you are using 8051 microcontroller or some latest ARM microcontroller the code which you wrote along with the process of execution will be similar for both.
There are many other benefits of using free RTOS over Vx works and other RTOS operating tools. Some of them can be stated as:
- Provides easier testing
- Promotes the concept of code reusability
- Lesser idle time
- Easy maintainability
- Abstract out timing information
Also, the basic Kernel, where Kernel refers to the central component of an operating system which is present within the free RTOS makes it accessible to use for various applications. Since it is easy to attach expanded modules on operating systems to get its more applications free RTOS becomes more powerful.
One of the examples of using free RTOS can be explained by using the concept of combining Free RTOS with Nabto. Nabto is a free web device used to transfer the information from the device to the browser.
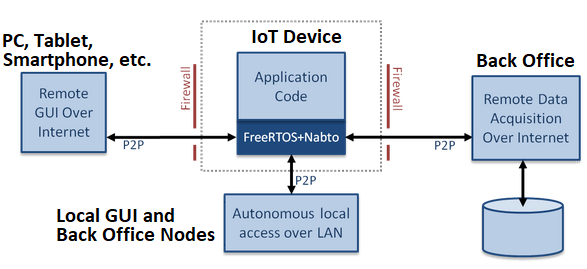
Therefore on combining Free RTOS with Nabto makes it a small piece of C code as explained in figure a. Now a days Internet of Things (IOT) is in trend and every IOT device we will be accessing has a unique URL over the internet and the technology allows secure and extremely low bandwidth point to point connections. In the absence of internet connectivity this combination can be helpful. Therefore, free RTOS is a popular choice when it comes to implementing IOT.





