
The race for wireless technology started long back in 1890’s when Marconi built the world’s first radio station and introduced wireless telegraphy, which completely re-defined the way how humans exchanged information back then. Today, we have advanced with many new cellular technologies to transmit large amount of data wirelessly to anyone living at even the deepest corner of the Earth. But, recently it’s not just humans who have to communicate among themselves. The machines and other electronic devices have also started to exchange information between one another to establish a connected network. These devices mostly operate on a battery from a remote location forcing it to communicate for long distance with minimum possible power. This requirement has prompted the need for new communication technologies like ZigBee, LoRa, Sigfox etc. We have already discussed on what is LoRa in our previous article and hence in this article we will learn about a similar wireless communication protocol called Sigfox and its significance in connected technology.
What is Sigfox Technology
Sigfox is a long range cellular wireless communication that offers custom solutions primarily for low-throughput Internet of Things (IoT) and M2M applications by availing its end-to-end IoT connectivity services using it's patented technologies. The Sigfox network protocol has patented base stations that are integrated with software defined radios. The end devices use binary phase-shift keying (BPSK) modulation to connect to the base stations.
The Sigfox network has been designed to facilitate effective communication over low power consumption. Low power consumption ensures that remote devices runs for long with minimal battery charging or maintenance. Sigfox enables IoT communication over long distances making it possible to transmit with minimal base stations. The Sigfox network uses cellular style approach to enable the remote nodes to use internet to communicate with base stations. This facilitates remote control and data collection from the Sigfox nodes over a wide geographical area as long as there is internet connectivity.
Features of Sigfox
Although Sigfox was introduced back in 2009, it was not until recently it gained popularity. Today with the advent of IoT, Sigfox is highly being used as a communication standard to connect low-power devices like smart electricity meters, smart watches etc. Let’s take a look at the features of Sigfox which makes it as a preferable network.
High network capacity
Sigfox has a high capacity that allows it to scale up to billions of objects, this is because of the ultra-narrow band modulation that accommodates resistant and resilience to interference. The Sigfox infrastructure uses random access that facilitates frequency and time diversity. The use of uplink and downlink bandwidth allows consistency regardless of the radio link used.
High energy efficiency
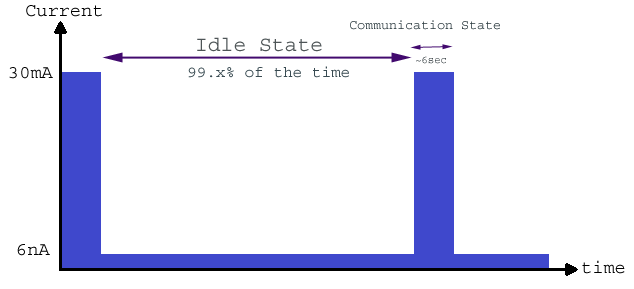
The Sigfox network boasts of high energy efficiency, thanks to the low power consuming semiconductors that are used when manufacturing the Sigfox hardware. These semiconductors allow the Sigfox modules to transmit data with only around 10mA – 50mA of current. The Sigfox network architecture does not execute message synchronization between the devices and the base station before conducting data transmission, this means there is no paring required. Lack of pairing between the devices and base station accommodates long battery life and gives Sigfox advantage over other technologies. Sigfox consumes only a few nano amperes when idle, this rate of power consumption is negligible further enhancing efficiency.
Long range
The deployment of Sigfox covers a large geographical area with minimal number of base stations. The radio frequency range (RF) is estimated by the data rate meaning for every output, long range is achieved with low data rate. Implementation of long range base stations enables implementation of a wide range Sigfox network at minimal costs. Sigfox’s long range is also facilitated by the fact that the base stations have less sensitivity and the objects have low output power. In rural areas, a Sigfox network covers an average range of 30km – 50km due to minimal interference. However, in town centres where there is a lot obstruction the Sigfox range reduces to 10km.
Resilience to interference
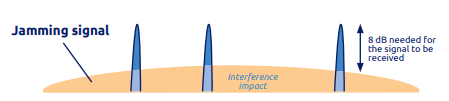
Sigfox utilizes 192KHz Ultra Barrow Band (UNB) integrated with the base station’s spatial diversity of +20 dB which facilitate its unique anti-jamming features. The Sigfox network utilizes Ultra Narrow Band to operate in Industrial, Scientific and Medical (ISM) band since spread spectrum signals are interfered by UNB signals. In Europe, the Uplink has a bandwidth of 100Hz while in the USA the bandwidth exceeds to 600Hz. The European Union has limited the maximum power to be 25mW. The downlink has a channel bandwidth of 1.5KHz and a data range of 600 bps. The downlink further limits the maximum power output to 500mW. The optimal resilience to interfere facilitate Sigfox to function effectively in the ISM band. This allows it to transmit even under jamming signals. However, the low noise overlap induces intrinsic ruggedness to the Ultra-Narrow band. As a result, for a message to be transmitted, the signal should have at least 8 dB.
Sigfox Network Architecture
Sigfox network architecture is horizontal and thin, and has 2 layers. Layer one comprises of the network equipment mostly the base stations, and other elements. The purpose of this layer is to receive messages from the IoT device ad transmit them to the Sigfox Support systems this network has a one-hop star topology allowing the IoT devices connect to any base station near it. The second layer is the Sigfox Support System where messages from the base stations are processed and sent through call-backs to the customer system. This layer also provides the entry point of the various actors such as Sigfox, end customers, Sigfox operators and channels to the ecosystem using web interfaces or APIs. The layer has repository and other tools for analysing the data that is collected by the network. The layer also contains modules and features that support the deployment, operation, and monitoring of the network. The features include the Business Support System(BSS) for billing and ordering, and Radio Planning for supporting network deployment and monitoring. The public internet connects the two layers over secure VPN connections.
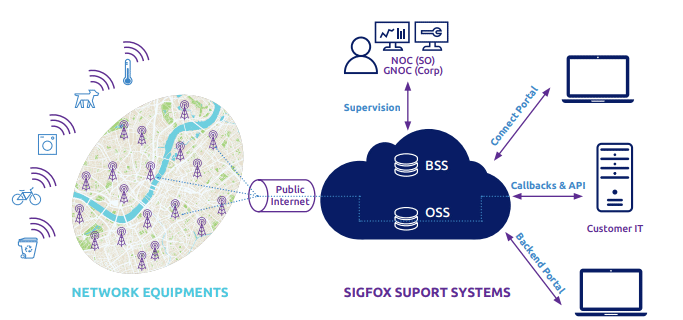
The data from the IoT devices is sent through air to the base stations, then goes through the backhaul which uses DSL connectivity with 4G backup. Satellite connectivity is used as backup in places where DSL and 4G are not available. Message processing is also handled by the backhaul, these messages arrive on the core network as many replicates but only one copy is stored which can be accessed by customers through a web interface.
Sigfox security and privacy
Since the primary focus of Sigfox is to be used with IoT, the network has been designed to enhance security by implementing firewalls to secure data in motion and at rest. You can also read this article on IoT Security challenges to get a better idea on how to secure your IoT devices. Now let’s take a look at the different security features in Sigfox.
Firewall security
Sigfox has an inbuilt firewall that restricts IoT objects to connect or communicate using the internet protocol. To communicate over the internet, an object sends a radio message that is picked up by the available access stations. The access station then relays the message to the Sigfox support system that in turn transmits it to the specified destination. The Sigfox support system also transmits the response to the sender object through the base stations. The security firewall thus secures the IoT objects from internet related attacks.
Data security
The Sigfox architecture provides a security mechanism that guarantees secure data authentication and replay avoidance; it also provides an extra anti-eavesdropping mechanism. The Sigfox’s IoT chain involves authentication keys stored which are stored by devices and the customer, this key will be required to access the data stored by the Sigfox System. As a result, Sigfox’s data mechanisms guarantees security within the diverse ecosystem and different local regulations. The authentication key for every device is unique meaning that a compromise of a device’s authentication security key does not affect the security of other devices. However, the security of any device is left at the discretion of the manufacturer.
Application of Sigfox
Sigfox technology is suited for low cost M2M application that operate over a wide area coverage. These areas include;
- People, Goods or other type of Asset tracking.
- Smart metering communication in the energy sector.
- Communication of mHealth applications
- Management of automotive communication in the transport sector
- Remote control and monitoring.
- Security.
Sigfox module manufacturers
Murata is among the leading Sigfox microcontroller manufacturers. The popular Sigfox modules utilize the STM32-based wireless microcontroller from ST Microcontrollers and also the SX127 Samtech RFIC. These microcontrollers operate at a frequency range of 860-930 MHz. This frequency range supports an output power of +14 dBm that can be enhanced to +20 dBm in case of poor signal areas.
|
Module |
Manufacturer |
|
WSSFM10R1: RCZ1 (Europe, Middle East, Africa) |
WiSOL Co. LTD |
|
TD1207 |
TD Next |
|
SN10-11 |
InnoComm |
|
ABZ Sigfox RC1 |
Murata Manufacturing Co. LTD |
|
SiPy 14dB |
Pycom |
|
S-Wing: Sigfox Extension board for Bosch XDK for Zone 2&4 |
InnoComm |
|
S-Wing: Sigfox Extension board for Bosch XDK for Zone 3 |
InnoComm |
|
SN10-12 |
InnoComm |
|
SN10-22 |
InnoComm |





