
Today's smartphones' fingerprint sensor in display technology represents the latest evolution in mobile fingerprint security, offering in screen fingerprint sensor capabilities that were once limited to flagship devices. As a result, these sensors are primarily used for smartphone security these days.
The cutthroat competition in the smartphone industry and evolving technology have gotten us into a phase, where we come across an innovation every other day. Types of fingerprint sensors in mobile devices have evolved significantly, with the current buzzword being in-display fingerprint sensors. Smartphone manufacturers like Xiaomi, Realme, and Oppo have made sure that the technology is not just limited to flagship devices.
Recent ultrasonic fingerprint sensor phones and optical variants like Realme X, Redmi K20, and OPPO K3 are offering fingerprint sensors in display technologies at a price that is hard to digest. With all that in mind, let's find out what this in-display fingerprint sensor technology is and how it works.
Investigating in display finger print mobile technology's various types of fingerprint sensor means requires both existing and the development of in screen fingerprint sensor systems.
Table of Contents
- History
- Types of Fingerprint Sensor in Mobile Phones
- In Display Finger print Mobile Sensor: Optical Technology
- Ultrasonic Fingerprint Sensor Phones and Technology
- Capacitive Scanners
- Algorithm and Cryptography
- In-Screen vs Traditional Fingerprint Sensors: Key Comparison
- Which is better, Optical or Ultrasonic?
- Best Smartphones with In Display Fingerprint Sensor
- Frequently Asked Questions
History
Let’s begin from the beginning when it all started. Diving into the history of fingerprint readers on Mobile devices takes us to the ‘Pantech GI100’, launched back in 2004. This device was equipped with a fingerprint reader, the first of its kind. The next devices following the trend ‘G900 and G500’ came from the likes of Toshiba in 2007. Later on, manufacturers like HTC, Acer, and Motorola joined the league with their respective devices. Apple too joined the party in 2013 with the iPhone 5s, getting a fingerprint sensor. The Cupertino-based giant went on to call it Touch ID. Since then, fingerprint sensor technologies have undergone some major changes.

Tech enthusiasts might know there are three different fingerprint authentication technologies in action. But the in-display fingerprint technology currently benefits only from the two.
Before we get into the big picture, let's understand the basic technology at work behind it. All fingerprint sensors work by tracking those unique ridges and lines on your fingers. However, different technologies can be at work in this tracking process, including optical scanning, capacitive scanning, or ultrasonic scanning.
Types of Fingerprint Sensor in Mobile Phones
- Optical Scanners (Used in In-display fingerprint sensors)
- Ultrasonic Scanners (Used in In-display fingerprint scanners)
- Capacitive Scanners
In Display Finger print Mobile Sensor: Optical Technology
Optical scanners have been around for quite a while now and are the oldest methods of fingerprint authentication. However, in-display optical sensors are comparatively new to smartphones. Vivo Apex, a concept device showcased at MWC 2018, turned many heads in the smartphone industry. The device featured ‘CLEAR ID 9500’, an optical fingerprint sensor developed by Synaptics, the US-based sensor maker. It was later brought to consumers in a new device called ‘ Vivo X20 Plus UD’. The new design was soon adopted by companies like OPPO, Samsung, Huawei, and more. Most of the fingerprint sensor we see is Optical fingerprint sensor, and they can be easily interfaced with Arduino, Raspberry Pi, and other microcontrollers.
Working of the Optical Fingerprint Sensor
The technology relies on capturing an image of your fingerprint and further analyzing if the current fingerprint matches the stored image. A charge-coupled device (CCD) sits at the heart of an optical sensor, the same sensor that is used in digital cameras and camcorders. For folks unaware, a CCD is an array of light-sensitive diodes called photosites, which generate electrical signals in response to light photons.
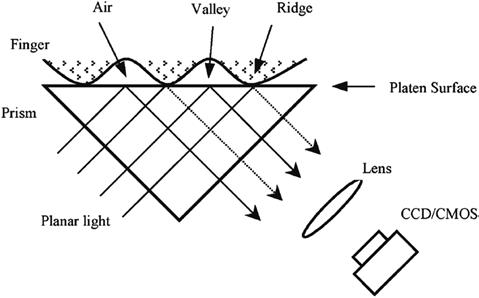
As soon as you place your finger on the sensor, an array of light-emitting diodes (LEDs) lights up to illuminate the ridges and gaps, and a CCD camera quickly captures an image of the same. The CCD system generates an inverted image of the finger, with darker areas representing more reflected light (the ridges of the finger) and lighter areas representing less reflected light (the valleys between the ridges). The image captured is then compared with the stored image.
The optical sensors are easy to fool, as the technology used captures a 2D image, and a good-quality image can possibly break through this security. It is worth noting that the technology works only with OLED displays, where there are gaps in the backplane. Initially, in-display fingerprint sensors weren’t as reliable and fast as they are now. But things have changed in favour of these sensors in recent times.
Ultrasonic Fingerprint Sensor Phones and Technology
Ultrasonic sensors are the newest of fingerprint technologies being used. As the name hints, these sensors make use of high-frequency ultrasonic sound to map your fingerprint. Samsung partnered with Qualcomm to bring the first device with an in-display ultrasonic fingerprint sensor, the ‘Galaxy S10/S10+. The device was also the first to feature Qualcomm’s 3D Sonic sensor, which is an iteration of Sense ID.
Qualcomm’s latest ultrasonic technology works through glass that’s up to 800 microns thick. The company claims a 250-millisecond latency for unlocking, which is close to what a capacitive fingerprint scanner can achieve.
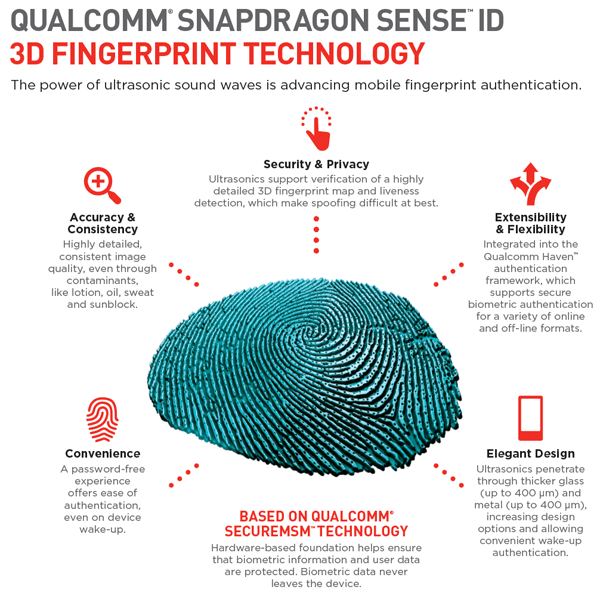
Working of Ultrasonic Fingerprint Sensor
The hardware on these scanners consists of an ultrasonic transmitter and receiver. The scanning process begins as soon as a fingertip is placed on the sensor. An ultrasonic pulse is transmitted by the transmitter, which collides with the ridges and valleys on the fingertip, some of the pulse pressure is absorbed, and some of it is bounced back to the sensor. The amount of absorption and bounce back of the pulse varies with varying fingerprints. Moving further, a sensor capable of detecting mechanical stress is used to calculate the intensity of the returning ultrasonic pulse at different points on the scanner. These scanners gain detailed in-depth information, resulting in a detailed 3D replica of the scanned fingerprint.
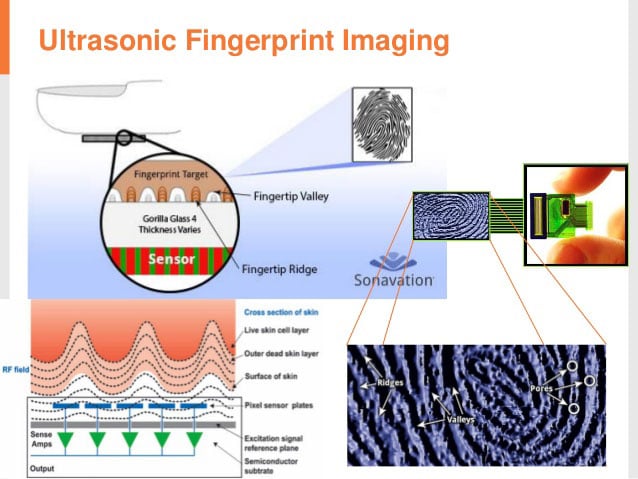
Since these scanners lie beneath the display. The waves from ultrasonic sensors have to travel through the display’s backplane, glass, and protective cover before reaching your finger. Therefore, manufacturers ensure that the glass used for display is not too thick. Having said that, it is advised not to add extra protection, such as a screen protector, which can prevent this technology from working properly.
Not many devices come with an ultrasonic sensor, being the costliest of available technologies. Flagship devices like the Samsung Galaxy S10/10+ come equipped with an ultrasonic sensor. However, there’s still some time until we see this technology penetrating the budget segment.
Capacitive Scanners
Capacitive Sensors are the most widely used sensors these days and can be found on every other device that you come across. These sensors use capacitors as the core component, which is an electronic component used for storing electrical energy. The technology is not currently used for in-display fingerprint scanning.
Working of the Capacitive Fingerprint Sensor
These sensors also scan the ridges and valleys on fingerprints. However, in this case, electric current is used to collect data instead of light. An array of capacitors is placed below the scanning surface to collect fingerprint detail. When a fingertip is placed on the scanning surface, the charge stored on the capacitor changes. This difference in charge is tracked by an op-amp integrator circuit, which is further recorded by an analogue-to-digital converter.
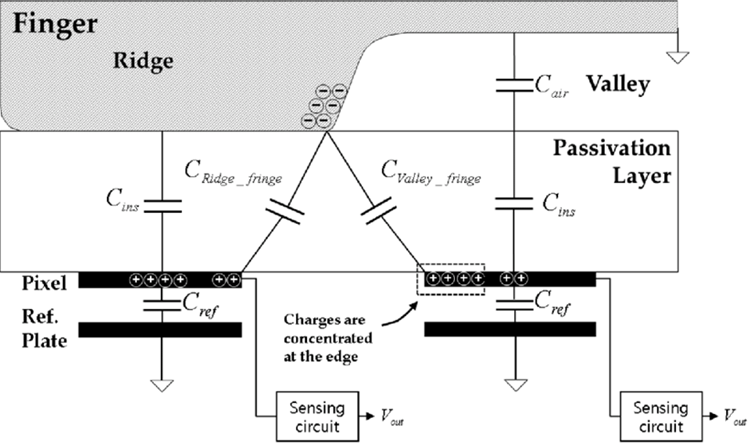
The captured data is used for authentication. It is worth noting that the ability of capacitive sensors increases with the increase in no of capacitors. These scanners offer better security, are fast, and are insanely difficult to fool. Capacitive sensors are costlier compared to optical ones and were used only in flagship devices back then. Moreover, this is 2019, and capacitive sensors have penetrated all segments in the smartphone industry. Capacitive touch pads are cheap and can be easily integrated into any device.
Algorithm and Cryptography
Scanning is just half the process; having said that, it is important to store the data in a secure place. For this process, a dedicated IC is added to the sensor, which deals with interpreting scanned data and further transmitting it to the processor. The secured place is inaccessible, and even rooting cannot help to break in. Every manufacturer has a different approach and uses different algorithms to identify key fingerprint characteristics. Generally, these algorithms look for very specific features called minutiae, where the lines in your fingerprint terminate or split in two. Hence, the scanner can match these minutiae instead of scanning the whole fingerprint again. Which makes the whole process a bit faster.
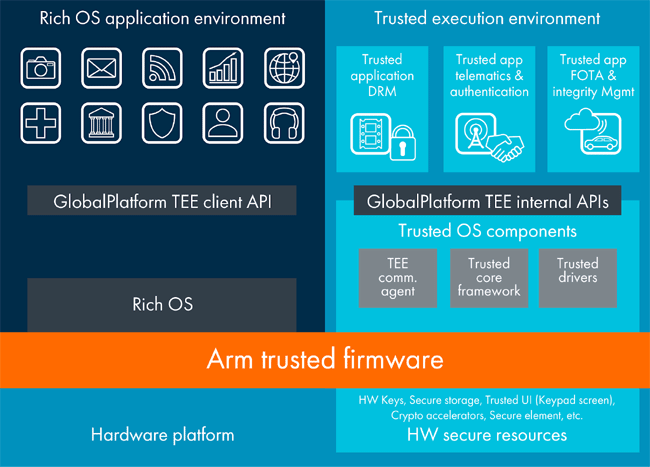
Moving further, these sensor manufacturers have separate systems for storage. ARM uses Trusted Execution Environment (TEE) based TrustZone technology, which stores data in a secure place inside the main processor. Qualcomm, on the other hand, uses Qualcomm Secure Execution Environment (QSEE) for securing private encryption keys and passwords. These systems might have different names, but all of them have a common goal of protecting data.
In-Screen vs Traditional Fingerprint Sensors: Key Comparison
Features | In-Screen Sensors | Traditional Sensors |
|---|---|---|
Design | Seamless, bezel-less | Requires physical space |
Speed | 0.2–0.5 seconds | 0.1–0.3 seconds ✓ |
Accuracy | 95–99% | 98–99.8% ✓ |
Cost | $15–50 per unit | $2–15 per unit ✓ |
Power Usage | Higher | Lower ✓ |
Wet Fingers | Poor–Fair | Fair–Good ✓ |
Durability | Good | Excellent ✓ |
User Experience | Modern, intuitive ✓ | Familiar, tactile |
Which is better, Optical or Ultrasonic?
Ultrasonic scanners, of course, are better as they benefit from the 3D scanning process, while optical scanners are just capable of 2D scanning, as mentioned before. Besides these, ultrasonic sensors are extremely small in size; Qualcomm’s latest 3D sonic sensor measures just 0.2 mm. The small form factor of these sensors meets the current demand for slim and bezel-less devices. Moving further, these sensors are also not affected by dust, grease, or wet hands.
However, there are not many devices that make use of ultrasonic sensors, and that has to do with manufacturing costs. These sensors are costly and are available only on select flagship devices as of now.
Best Smartphones with In Display Fingerprint Sensor
Well, now that you are aware of the current technologies and their working. It would be even better if you were aware of the recent devices with in-display fingerprint sensors and their type.
Devices with optical in-display scanners | Devices with ultrasonic in-display scanners |
Redmi K20/k20 Pro | Samsung Galaxy S10/S10+ |
Realme X |
|
One Plus 7/ 7 Pro |
|
OPPO K3 |
|
Samsung Galaxy A50/A70/A80 |
|
OPPO K1 |
|
Vivo V15 Pro |
|
One Plus 6T |
|
Huawei P30 Pro |
|
Xiaomi Mi 9 |
|
Frequently Asked Questions
⇥ What are the different fingerprint sensors found in mobile phones?
Mobile phones are equipped with three major types of fingerprint sensors: optical scanners, which are the most prevalent (often in in-display sensors), ultrasonic scanners, which are more secure and commonly found on flagship devices, and capacitive scanners, the traditional physical sensor.
⇥ Which smartphones include in display fingerprint sensors?
The notable smartphones that incorporate in-display fingerprint sensors include the Samsung Galaxy S10/S10+ (ultrasonic), the OnePlus 7 and 7 Pro, the Xiaomi Mi 9, the Realme X, the OPPO K3, and the Huawei P30 Pro (which uses optical sensors).
⇥ How do ultrasonic fingerprint sensors work in smartphones?
The ultrasonic fingerprint sensor relies on sound waves in a high-frequency range that create a complete 3D map of your ridges and valleys in your fingerprint, unlike the optical sensors that only view a series of images in 2D. Therefore is a more secure option.





